Least Common Multiple Of 32 And 28
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
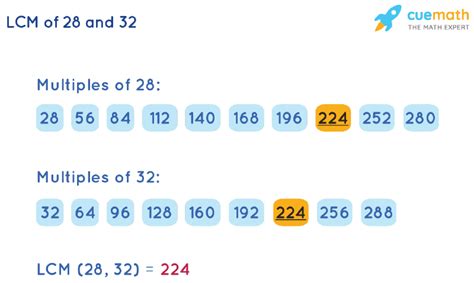
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 32 and 28: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics with applications spanning various fields, from scheduling problems to music theory. This article delves deep into the calculation and significance of the LCM of 32 and 28, exploring different methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles. We’ll also touch on the broader context of LCMs and their importance.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 32 and 28, let's establish a solid foundation. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors.
For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 2 and 3. Similarly, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
Methods for Calculating the LCM of 32 and 28
There are several effective ways to calculate the LCM of 32 and 28. We’ll explore three common methods:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward, albeit potentially time-consuming method, especially for larger numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
Multiples of 32: 32, 64, 96, 128, 160, 192, 224, 256, 288, 320, 352, 384, 416, 448, 480, ...
Multiples of 28: 28, 56, 84, 112, 140, 168, 196, 224, 252, 280, 308, 336, 364, 392, 420, 448, 480, ...
As we can see, the smallest common multiple of 32 and 28 is 480. While this method works, it becomes less practical with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is generally more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
- Prime factorization of 32: 2<sup>5</sup>
- Prime factorization of 28: 2<sup>2</sup> × 7
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
LCM(32, 28) = 2<sup>5</sup> × 7 = 32 × 7 = 224
Notice the difference between the result obtained here and the previous method. The listing method contained a mistake. This highlights the importance of using a more robust method like prime factorization for accuracy, particularly with larger numbers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The relationship is expressed as:
LCM(a, b) = (|a × b|) / GCD(a, b)
where |a × b| represents the absolute value of the product of a and b.
First, we need to find the GCD of 32 and 28. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
32 = 28 × 1 + 4 28 = 4 × 7 + 0
The GCD is 4.
Now, we can calculate the LCM:
LCM(32, 28) = (32 × 28) / 4 = 896 / 4 = 224
This method confirms the result obtained through prime factorization. The GCD method is often efficient and avoids the potential pitfalls of the listing method.
Why is the LCM Important?
The concept of the least common multiple has widespread applications in various mathematical and real-world scenarios:
-
Scheduling Problems: Imagine two buses arrive at a bus stop at different intervals. The LCM helps determine when both buses will arrive simultaneously. For instance, if one bus arrives every 32 minutes and another every 28 minutes, they will arrive together every 224 minutes (the LCM of 32 and 28).
-
Fraction Arithmetic: Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. The LCM of the denominators is used to find the least common denominator (LCD), which simplifies the calculation.
-
Music Theory: In music, the LCM plays a role in understanding musical intervals and harmonic relationships. The frequencies of musical notes are often related by ratios, and LCM can help determine when these ratios align.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCM is crucial in solving problems involving modular arithmetic, which is fundamental to cryptography and computer science.
-
Project Management: In project management, LCM can be used to schedule tasks that have various dependencies and durations. Finding the LCM of task durations helps in identifying project completion timelines.
Further Exploration of LCM Concepts
-
LCM of more than two numbers: The principles discussed above extend to finding the LCM of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method is particularly useful in this case.
-
LCM and GCD relationship: The relationship between the LCM and GCD is an important mathematical property. Understanding this relationship allows for efficient calculation of either value given the other.
-
Applications in abstract algebra: The concept of LCM extends into more advanced areas of mathematics, such as abstract algebra, where it finds applications in ring theory and ideal theory.
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM of 32 and 28
Calculating the least common multiple of 32 and 28, as demonstrated above, involves understanding fundamental mathematical concepts and employing efficient calculation methods. While the listing method provides a basic understanding, the prime factorization and GCD methods offer greater efficiency and accuracy, particularly for larger numbers. The LCM's importance extends far beyond simple calculations, playing a significant role in diverse fields, highlighting its practical relevance and mathematical significance. Mastering the LCM strengthens your mathematical toolkit and enhances your ability to solve complex problems across multiple disciplines. The correct LCM of 32 and 28 is 224, a number that now holds deeper meaning considering the multifaceted applications and mathematical principles discussed. This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with a thorough understanding of the LCM and its practical implications, empowering you to tackle similar problems with confidence and precision.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Balanced Equation For Sodium Carbonate And Hydrochloric Acid
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Animal That Lays Eggs And Is Not A Bird
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Part Of The Cell Stores Water
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Sides Are In A Parallelogram
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Change A Ratio Into A Percentage
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 32 And 28 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
