What Is The Difference Between Deoxyribose And Ribose
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
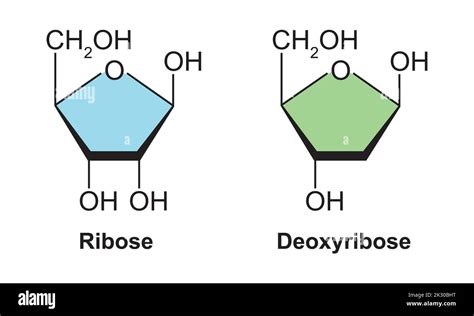
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Deoxyribose and Ribose? A Deep Dive into Sugar Structures
Deoxyribose and ribose are both pentose sugars – meaning they contain five carbon atoms – that play crucial roles in the building blocks of life. While seemingly similar at first glance, their subtle structural differences have profound implications for the functionality of DNA and RNA, the two nucleic acids that govern the genetic blueprint and protein synthesis within all living organisms. This article will explore the key distinctions between deoxyribose and ribose, delving into their chemical structures, biological roles, and the significance of these differences in the context of genetic information storage and transfer.
Understanding the Basic Structure: Pentose Sugars
Both deoxyribose and ribose belong to the aldopentose family, a category of monosaccharides characterized by five carbon atoms and an aldehyde functional group (–CHO). However, it's the subtle variations in their hydroxyl (-OH) groups that set them apart.
Ribose: The Foundation of RNA
Ribose, a crucial component of ribonucleic acid (RNA), is a pentose sugar with the chemical formula C₅H₁₀O₅. Its structure features a five-membered ring containing four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Each carbon atom, numbered 1' to 5', bears a hydroxyl group (-OH) except for the 5' carbon, which is usually attached to a phosphate group in RNA's structure. The presence of a hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon is a key distinguishing feature of ribose. This 2'-OH group imparts properties that influence RNA's structure and reactivity.
Deoxyribose: The Backbone of DNA
Deoxyribose, the foundational sugar of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), is very similar to ribose, also having a five-membered ring structure with the same chemical formula (C₅H₁₀O₄) except for one less oxygen atom. The crucial difference lies at the 2' carbon: deoxyribose lacks the hydroxyl group (-OH) at this position. Instead, it has only a hydrogen atom (–H) attached to the 2' carbon, hence the "deoxy" prefix. This seemingly small change has significant consequences for the stability and function of DNA.
Chemical Differences and their Biological Implications
The absence of the 2'-hydroxyl group in deoxyribose directly affects several key properties of DNA, leading to its distinct characteristics compared to RNA:
1. Increased Stability of DNA:
The 2'-OH group in ribose is relatively reactive. It can participate in acid-base reactions and even undergo spontaneous hydrolysis (breaking down through reaction with water), making RNA molecules comparatively less stable than DNA. The absence of this hydroxyl group in deoxyribose significantly reduces the reactivity and susceptibility to hydrolysis, resulting in the much greater stability of DNA – essential for preserving the integrity of genetic information over long periods.
2. Conformational Differences:
The presence of the 2'-OH group in ribose influences the sugar's conformation, affecting the overall structure of RNA. This group introduces steric hindrance (spatial interference), influencing RNA's ability to adopt specific secondary and tertiary structures, contributing to its functional diversity. In contrast, deoxyribose’s lack of a 2'-OH group provides more flexibility but restricts the range of conformational changes possible in DNA.
3. Differential Reactivity:
The 2'-OH group in ribose allows RNA to participate in various chemical reactions, influencing its catalytic abilities. RNA molecules, particularly ribosomal RNA (rRNA), exhibit catalytic activity (ribozymes), playing crucial roles in protein synthesis. This enhanced reactivity isn't as prominent in DNA, which primarily functions as a stable repository of genetic information.
Biological Roles: DNA vs. RNA
The structural differences between deoxyribose and ribose are directly reflected in the vastly different roles that DNA and RNA play in cellular processes:
DNA: The Genetic Blueprint
DNA, built with deoxyribose, serves as the primary repository of genetic information. Its double-helix structure, stabilized by the relative stability of deoxyribose, ensures the long-term storage and accurate transmission of hereditary material across generations. The lack of reactivity of deoxyribose safeguards against unwanted chemical modifications and spontaneous mutations that could corrupt the genetic code.
RNA: The Versatile Messenger and Worker
RNA, constructed with ribose, possesses a more versatile range of functions:
-
Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis. The ribose sugar's increased reactivity contributes to the mRNA's relatively short lifespan, which is crucial for regulating gene expression.
-
Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transports amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis. The specific folding patterns of tRNA molecules, shaped by the ribose sugar's conformation, are essential for its ability to recognize and interact with mRNA and amino acids.
-
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms a structural component of ribosomes, the protein synthesis machinery. The catalytic activity of rRNA (as ribozymes) is directly attributed to its ribose backbone.
-
MicroRNAs (miRNAs): Regulate gene expression by binding to mRNA molecules and influencing their translation into proteins. The flexibility and reactivity of RNA, enabled by ribose, allow for intricate regulation of gene expression.
Significance of the Differences: Evolutionary Perspective
The distinct properties of deoxyribose and ribose are not mere coincidences; they reflect an evolutionary optimization process. The greater stability of DNA, thanks to its deoxyribose backbone, is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the genetic code over generations. In contrast, the reactivity and structural versatility of RNA, endowed by its ribose backbone, allow it to perform a myriad of functions in gene expression and protein synthesis. This functional division of labor between DNA and RNA is a cornerstone of life’s molecular machinery.
The evolutionary history of RNA world hypothesis suggests that RNA, with its catalytic properties and capacity for information storage, might have predated DNA in early life forms. The evolution of DNA with its greater stability provided a more reliable system for long-term storage of genetic information, resulting in a more stable and efficient mechanism for heredity.
Conclusion: A Tale of Two Sugars
The subtle chemical difference between deoxyribose and ribose—the presence or absence of a hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon—has profound implications for the structure and function of DNA and RNA. The stability of DNA, built on a deoxyribose backbone, ensures the faithful transmission of genetic information across generations. The reactivity and versatility of RNA, built on a ribose backbone, allow it to perform a wide array of vital functions in gene expression and protein synthesis. Understanding these fundamental differences is crucial for grasping the complexities of molecular biology and the very essence of life itself. The two sugars, despite their similarities, play distinctly different yet equally crucial roles in the intricate dance of life, their properties perfectly tailored to their respective roles in the molecular orchestra of the cell. This intricate interplay underscores the elegance and efficiency of evolution’s design, a testament to the power of even small molecular modifications in shaping the grand narrative of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 25 And 35
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Are All The Factors Of 11
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is The Factors Of 25
Mar 27, 2025
-
How Much Electrons Does Sodium Have
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Is Larger 3 8 Or 1 2
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Deoxyribose And Ribose . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
