Is Square Root Of 9 A Rational Number
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
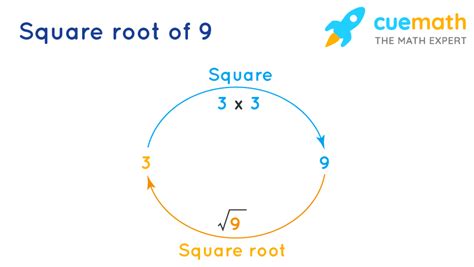
Table of Contents
Is the Square Root of 9 a Rational Number? A Deep Dive into Number Systems
The question, "Is the square root of 9 a rational number?" might seem trivial at first glance. However, exploring this seemingly simple question provides a valuable opportunity to delve into the fascinating world of number systems, clarifying the distinctions between rational and irrational numbers, and reinforcing fundamental mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question definitively but also provide a robust understanding of the underlying principles.
Understanding Rational Numbers
Before we tackle the square root of 9, let's establish a clear definition of a rational number. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where both p and q are integers, and q is not equal to zero. This seemingly simple definition encompasses a wide range of numbers, including:
-
Integers: Whole numbers, both positive and negative, including zero (e.g., -3, 0, 5). These can be expressed as fractions with a denominator of 1 (e.g., -3/1, 0/1, 5/1).
-
Fractions: Numbers expressed as the ratio of two integers (e.g., 1/2, 3/4, -2/5).
-
Terminating Decimals: Decimals that end after a finite number of digits (e.g., 0.5, 0.75, 2.375). These can always be converted into fractions. For example, 0.75 = 3/4.
-
Repeating Decimals: Decimals where a sequence of digits repeats indefinitely (e.g., 0.333..., 0.666..., 0.142857142857...). These also have equivalent fraction representations; for example, 0.333... = 1/3.
Understanding Irrational Numbers
In contrast to rational numbers, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Their decimal representations are non-terminating and non-repeating, meaning they go on forever without any pattern. Famous examples of irrational numbers include:
-
π (Pi): The ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter (approximately 3.14159...).
-
e (Euler's number): The base of the natural logarithm (approximately 2.71828...).
-
√2 (the square root of 2): This number, approximately 1.41421..., cannot be expressed as a fraction.
Calculating the Square Root of 9
Now, let's focus on the main question: Is √9 a rational number? The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. In this case, we are looking for a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 9.
The answer is straightforward: 3 x 3 = 9. Therefore, the square root of 9 is 3.
Is 3 a Rational Number?
Since we've determined that √9 = 3, we can now assess whether 3 is a rational number. The integer 3 can easily be expressed as a fraction: 3/1. This fulfills the definition of a rational number: it's a fraction where both the numerator (3) and the denominator (1) are integers, and the denominator is not zero.
Therefore, the answer to our main question is a resounding yes. The square root of 9 is a rational number.
Deeper Exploration: Why Rational Numbers are Important
The distinction between rational and irrational numbers is fundamental to mathematics. Rational numbers form the basis for many mathematical operations and concepts, including:
-
Arithmetic: The four basic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) can be performed on rational numbers, resulting in rational numbers (except in cases of division by zero).
-
Algebra: Rational numbers are crucial in solving algebraic equations and inequalities.
-
Calculus: Rational functions, which involve ratios of polynomials, are an essential part of calculus.
-
Geometry: Rational numbers are frequently used in geometric calculations, such as finding the area or perimeter of shapes.
Expanding on Decimal Representations
The decimal representation of a number can provide a quick way to assess whether it's rational or irrational. As mentioned earlier, rational numbers have either terminating or repeating decimal expansions. Irrational numbers, on the other hand, have non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansions. The decimal representation of 3 (which is 3.0) is clearly a terminating decimal, further supporting its classification as a rational number.
Practical Applications of Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are ubiquitous in everyday life. They're essential in:
-
Measurement: Lengths, weights, and volumes are often expressed using rational numbers.
-
Finance: Money, interest rates, and financial calculations extensively utilize rational numbers.
-
Engineering: Precise measurements and calculations in engineering rely heavily on rational numbers.
-
Computer Science: Representing numbers in computers frequently uses rational number approximations due to the limitations of representing irrational numbers with finite precision.
Further Exploration: Proving the Irrationality of Numbers
While proving that a number is rational is relatively straightforward, proving that a number is irrational often requires more sophisticated mathematical techniques. The classic example is the proof of the irrationality of √2, which relies on proof by contradiction. Such proofs highlight the richness and complexity of number theory.
Conclusion: The Square Root of 9 and the Broader Mathematical Landscape
The question of whether the square root of 9 is a rational number may seem simple, but it serves as an excellent entry point into the deeper world of number systems. Understanding the distinctions between rational and irrational numbers is crucial for anyone pursuing further studies in mathematics or related fields. The fact that √9 (which equals 3) is a rational number is not merely a trivial fact but a fundamental building block in the vast and intricate structure of mathematics. This exploration has reinforced the importance of rational numbers in various aspects of mathematics and real-world applications, highlighting their pervasive role in our understanding of the numerical world. The simplicity of this specific example allows for a clear and accessible introduction to the broader and more complex world of number theory and its countless applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Is Ice Melting Not A Chemical Change
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Does Aq Mean In A Chemical Equation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Diagram Of An Animal Cell And Plant Cell
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 10 And 25
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 32 And 28
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Square Root Of 9 A Rational Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
