One To One Function And Inverse Function
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
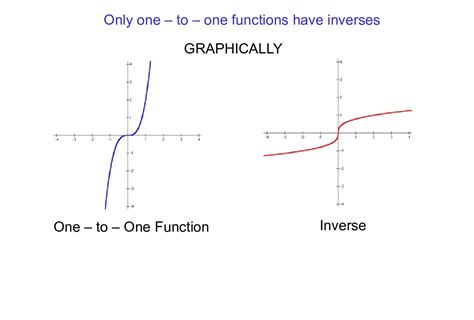
Table of Contents
One-to-One Functions and Inverse Functions: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding one-to-one functions and their inverse counterparts is crucial in various areas of mathematics, particularly in calculus and linear algebra. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of these functions, exploring their definitions, properties, and applications, with a focus on clarity and practical examples.
What is a One-to-One Function?
A function, fundamentally, maps each element from its domain to a unique element in its codomain (or range). However, a one-to-one function, also known as an injective function, imposes a stricter condition: each element in the codomain is mapped to by at most one element in the domain. In simpler terms, no two distinct elements in the domain map to the same element in the codomain.
Formally: A function f: A → B is one-to-one if for all x₁ and x₂ in A, if f(x₁) = f(x₂), then x₁ = x₂. This is equivalent to stating that if x₁ ≠ x₂, then f(x₁) ≠ f(x₂).
How to determine if a function is one-to-one:
Several methods can help determine if a function is one-to-one:
-
Horizontal Line Test: Graphically, if no horizontal line intersects the graph of the function more than once, the function is one-to-one. This is a visual and intuitive approach.
-
Algebraic Method: Use the formal definition. Assume f(x₁) = f(x₂) and show that this implies x₁ = x₂. This method is rigorous and suitable for functions expressed algebraically.
-
Derivative Test (for differentiable functions): If the derivative of a function is strictly positive or strictly negative over its entire domain, the function is strictly monotonic (either strictly increasing or strictly decreasing), and therefore one-to-one.
Examples:
-
f(x) = 2x + 1: This is a one-to-one function. If f(x₁) = f(x₂), then 2x₁ + 1 = 2x₂ + 1, which implies x₁ = x₂.
-
f(x) = x²: This is not a one-to-one function. For example, f(2) = f(-2) = 4.
-
f(x) = eˣ: This is a one-to-one function because the exponential function is strictly increasing.
What is an Inverse Function?
An inverse function reverses the action of a given function. If a function maps x to y, its inverse function (if it exists) maps y back to x. Crucially, only one-to-one functions can have inverse functions. If a function maps multiple x values to the same y value, there's ambiguity in defining its inverse.
Formally: If f: A → B is a one-to-one and onto (surjective) function, then its inverse function, denoted as f⁻¹: B → A, satisfies the following conditions:
- f⁻¹(f(x)) = x for all x in A
- f(f⁻¹(y)) = y for all y in B
Finding the Inverse Function:
To find the inverse of a one-to-one function, follow these steps:
-
Replace f(x) with y: This simplifies the notation.
-
Swap x and y: This reflects the reversal of the function's action.
-
Solve for y: This expresses y in terms of x, giving the inverse function.
-
Replace y with f⁻¹(x): This denotes the inverse function explicitly.
Examples:
Let's find the inverse of f(x) = 2x + 1:
- y = 2x + 1
- x = 2y + 1
- x - 1 = 2y
- y = (x - 1)/2 Therefore, f⁻¹(x) = (x - 1)/2
Let's verify this:
f(f⁻¹(x)) = f((x-1)/2) = 2((x-1)/2) + 1 = x - 1 + 1 = x f⁻¹(f(x)) = f⁻¹(2x + 1) = ((2x + 1) - 1)/2 = 2x/2 = x
Relationship between One-to-One and Inverse Functions
The connection between one-to-one and inverse functions is fundamental: a function has an inverse if and only if it is one-to-one and onto. The "onto" condition means that every element in the codomain is mapped to by at least one element in the domain. If a function isn't onto, its inverse wouldn't be defined for all elements in the codomain.
For many practical applications, we often focus on a restricted domain where a function is both one-to-one and onto, allowing us to define an inverse function within that restricted domain. For example, f(x) = x² is not one-to-one over its entire domain (all real numbers), but if we restrict its domain to x ≥ 0, it becomes one-to-one, and its inverse is f⁻¹(x) = √x.
Applications of One-to-One and Inverse Functions
One-to-one and inverse functions find widespread applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Encryption and decryption algorithms often rely on one-to-one functions to ensure that each encrypted message corresponds to a unique decrypted message.
-
Computer Science: Data compression techniques sometimes utilize one-to-one mappings to represent data more efficiently.
-
Calculus: Inverse functions are critical in differentiation and integration, especially when dealing with inverse trigonometric functions and logarithmic functions. The derivative of an inverse function can be computed using the formula for the derivative of an inverse function.
-
Linear Algebra: Linear transformations are crucial in linear algebra. Invertible linear transformations, which correspond to one-to-one and onto linear functions, play a central role in solving systems of linear equations and analyzing vector spaces.
-
Economics: Demand and supply functions are often modeled as inverse functions of each other.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
-
Composition of Functions: The composition of a function and its inverse results in the identity function.
-
Graphs of Inverse Functions: The graph of an inverse function is the reflection of the graph of the original function across the line y = x.
-
Continuity and Differentiability of Inverse Functions: If a function is continuous and strictly monotonic, its inverse function will also be continuous. Similarly, under certain conditions, the differentiability of a function implies the differentiability of its inverse.
-
Implicit Functions: Sometimes, the inverse function can't be expressed explicitly. In such cases, the inverse function can be understood as an implicit function.
-
Multivariable Calculus: The concepts of one-to-one and inverse functions extend to multivariable functions, albeit with added complexities. Jacobian matrices are used in this context to determine whether a function is locally invertible.
Conclusion
One-to-one functions and their inverses are fundamental mathematical concepts with wide-ranging applications. Understanding their properties and how to determine whether a function is one-to-one is essential for mastering various areas of mathematics and its applications in other disciplines. This comprehensive exploration has covered the core definitions, methods for identification, processes for finding inverse functions, and a glimpse into their broader significance. Further investigation into advanced concepts will solidify your understanding and expand your capabilities in working with these crucial mathematical tools.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
All Of The Multiples Of 7
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is Not A Pure Substance
Mar 26, 2025
-
Lowest Common Denominator Of 7 And 9
Mar 26, 2025
-
Label The Cross Section Of A Leaf
Mar 26, 2025
-
Difference Between Plant Mitosis And Animal Mitosis
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about One To One Function And Inverse Function . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
