Is Dry Ice An Element Compound Or Mixture
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
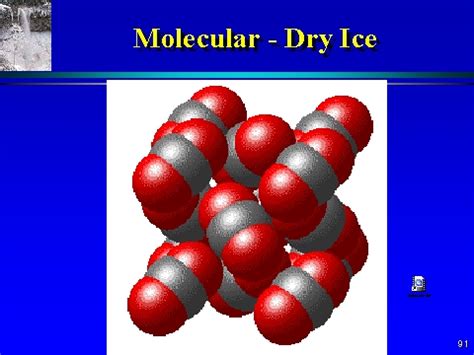
Table of Contents
Is Dry Ice an Element, Compound, or Mixture? A Deep Dive into Carbon Dioxide
Dry ice, that fascinating substance that transforms directly from a solid to a gas (sublimation), is a topic of frequent curiosity. Many wonder about its fundamental nature: is dry ice an element, a compound, or a mixture? The answer, as we'll explore in depth, is relatively straightforward, but understanding why requires delving into the basics of chemistry.
Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter
Before we classify dry ice, let's review the fundamental classifications of matter:
Elements: The Fundamental Building Blocks
Elements are pure substances consisting of only one type of atom. These atoms cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. The periodic table organizes all known elements, each represented by a unique symbol (e.g., H for hydrogen, O for oxygen, C for carbon). Elements are the fundamental building blocks upon which all other substances are constructed.
Compounds: A Union of Elements
Compounds are substances formed when two or more different elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio. This combination involves the formation of chemical bonds, which hold the atoms together. The properties of a compound are distinct from the properties of its constituent elements. For example, water (H₂O) is a compound composed of hydrogen and oxygen, but its properties are vastly different from those of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. These chemical bonds are strong and require significant energy to break.
Mixtures: A Physical Combination of Substances
Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The components of a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical methods, such as filtration, distillation, or evaporation. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform composition throughout, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (non-uniform composition, like sand and water).
Dry Ice: Unveiling its Chemical Identity
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide (CO₂). Carbon dioxide is a compound, not an element or a mixture. Let's break down why:
The Composition of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is composed of two elements:
- Carbon (C): A nonmetal element crucial for life on Earth. It forms the backbone of organic molecules.
- Oxygen (O): Another nonmetal element essential for respiration and numerous other biological processes.
These two elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio of one carbon atom to two oxygen atoms. This bonding is covalent, meaning the atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. This strong chemical bond distinguishes carbon dioxide from a mere mixture of carbon and oxygen.
The Distinct Properties of Carbon Dioxide
The properties of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) are distinct from those of its constituent elements:
- Sublimation: Dry ice's most striking property is its ability to sublime—transitioning directly from a solid to a gas without passing through a liquid phase at standard atmospheric pressure. This is not a property of either carbon or oxygen in their elemental forms.
- Low Temperature: Dry ice has an extremely low temperature (-78.5°C or -109.3°F), making it useful as a refrigerant. Neither carbon nor oxygen exhibit this property in their elemental states.
- Non-flammable: Dry ice is non-flammable and acts as an excellent fire extinguisher by displacing oxygen. Elemental carbon, in certain forms, can be combustible, while oxygen is a key component of combustion.
These unique properties are a direct result of the chemical bonding between carbon and oxygen atoms in the CO₂ molecule.
Why Dry Ice Isn't a Mixture
The key distinction between a compound and a mixture lies in the presence or absence of chemical bonds. A mixture can be easily separated into its components by physical means, while a compound requires chemical processes to break the bonds and separate its constituent elements. Dry ice cannot be separated into carbon and oxygen by simple physical processes. To decompose CO₂, a chemical reaction is needed.
Imagine trying to separate the components of saltwater (a mixture). Evaporation would easily leave the salt behind. However, attempting to "separate" the carbon and oxygen in CO₂ through physical means is impossible. The chemical bond must be broken, typically through a chemical reaction.
The Role of Chemical Bonding
The covalent bond in CO₂ is critical in defining its properties. This strong bond results in a stable molecule with predictable behavior, unlike a mixture where the components interact weakly. The electron sharing between carbon and oxygen atoms establishes a specific molecular geometry, leading to the unique properties we observe in dry ice. In contrast, a mixture's properties would be merely an average of the properties of its components, a characteristic not seen in dry ice.
Dry Ice in Various Applications
The unique properties of dry ice, stemming from its nature as a compound, lead to a wide range of applications:
- Refrigeration: Its low temperature makes it ideal for preserving food, transporting temperature-sensitive materials, and creating special effects (e.g., fog).
- Food Industry: Dry ice is used extensively in the food and beverage industry to keep products cold during transport.
- Medical Industry: It's utilized in medical settings to preserve biological samples and maintain low temperatures in specific procedures.
- Industrial Processes: Dry ice is employed in various industrial processes, including cleaning, blasting, and creating special effects.
These varied applications highlight the versatility of dry ice, a consequence of its unique chemical structure as a compound.
Conclusion: Dry Ice is a Compound, Not an Element or Mixture
To reiterate, dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide (CO₂), which is unequivocally a compound. It's a pure substance formed by the chemical combination of carbon and oxygen atoms in a fixed ratio, held together by strong covalent bonds. Its unique properties, such as sublimation and low temperature, are a direct result of this chemical bonding. It cannot be separated into its constituent elements using simple physical means, further solidifying its classification as a compound and not a mixture. Understanding this fundamental difference helps appreciate the multifaceted role of dry ice in diverse scientific and industrial applications. The specific chemical interaction between carbon and oxygen creates a substance that is vastly different from its component elements and cannot be described as a mere mixture. Therefore, the definitive answer remains: dry ice is a compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 15 As A Decimal
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Plasma And Serum
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Ultimate Source Of Energy For The Earth
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Unit Of Electrostatic Potential
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Digestion Of Starch Begins In The
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Dry Ice An Element Compound Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
