What Is The Difference Between Psychology And Philosophy
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
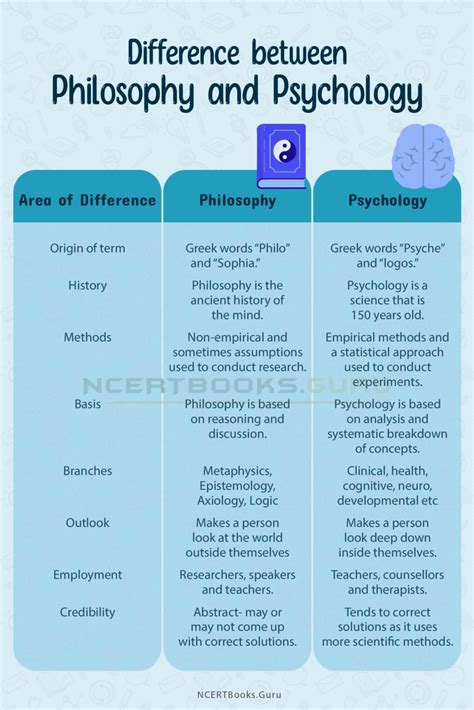
Table of Contents
Delving into the Depths: Psychology vs. Philosophy – A Comparative Exploration
Psychology and philosophy, while seemingly disparate fields, share a fascinating history and surprisingly intertwined methodologies. Both grapple with the nature of the human experience, exploring consciousness, behavior, and the search for meaning. However, their approaches, methodologies, and ultimate goals differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for appreciating the unique contributions of each discipline.
Defining the Disciplines: A Foundation for Comparison
Before diving into the contrasts, let's establish clear definitions.
Psychology: The Science of the Mind and Behavior
Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behavior. It employs empirical methods, such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis, to investigate a wide range of topics, including:
- Cognitive processes: Memory, perception, attention, language, problem-solving.
- Emotional processes: Mood, feelings, stress, motivation.
- Social processes: Interpersonal relationships, group dynamics, social influence.
- Biological processes: The impact of genetics, neurotransmitters, and brain structures on behavior.
- Developmental processes: Changes in behavior and cognition across the lifespan.
- Abnormal psychology: Mental disorders, their causes, and treatments.
Psychology strives for objectivity and generalizability. Researchers aim to identify patterns and principles that apply across individuals and situations. The emphasis is on what is, based on observable evidence.
Philosophy: The Pursuit of Wisdom and Understanding
Philosophy, on the other hand, is the love of wisdom. It's a broader, more abstract discipline that explores fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Unlike psychology, philosophy doesn't rely primarily on empirical data. Instead, it utilizes:
- Logic: Analyzing arguments and identifying fallacies.
- Conceptual analysis: Examining the meaning and implications of concepts.
- Thought experiments: Exploring hypothetical scenarios to illuminate philosophical issues.
- Critical reasoning: Evaluating arguments and perspectives.
Philosophical inquiry seeks to understand why things are and explore the fundamental nature of reality. It grapples with abstract concepts, often lacking the concrete data that defines psychological research. While some philosophical arguments may inform psychological theories, the primary goal of philosophy isn't to generate testable hypotheses in the same way as psychology.
Key Differences: A Comparative Analysis
While both disciplines aim to understand human experience, their approaches diverge in several crucial aspects.
1. Methodology: Empirical vs. Conceptual
This is perhaps the most significant difference. Psychology employs rigorous scientific methods, including quantitative and qualitative research designs, to collect and analyze data. Experiments are conducted to test hypotheses, and results are evaluated statistically to determine their reliability and validity. Philosophy, however, relies primarily on conceptual analysis, logical reasoning, and argumentation. While philosophical inquiries might be informed by empirical findings, they don't necessarily require empirical evidence to support their claims. Philosophical arguments are evaluated based on their internal consistency, logical coherence, and persuasiveness.
2. Focus: Observable Behavior vs. Abstract Concepts
Psychology predominantly focuses on observable behavior and mental processes. It seeks to understand how individuals perceive, think, feel, and act in specific situations. Philosophy, on the other hand, deals with more abstract concepts, such as the nature of consciousness, free will, morality, and the meaning of life. These concepts are not directly observable and often require intricate conceptual analysis and argumentation.
3. Goals: Prediction and Control vs. Understanding and Interpretation
A primary goal of psychology is to predict and control behavior. By understanding the factors that influence behavior, psychologists aim to develop interventions to improve mental health, enhance performance, or address social problems. Philosophy's goal is more focused on understanding and interpreting the world, exploring fundamental questions about existence and knowledge. While philosophical insights can inform practical applications, the primary focus is on conceptual clarity and the development of coherent perspectives.
4. Scope: Specific Phenomena vs. Broad Questions
Psychology typically focuses on specific phenomena, such as memory deficits, anxiety disorders, or social conformity. Researchers may investigate specific aspects of human behavior within a clearly defined context. Philosophy, in contrast, grapples with broader, more fundamental questions, encompassing the nature of reality, knowledge, ethics, and the human condition. The scope of philosophical inquiry is far-reaching, exploring the interconnectedness of different domains of human experience.
5. Types of Evidence: Empirical Data vs. Logical Arguments
Psychology relies on empirical data collected through research studies. This data provides evidence for or against specific hypotheses. The validity and reliability of the data are crucial for evaluating the strength of research findings. Philosophy, however, primarily uses logical arguments and conceptual analysis to support its claims. The persuasiveness of these arguments depends on their logical coherence, consistency, and the strength of the supporting premises.
Overlapping Areas: Where Psychology and Philosophy Converge
Despite their differences, psychology and philosophy share some overlapping areas, particularly in:
- Cognitive science: This interdisciplinary field combines insights from psychology, philosophy, neuroscience, computer science, and linguistics to understand the nature of thought and intelligence.
- Moral psychology: This field explores the relationship between morality and psychological processes, examining the cognitive, emotional, and social factors that influence moral judgments and behavior.
- Philosophy of mind: This branch of philosophy examines the nature of consciousness, mental states, and the mind-body problem, drawing upon insights from cognitive neuroscience and psychology.
- Philosophy of science: This area of philosophy explores the nature of scientific knowledge, the methods of science, and the relationship between science and society. This is particularly relevant for understanding the philosophical underpinnings of psychological research.
Conclusion: Two Sides of the Same Coin?
Psychology and philosophy, while distinct disciplines, offer complementary perspectives on the human experience. Psychology provides empirical data and testable hypotheses about specific aspects of behavior and mental processes, while philosophy grapples with broader, more abstract questions about the nature of reality, knowledge, and the human condition. By understanding the unique strengths and limitations of each approach, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the complexities of the human mind and behavior. Both are essential for a complete picture, and their ongoing dialogue enriches our understanding of ourselves and the world around us. The ongoing interaction and cross-pollination between these fields continue to generate new insights and drive progress in our quest to understand the human experience in all its complexity. Ultimately, both disciplines contribute to a richer, more nuanced perspective on what it means to be human.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Common Factors Of 3 And 9
Mar 28, 2025
-
Write 70 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 2 And 8
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Name Of Mg No3 2
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Hiv
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Psychology And Philosophy . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
