Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 15
Juapaving
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
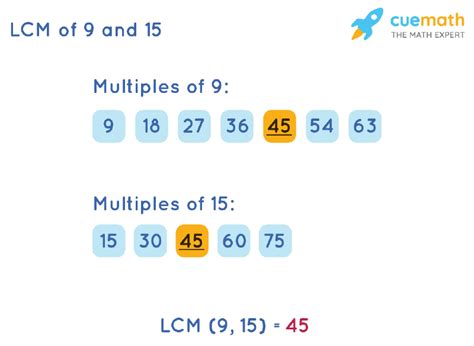
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 9 and 15: A Deep Dive
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in number theory with widespread applications in various fields, from scheduling problems to music theory. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of how to find the LCM of 9 and 15, demonstrating multiple methods and delving into the underlying mathematical principles. We'll also discuss the significance of the LCM and its broader implications.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
Before we delve into the specifics of finding the LCM of 9 and 15, let's establish a solid understanding of what the LCM represents. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that can be evenly divided by all the numbers in question.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, and so on. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, and so on. The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so forth. The smallest of these common multiples is 6; therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Calculating the LCM of 9 and 15
There are several effective methods for calculating the LCM of two or more numbers. We will explore three common approaches: the listing method, the prime factorization method, and the greatest common divisor (GCD) method.
1. Listing Method
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. While straightforward for smaller numbers, it can become cumbersome for larger numbers.
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, 99, 108, 117, 126, 135...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest common multiple of 9 and 15 is 45. Therefore, the LCM(9, 15) = 45.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is generally more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present in the factorizations.
- Prime factorization of 9: 3²
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- The highest power of 3 is 3² = 9
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ = 5
Therefore, the LCM(9, 15) = 3² x 5 = 9 x 5 = 45.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The formula is:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
First, we need to find the GCD of 9 and 15. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide the larger number (15) by the smaller number (9): 15 ÷ 9 = 1 with a remainder of 6.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (9) and the smaller number with the remainder (6): 9 ÷ 6 = 1 with a remainder of 3.
- Repeat the process: 6 ÷ 3 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
The last non-zero remainder is the GCD, which is 3.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(9, 15) = (9 x 15) / 3 = 135 / 3 = 45
Therefore, the LCM(9, 15) = 45 using the GCD method.
Applications of LCM
The least common multiple finds practical applications in various areas:
-
Scheduling: Determining when events will occur simultaneously. For instance, if one event happens every 9 days and another every 15 days, the LCM (45) tells us when they will both occur again on the same day.
-
Fractions: Finding the least common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions. To add 1/9 and 1/15, the LCM of 9 and 15 (45) is used to find the common denominator.
-
Music Theory: Calculating rhythmic patterns and determining when different musical phrases will align.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Solving problems involving congruences and remainders.
-
Engineering: Synchronizing mechanical systems or processes with different periodicities.
Why is the LCM Important?
Understanding the LCM is crucial for several reasons:
-
Problem Solving: It's a fundamental tool for solving a wide range of mathematical problems, including those involving fractions, ratios, and scheduling.
-
Efficiency: Efficiently determining the LCM allows for streamlined calculations and optimized solutions, avoiding unnecessary steps and computations.
-
Foundation for Advanced Concepts: It serves as a building block for more advanced mathematical concepts and applications in higher-level mathematics, physics, and computer science.
-
Real-World Applications: As demonstrated, the LCM has practical applications across various fields, making it a relevant and valuable concept in everyday life and professional settings.
Expanding on the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For example, to find the LCM of 9, 15, and 6:
Prime Factorization Method:
- Prime factorization of 9: 3²
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 x 3
The highest powers of the prime factors are 2¹, 3², and 5¹. Therefore, the LCM(9, 15, 6) = 2 x 3² x 5 = 2 x 9 x 5 = 90.
GCD Method Extension: While the direct application of the formula (a x b)/GCD(a,b) doesn't directly extend, you can find the LCM iteratively. Find the LCM of 9 and 15 (which is 45), then find the LCM of 45 and 6, using either the prime factorization method or the GCD method again.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of the LCM
The least common multiple, while seemingly a simple concept, holds profound mathematical significance and practical relevance. Mastering the different methods for calculating the LCM, as demonstrated with the example of 9 and 15, empowers individuals to solve a wide range of problems and develop a deeper understanding of number theory. Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, demonstrating its enduring relevance across diverse fields and disciplines. Understanding the LCM is not merely about memorizing formulas; it's about grasping a fundamental mathematical principle that unlocks efficient problem-solving strategies and provides valuable insights into the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Factors Of 88
Mar 30, 2025
-
In An Endothermic Reaction Energy Is
Mar 30, 2025
-
The Numerical Ratio Of Average Velocity To Average Speed Is
Mar 30, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Vector
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Was Darwin Influences On Malthus
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
