Lateral Area Formula For A Rectangular Prism
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
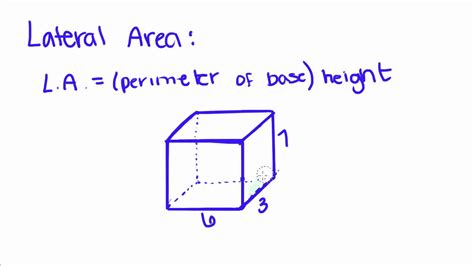
Table of Contents
Decoding the Lateral Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the lateral surface area of a three-dimensional shape is crucial in various fields, from architecture and engineering to packaging and design. This article delves deep into the concept of lateral surface area, specifically focusing on rectangular prisms. We'll explore its formula, derivation, practical applications, and related concepts, providing a comprehensive understanding for both beginners and those seeking a refresher.
What is a Rectangular Prism?
A rectangular prism, also known as a cuboid, is a three-dimensional solid object characterized by six rectangular faces. These faces meet at right angles, forming 12 edges and 8 vertices. Think of a shoebox, a brick, or a standard building block – these are all excellent real-world examples of rectangular prisms. The key distinguishing feature is the rectangular shape of each face.
Understanding Lateral Surface Area
The lateral surface area of a three-dimensional shape refers to the total area of all its sides excluding the area of its bases. For a rectangular prism, this means we're calculating the area of the four vertical faces. It's important to distinguish this from the total surface area, which includes the areas of all six faces (including the top and bottom bases).
Deriving the Formula for Lateral Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism
The lateral surface area of a rectangular prism can be easily calculated using a simple formula derived from the fundamental principles of area calculation. Let's break down the derivation:
-
Identifying the Faces: A rectangular prism has four lateral faces. These are the faces that are not the top or bottom.
-
Dimensions: Let's denote the dimensions of the rectangular prism as follows:
- Length (l): The length of the rectangular base.
- Width (w): The width of the rectangular base.
- Height (h): The height of the prism.
-
Area of Each Lateral Face: Each lateral face is a rectangle. The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length and width. Therefore:
- Area of two faces with length 'l' and height 'h' = 2 * (l * h)
- Area of two faces with width 'w' and height 'h' = 2 * (w * h)
-
Total Lateral Surface Area: To find the total lateral surface area, we simply add the areas of all four lateral faces:
Lateral Surface Area (LSA) = 2(lh) + 2(wh) = 2h(l + w)
Therefore, the formula for the lateral surface area of a rectangular prism is:
LSA = 2h(l + w)
Applying the Formula: Step-by-Step Examples
Let's solidify our understanding with some practical examples.
Example 1:
A rectangular prism has a length of 5 cm, a width of 3 cm, and a height of 4 cm. Calculate its lateral surface area.
Solution:
- Identify the dimensions: l = 5 cm, w = 3 cm, h = 4 cm
- Apply the formula: LSA = 2h(l + w) = 2 * 4 cm * (5 cm + 3 cm) = 8 cm * 8 cm = 64 cm²
Therefore, the lateral surface area of the rectangular prism is 64 square centimeters.
Example 2:
A shipping container has dimensions of 12 feet, 8 feet, and 10 feet. What is the lateral surface area of the container?
Solution:
- Identify the dimensions: l = 12 ft, w = 8 ft, h = 10 ft
- Apply the formula: LSA = 2h(l + w) = 2 * 10 ft * (12 ft + 8 ft) = 20 ft * 20 ft = 400 ft²
The lateral surface area of the shipping container is 400 square feet.
Example 3: A Real-World Application - Painting a Wall
Imagine you need to paint the walls of a room (ignoring doors and windows for simplicity). The room is rectangular with a length of 15 feet, a width of 12 feet, and a height of 8 feet. To determine the amount of paint needed, you would calculate the lateral surface area of the room:
Solution:
- Identify the dimensions: l = 15 ft, w = 12 ft, h = 8 ft
- Apply the formula: LSA = 2h(l + w) = 2 * 8 ft * (15 ft + 12 ft) = 16 ft * 27 ft = 432 ft²
You would need enough paint to cover 432 square feet of wall space.
Beyond the Basics: Total Surface Area and Volume
While we've focused on lateral surface area, it's important to understand its relationship to total surface area and volume:
Total Surface Area (TSA): This includes the area of all six faces of the rectangular prism. The formula is:
TSA = 2(lw + wh + lh)
Volume (V): The volume represents the space enclosed within the rectangular prism. The formula is:
V = lwh
Understanding these three concepts – lateral surface area, total surface area, and volume – provides a complete picture of a rectangular prism's geometric properties.
Practical Applications in Various Fields
The concept of lateral surface area has wide-ranging applications:
- Architecture and Construction: Calculating the amount of material needed for walls, fences, or other structures.
- Packaging and Design: Determining the surface area of boxes or containers for product packaging and shipping.
- Manufacturing: Calculating the surface area of components for industrial design and production.
- Civil Engineering: Estimating the surface area of structures like dams or bridges.
- Graphic Design: Designing packaging, labels, and other materials requiring accurate surface area calculations.
Advanced Concepts and Related Shapes
While we've focused on rectangular prisms, the concept of lateral surface area extends to other three-dimensional shapes. Understanding the lateral surface area of a rectangular prism forms a strong foundation for exploring more complex shapes like:
- Cylinders: The lateral surface area of a cylinder is 2πrh, where 'r' is the radius and 'h' is the height.
- Triangular Prisms: The lateral surface area is the perimeter of the triangular base multiplied by the height.
- Other Prisms: The lateral surface area of any prism is the perimeter of the base multiplied by the height.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when calculating lateral surface area:
- Confusing lateral surface area with total surface area: Remember that lateral surface area excludes the bases.
- Incorrectly applying the formula: Double-check your substitution of values into the formula.
- Unit inconsistencies: Ensure all dimensions are in the same units before calculation.
Conclusion
The lateral surface area of a rectangular prism is a fundamental concept with numerous real-world applications. By understanding its formula, derivation, and practical applications, you can confidently tackle problems involving surface area calculations in various fields. This article provides a thorough guide to mastering this essential geometric concept. Remember to practice applying the formula to various examples to build your understanding and confidence. From simple calculations to complex engineering projects, the ability to accurately determine lateral surface area is a valuable skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Terminal Electron Acceptor In Aerobic Respiration Is
Mar 14, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between Alternator And Generator
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Does Xlv Mean In Roman Numbers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Melting Ice Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Strontium
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lateral Area Formula For A Rectangular Prism . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
