Is Zero A Multiple Of 3
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
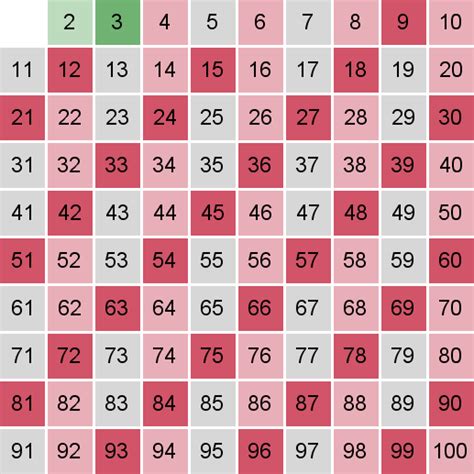
Table of Contents
Is Zero a Multiple of 3? A Deep Dive into Divisibility and Number Theory
The question, "Is zero a multiple of 3?" might seem trivial at first glance. Many intuitively answer "no," perhaps associating multiples with the idea of repeated addition. However, a deeper understanding of number theory reveals a more nuanced and mathematically precise answer: yes, zero is a multiple of 3 (and indeed, any non-zero integer). This article will explore this concept, delving into the definitions, properties, and implications of this seemingly simple yet crucial mathematical fact.
Understanding Multiples and Divisibility
Before diving into the specifics of zero, let's establish a firm understanding of multiples and divisibility.
A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any integer. For instance, the multiples of 3 are: …, -9, -6, -3, 0, 3, 6, 9, … We obtain these multiples by multiplying 3 by different integers: 3 x (-3) = -9, 3 x (-2) = -6, 3 x (-1) = -3, 3 x 0 = 0, 3 x 1 = 3, 3 x 2 = 6, 3 x 3 = 9, and so on.
Divisibility, on the other hand, refers to whether one number can be divided by another without leaving a remainder. If a number a is divisible by another number b, then there exists an integer k such that a = b x k. This is directly related to the concept of multiples: if a is divisible by b, then a is a multiple of b.
The Case of Zero: A Mathematical Perspective
The confusion surrounding whether zero is a multiple of 3 often stems from a limited understanding of multiplication involving zero. We typically visualize multiples as repeated additions. For example, 6 is a multiple of 3 because we can add 3 to itself twice: 3 + 3 = 6. But how can we add 3 to itself zero times to arrive at 0? This is where the standard visualization falls short.
The mathematical definition of a multiple, however, doesn't rely on repeated addition; it relies on multiplication. According to this definition:
- 0 = 3 x 0
Since 0 is an integer, and the equation conforms to the definition of a multiple (a = b x k), 0 is undeniably a multiple of 3. This logic applies to any non-zero integer; 0 is a multiple of every non-zero integer.
Zero's Unique Properties in Number Theory
Zero possesses several unique properties in number theory that contribute to its status as a multiple of all integers:
-
Additive Identity: Zero is the additive identity, meaning that adding zero to any number leaves that number unchanged. This fundamental property is crucial in various mathematical operations and contributes to zero's role as a multiple.
-
Multiplicative Property: Any number multiplied by zero results in zero. This property is central to why zero is a multiple of every integer. The equation n x 0 = 0 holds true for all integers n.
-
Neutral Element: Zero acts as a neutral element in multiplication. This property is closely linked to its role as a multiple.
These properties are not merely mathematical quirks; they are fundamental building blocks of number theory, and understanding them is vital for comprehending the concept of zero as a multiple.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several misconceptions frequently arise when discussing zero as a multiple:
Misconception 1: Zero isn't a number. This is incorrect. Zero is a number with crucial properties in various mathematical systems.
Misconception 2: Multiples must involve repeated addition. As discussed, this visualization is useful for certain cases but doesn't encompass the full mathematical definition of a multiple. The multiplication definition is more general and includes zero.
Misconception 3: Dividing by zero is undefined, so zero can't be a multiple. Dividing by zero is indeed undefined, but the concept of being a multiple is about multiplication, not division. The fact that 3 x 0 = 0 establishes that 0 is a multiple of 3.
Implications and Applications
The fact that zero is a multiple of 3 (and all integers) has various important implications:
-
Consistent Mathematical System: Including zero as a multiple ensures consistency within the framework of number theory and avoids creating exceptions that would complicate mathematical operations.
-
Modular Arithmetic: In modular arithmetic, where numbers "wrap around" after reaching a certain modulus (like in a clock), zero plays a crucial role as a multiple of the modulus.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concept extends to more abstract algebraic structures where the properties of zero as a multiple are essential for defining and understanding various algebraic operations.
Conclusion: The Definitive Answer
The definitive answer is a resounding yes. Zero is a multiple of 3, and indeed, any non-zero integer. This stems from the precise mathematical definition of a multiple based on multiplication, not repeated addition, and from the unique properties of zero within the number system. Understanding this seemingly simple concept is crucial for a solid foundation in number theory and its various applications. The consistent inclusion of zero as a multiple ensures a cohesive and robust mathematical framework. By clarifying this concept, we not only solidify our understanding of elementary number theory but also appreciate the subtle yet powerful role zero plays in the broader world of mathematics.
Further Exploration
For readers seeking a deeper dive, further exploration into these topics is highly recommended:
- Modular Arithmetic: Learn about the applications of modular arithmetic in cryptography and computer science.
- Abstract Algebra: Explore the concepts of rings, fields, and groups, where the properties of zero take on greater significance.
- Divisibility Rules: Delve deeper into the rules of divisibility for various integers, which build upon the fundamental principles discussed in this article. This will enhance your understanding of the relationship between numbers and their multiples.
This extended exploration will not only reinforce the understanding of zero as a multiple but will also provide a richer understanding of the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts. The seemingly simple question, "Is zero a multiple of 3?", opens doors to a vast and fascinating world of mathematical inquiry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Diagonals Of An Isosceles Trapezoid Are Congruent
Mar 21, 2025
-
Composite Numbers And Prime Numbers Chart
Mar 21, 2025
-
Adjectives That Start With The Letter K
Mar 21, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 121
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Deoxyribose And Ribose
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Zero A Multiple Of 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
