Lcm Of 5 10 And 15
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
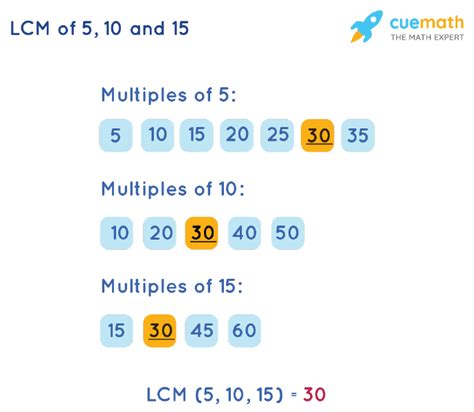
Table of Contents
Finding the LCM of 5, 10, and 15: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of a set of numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex problems in various fields. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of finding the LCM of 5, 10, and 15, explaining different methods and providing a deeper understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also explore the relevance of LCM in real-world scenarios and its connection to other mathematical concepts.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific example of 5, 10, and 15, let's define what the least common multiple actually is. The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and so on. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on. The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Finding the LCM
Several methods exist to calculate the LCM of a set of numbers. Let's explore the most common approaches, and then apply them to find the LCM of 5, 10, and 15.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method is straightforward, especially for smaller numbers. You list the multiples of each number until you find the smallest multiple that is common to all.
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35...
- Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60...
By inspecting the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple of 5, 10, and 15 is 30.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This is a more systematic and efficient method, especially for larger numbers or a larger set of numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
Now, we identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2¹ = 2
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ = 5
To find the LCM, we multiply these highest powers together: 2 x 3 x 5 = 30. Therefore, the LCM of 5, 10, and 15 is 30.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of a set of numbers are related. We can use the GCD to find the LCM using the following formula:
LCM(a, b, c) = (|a x b x c|) / GCD(a, b, c)
First, we need to find the GCD of 5, 10, and 15. The GCD is the largest number that divides all three numbers without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD(5, 10, 15) = 5.
Now, we apply the formula:
LCM(5, 10, 15) = (5 x 10 x 15) / 5 = 150 / 5 = 30
Therefore, the LCM of 5, 10, and 15 is 30. Note that this formula is most useful when dealing with larger numbers where finding the prime factorization might be more time-consuming. It's crucial to understand how to find the GCD, which can be done using various methods, including the Euclidean algorithm.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has practical applications in various fields, including:
-
Scheduling: Imagine you have three machines that complete a cycle in 5, 10, and 15 minutes respectively. To determine when all three machines will complete a cycle simultaneously, you need to find the LCM (30 minutes).
-
Fractions: Finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions. It allows you to find a common denominator, simplifying the calculation process.
-
Measurement Conversions: LCM helps in converting between different units of measurement, ensuring accurate results.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCM is essential in solving problems related to modular arithmetic, which has applications in cryptography and computer science.
-
Music Theory: Understanding LCM is helpful in music theory when working with different rhythmic patterns and finding the least common multiple of their durations.
LCM and Real-World Examples
Let's explore a few real-world scenarios where finding the LCM is beneficial:
Scenario 1: Synchronized Traffic Lights: Imagine three intersections with traffic lights that cycle every 5, 10, and 15 seconds, respectively. To determine when all three traffic lights will simultaneously be green (or red), you'd need to find the LCM of 5, 10, and 15, which is 30 seconds.
Scenario 2: Baking: A recipe calls for adding ingredient A every 5 minutes, ingredient B every 10 minutes, and ingredient C every 15 minutes. To find the timing when all three ingredients are added at the same time, you'd use the LCM, which, in this case, is 30 minutes.
Scenario 3: Project Management: Three teams working on a project need to submit their parts every 5, 10, and 15 days. The LCM (30 days) determines the shortest interval when all three teams would submit their parts together, enabling a unified progress check.
Conclusion
Finding the LCM of 5, 10, and 15, whether through listing multiples, prime factorization, or the GCD method, consistently yields the answer of 30. This seemingly simple calculation underscores a fundamental concept with broad applications in mathematics and various real-world scenarios. Understanding different methods for calculating LCM provides flexibility and efficiency in tackling diverse mathematical problems, making it a valuable tool in various fields. Mastering LCM strengthens your problem-solving skills and enhances your understanding of number theory, ultimately contributing to a more comprehensive mathematical foundation. The ability to identify and apply LCM to real-world situations demonstrates a practical understanding of mathematical principles and their relevance beyond the classroom.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Cell Has Large Vacuoles
Mar 25, 2025
-
Light Microscope And Electron Microscope Differences
Mar 25, 2025
-
A Catalyst Lowers The Activation Energy Of A Reaction By
Mar 25, 2025
-
Whats The Lcm Of 8 And 10
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 11 Cm In Inches
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lcm Of 5 10 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
