Simple Compound Complex Compound Complex Sentences Worksheet With Answers
Juapaving
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
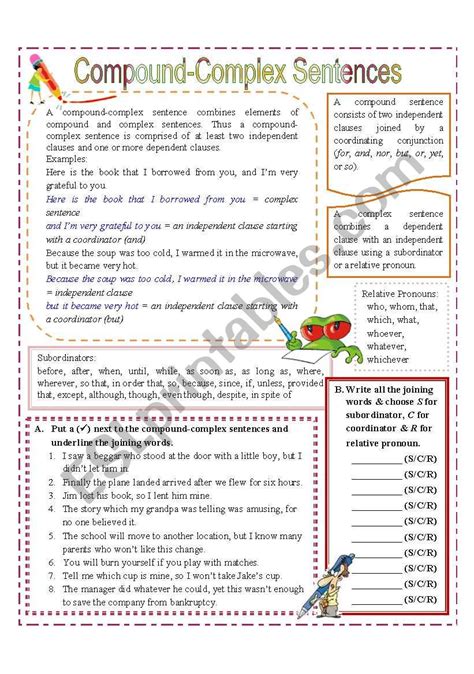
Table of Contents
Simple, Compound, Complex, and Compound-Complex Sentences Worksheet with Answers
Understanding sentence structure is fundamental to effective writing. This worksheet will help you master the difference between simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences. We'll provide examples and exercises to solidify your understanding. By the end, you'll be confidently identifying and constructing each sentence type.
What are the Different Sentence Types?
Before diving into the worksheet, let's review the definitions of each sentence type:
1. Simple Sentences: A simple sentence contains one independent clause. An independent clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb and expresses a complete thought.
- Example: The dog barked. (Subject: dog; Verb: barked)
2. Compound Sentences: A compound sentence contains two or more independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) or a semicolon (;).
- Example: The dog barked, and the cat hissed. (Two independent clauses joined by "and")
3. Complex Sentences: A complex sentence contains one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. A dependent clause cannot stand alone as a sentence because it doesn't express a complete thought. It often begins with a subordinating conjunction (because, since, although, if, when, while, etc.) or a relative pronoun (who, whom, whose, which, that).
- Example: Because the dog barked, the cat hissed. (Independent clause: The cat hissed; Dependent clause: Because the dog barked)
4. Compound-Complex Sentences: A compound-complex sentence contains two or more independent clauses and at least one dependent clause.
- Example: Although the dog barked, the cat hissed; however, the bird remained silent. (Independent clauses: The cat hissed; The bird remained silent; Dependent clause: Although the dog barked)
Worksheet: Identifying Sentence Types
Instructions: Identify each sentence below as simple (S), compound (CD), complex (CX), or compound-complex (CC).
Part 1: Identification
- The sun shone brightly.
- The birds sang sweetly, and the flowers bloomed beautifully.
- Although it was raining, we went for a walk.
- The children played in the park, and their parents watched them from a bench; it was a lovely afternoon.
- Because she was tired, she went to bed early.
- The storm raged violently, and the trees swayed dramatically; the wind howled fiercely.
- If you study hard, you will succeed.
- He laughed, and she smiled; they were happy together.
- While she cooked dinner, he cleaned the house.
- The dog chased its tail, and the cat watched from the window; it was a funny sight.
- Since it was late, we decided to go home.
- They went to the movies, and then they went out to dinner; they had a wonderful evening.
- The flowers are blooming.
- He is tall, and she is short.
- After the rain, the sun came out.
Part 2: Writing Sentences
Instructions: Write one sentence of each type (simple, compound, complex, compound-complex).
- Simple Sentence: _________________________________________________________
- Compound Sentence: _______________________________________________________
- Complex Sentence: ________________________________________________________
- Compound-Complex Sentence: _______________________________________________
Answers to Worksheet: Identifying Sentence Types
Part 1: Identification
- S
- CD
- CX
- CC
- CX
- CC
- CX
- CD
- CX
- CC
- CX
- CC
- S
- CD
- CX
Understanding Sentence Structure: A Deeper Dive
Knowing the different sentence types is only part of mastering sentence structure. Let's delve deeper into the elements that make up each type and explore how to use them effectively in your writing.
1. Simple Sentences: The Building Blocks
Simple sentences are the foundation upon which all other sentence structures are built. They are straightforward and easy to understand. However, don't mistake simplicity for lack of impact. A well-crafted simple sentence can be powerful and memorable. Consider using simple sentences for emphasis or to create a sense of urgency.
2. Compound Sentences: Combining Ideas
Compound sentences allow you to connect two related ideas with equal importance. The coordinating conjunction you choose subtly alters the relationship between the clauses. "And" suggests addition, "but" indicates contrast, "or" presents alternatives, etc. Using semicolons creates a closer relationship between the ideas than conjunctions, suggesting a stronger connection.
3. Complex Sentences: Adding Nuance and Detail
Complex sentences introduce subordinate ideas that provide context, explanation, or qualification to the main idea. The choice of subordinating conjunction dramatically impacts the meaning. "Because" implies cause and effect; "although" indicates contrast; "if" suggests conditionality. Mastering complex sentences enhances your ability to express nuanced ideas effectively.
4. Compound-Complex Sentences: Mastering Complexity
Compound-complex sentences are the most intricate, allowing you to express a range of interwoven ideas. These sentences demonstrate sophisticated writing skills. They allow you to present several connected ideas with varying levels of importance. However, overuse can lead to confusing and cumbersome prose. Use them strategically for a clear and powerful impact.
Advanced Exercises: Putting it All Together
Now let's apply our knowledge to some more challenging exercises.
Exercise 1: Sentence Combining
Combine the following simple sentences into a compound-complex sentence:
- The rain started to fall.
- The children were playing outside.
- They quickly ran for cover.
- They were having fun.
Exercise 2: Sentence Revision
Revise the following sentences to improve their clarity and effectiveness by using different sentence structures.
- The dog barked loudly. The cat ran away. The bird flew away.
- I went to the store. I bought milk. I also bought bread. I was hungry.
Answers to Advanced Exercises
Exercise 1: Sentence Combining
Although the children were playing outside and having fun, the rain started to fall; therefore, they quickly ran for cover.
Exercise 2: Sentence Revision
- When the dog barked loudly, both the cat and the bird ran away.
- Because I was hungry, I went to the store and bought milk and bread.
Conclusion: Mastering Sentence Structure for Effective Writing
Understanding and effectively using simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences is crucial for clear and engaging writing. By mastering these sentence structures, you will improve the flow, clarity, and impact of your writing. Remember to practice regularly and vary your sentence structure to keep your writing dynamic and interesting for your readers. Through consistent practice and attention to detail, you'll become proficient in crafting sentences that effectively communicate your ideas.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Single Celled Organism
Apr 02, 2025
-
If Diagonals Of A Quadrilateral Bisect Each Other
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is Pure Water A Mixture Or Compound
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Type Of Device Is A Keyboard
Apr 02, 2025
-
Lcm Of 7 4 And 2
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Simple Compound Complex Compound Complex Sentences Worksheet With Answers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
