Movement Of Earth Around The Sun Is Called
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
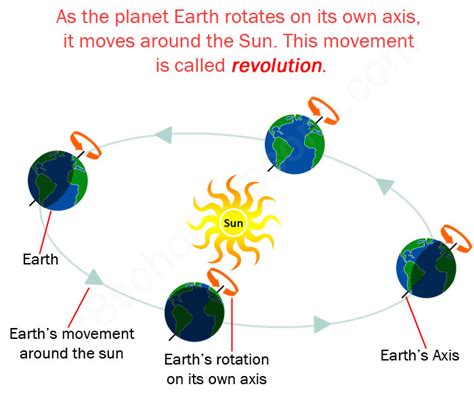
Table of Contents
The Movement of Earth Around the Sun: A Deep Dive into Revolution and its Effects
The movement of Earth around the Sun is called revolution. This seemingly simple statement belies a complex interplay of gravitational forces, orbital mechanics, and the profound impact this movement has on our planet's climate, seasons, and even the very existence of life as we know it. Understanding Earth's revolution is fundamental to comprehending our place in the cosmos and the intricate workings of our solar system. This comprehensive article will delve into the specifics of Earth's revolution, exploring its characteristics, consequences, and the scientific principles that govern it.
Understanding Earth's Orbit: An Elliptical Journey
Contrary to popular depictions of a perfectly circular orbit, Earth's path around the Sun is actually an ellipse. This means that the distance between Earth and the Sun varies throughout the year. The point in Earth's orbit where it is closest to the Sun is called perihelion, typically occurring around January 3rd. The point where Earth is farthest from the Sun is called aphelion, occurring around July 4th. This variation in distance, while significant, doesn't drastically affect Earth's overall temperature, as other factors like axial tilt play a much more crucial role in determining seasons.
Kepler's Laws and Orbital Mechanics
Johannes Kepler's laws of planetary motion are crucial to understanding Earth's revolution. These laws, derived from meticulous observations of planetary movements, state:
- Kepler's First Law (Law of Ellipses): The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the two foci.
- Kepler's Second Law (Law of Equal Areas): A line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time. This means that Earth moves faster when it's closer to the Sun (perihelion) and slower when it's farther away (aphelion).
- Kepler's Third Law (Law of Harmonies): The square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit. This law relates the time it takes a planet to orbit the Sun (its period) to the size of its orbit.
These laws, later explained by Newton's law of universal gravitation, are fundamental to understanding the dynamics of Earth's orbit and the orbits of all celestial bodies.
The Significance of Earth's Axial Tilt: The Engine of Seasons
While revolution around the Sun is responsible for the year, the axial tilt of Earth – approximately 23.5 degrees – is the primary driver of our seasons. This tilt means that different parts of the Earth receive varying amounts of direct sunlight throughout the year.
Understanding Seasonal Variations
- Summer Solstice: In the Northern Hemisphere, the summer solstice occurs around June 21st, when the North Pole is tilted most directly towards the Sun. This results in longer days and shorter nights in the Northern Hemisphere, leading to warmer temperatures. Simultaneously, the Southern Hemisphere experiences winter.
- Winter Solstice: The winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere occurs around December 21st, with the North Pole tilted farthest away from the Sun. This leads to shorter days and longer nights, resulting in colder temperatures. The Southern Hemisphere experiences summer.
- Equinoxes: The spring equinox (around March 20th) and autumnal equinox (around September 23rd) occur when Earth's axis is not tilted towards or away from the Sun. Day and night are approximately equal in length at all latitudes.
The interplay between Earth's revolution and its axial tilt creates the cyclical pattern of seasons we experience, profoundly impacting weather patterns, ecosystems, and human activities.
The Duration of Earth's Revolution: A Year's Definition
One complete revolution of Earth around the Sun defines a year. However, the precise length of a year isn't a perfectly round number. The sidereal year, measured relative to the stars, is approximately 365.256 days. This is why we have leap years every four years, adding an extra day (February 29th) to account for the extra quarter of a day.
The Impact of Earth's Revolution: Beyond Seasons
The effects of Earth's revolution extend far beyond the simple experience of seasons. It plays a vital role in:
- Climate Regulation: The variations in Earth's distance from the Sun and the distribution of sunlight due to axial tilt influence global climate patterns.
- Ocean Currents: Earth's revolution and the Coriolis effect, caused by the Earth's rotation, influence the direction and patterns of ocean currents, impacting global heat distribution.
- Biological Rhythms: Many biological processes, including migration patterns of animals and plant growth cycles, are synchronized with the annual cycle dictated by Earth's revolution.
- Human Activities: Agriculture, tourism, and various other human activities are heavily influenced by seasonal changes driven by Earth's revolution.
The Future of Earth's Orbit: Subtle Changes Over Time
While Earth's orbit remains relatively stable over short time scales, it undergoes subtle changes over vast periods. Gravitational interactions with other planets, particularly Jupiter, cause slow variations in Earth's orbital eccentricity (the degree of ellipticity) and precession (the wobble of Earth's axis). These variations influence long-term climate patterns and have been implicated in past ice ages.
Milankovitch Cycles and Climate Change
Milankovitch cycles refer to these long-term variations in Earth's orbital parameters, including eccentricity, obliquity (axial tilt), and precession. These cycles, spanning tens of thousands of years, are believed to have played a significant role in past ice ages and are considered a factor in understanding long-term climate change.
Conclusion: A Dynamic System in Constant Motion
The movement of Earth around the Sun, or revolution, is far more than a simple orbital path. It's a dynamic process driven by gravity, influenced by axial tilt, and responsible for the fundamental rhythms of life on Earth. Understanding this movement is crucial to comprehending our planet's climate, seasons, and the intricate interplay of forces that shape our world. From Kepler's laws to Milankovitch cycles, the scientific understanding of Earth's revolution continues to evolve, providing valuable insights into our planet's past, present, and future. The study of this seemingly simple phenomenon underscores the profound interconnectedness of our solar system and the elegant mechanics that govern the celestial dance of our planet around its star. The more we learn about Earth's revolution, the better equipped we are to address the challenges and opportunities presented by our ever-changing planet. Further research into the complexities of Earth's orbit and its interaction with other celestial bodies will undoubtedly continue to refine our understanding of this fundamental aspect of our existence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Does Temperature Relate To Kinetic Energy
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Flow Of Electrons Is Called
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Movement Of Materials From Low To High Concentration
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Thousands Are In A Billion
Mar 26, 2025
-
Protons Neutrons And Electrons Of Potassium
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Movement Of Earth Around The Sun Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
