Least Common Multiple Of 2 3 And 5
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
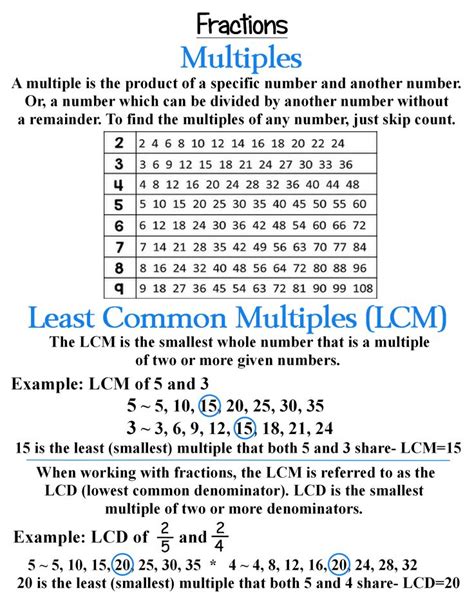
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of the Least Common Multiple of 2, 3, and 5
The seemingly simple question of finding the least common multiple (LCM) of 2, 3, and 5 might appear trivial at first glance. However, understanding how to calculate the LCM, its significance in mathematics, and its practical applications reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts. This comprehensive exploration delves into the intricacies of finding the LCM of 2, 3, and 5, while also providing a broader perspective on LCM's role in various fields.
Understanding the Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we dive into the specifics of finding the LCM of 2, 3, and 5, let's establish a firm understanding of what the LCM actually represents. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
Key Concepts:
- Multiple: A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any integer. For example, multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on.
- Common Multiple: A common multiple of two or more numbers is a number that is a multiple of all the given numbers. For instance, common multiples of 2 and 3 include 6, 12, 18, 24, etc.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): The smallest of these common multiples is the least common multiple.
Calculating the LCM of 2, 3, and 5
There are several methods to determine the LCM of 2, 3, and 5. Let's explore the most common approaches:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30...
By inspecting the lists, we can see that the smallest number common to all three lists is 30. Therefore, the LCM(2, 3, 5) = 30.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method leverages the prime factorization of each number. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 2: 2
- Prime factorization of 3: 3
- Prime factorization of 5: 5
To find the LCM using prime factorization, we identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2¹ = 2
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ = 5
Now, multiply these highest powers together: 2 × 3 × 5 = 30. Therefore, LCM(2, 3, 5) = 30.
Method 3: Using the Formula (for two numbers)
While this method is primarily designed for two numbers, we can extend it to multiple numbers by finding the LCM of the first two, then finding the LCM of that result and the third number, and so on. The formula for the LCM of two numbers, 'a' and 'b', is:
LCM(a, b) = (|a × b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where GCD(a, b) represents the greatest common divisor of 'a' and 'b'.
Let's apply this sequentially:
- LCM(2, 3) = (|2 × 3|) / GCD(2, 3) = 6 / 1 = 6
- LCM(6, 5) = (|6 × 5|) / GCD(6, 5) = 30 / 1 = 30
Therefore, LCM(2, 3, 5) = 30.
The Significance of LCM
The least common multiple has far-reaching applications across various mathematical and real-world scenarios. Let's examine some key examples:
1. Fraction Arithmetic
LCM plays a crucial role in adding and subtracting fractions. To add or subtract fractions with different denominators, we need to find the LCM of the denominators to create a common denominator. This allows us to perform the arithmetic operations efficiently.
2. Scheduling Problems
LCM is vital in solving scheduling problems. Imagine two events occurring at regular intervals. The LCM of these intervals determines when both events will coincide again. For instance, if one event occurs every 2 days and another every 3 days, they will coincide every 6 days (LCM(2, 3) = 6).
3. Modular Arithmetic
In modular arithmetic (a branch of number theory), the LCM is used in various calculations, particularly when dealing with congruences and solving systems of congruences.
4. Music Theory
Interestingly, the LCM finds applications in music theory, especially when dealing with rhythmic patterns and determining the least common denominator for different time signatures.
Real-world Applications of LCM
Beyond purely mathematical applications, the LCM has practical relevance in diverse fields:
- Manufacturing and Production: In manufacturing, LCM helps determine the optimal production cycle for multiple product lines with different production rates.
- Construction and Engineering: LCM assists in coordinating construction schedules, ensuring that different stages of a project align seamlessly.
- Computer Science: LCM finds applications in algorithms and data structures, especially when dealing with synchronization or cyclic processes.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Three Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than three numbers. For example, to find the LCM of 2, 3, 5, and 7, we can either list multiples, use prime factorization, or apply the sequential LCM calculation method. The prime factorization method remains the most efficient for larger sets of numbers.
For instance, using prime factorization:
- 2 = 2
- 3 = 3
- 5 = 5
- 7 = 7
LCM(2, 3, 5, 7) = 2 × 3 × 5 × 7 = 210
Conclusion: The Ubiquitous LCM
The least common multiple, although seemingly a simple mathematical concept, plays a significant role in numerous areas of mathematics and its applications in the real world. Understanding how to calculate the LCM, particularly using the efficient prime factorization method, equips individuals with a powerful tool for solving a wide range of problems, from basic fraction arithmetic to complex scheduling challenges. The seemingly simple LCM of 2, 3, and 5 – 30 – serves as a foundational stepping stone to understanding this fundamental concept and its broader implications. Mastering the LCM not only enhances mathematical proficiency but also fosters problem-solving skills applicable across various disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Dry Ice An Element Compound Or Mixture
Mar 20, 2025
-
Questions On Balancing Chemical Equations With Answers
Mar 20, 2025
-
Volume Of A Bcc Unit Cell
Mar 20, 2025
-
Is Kinetic Energy Scalar Or Vector
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Are Raw Materials For Photosynthesis
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 2 3 And 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
