Is Nitrogen A Metal Metalloid Or Nonmetal
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
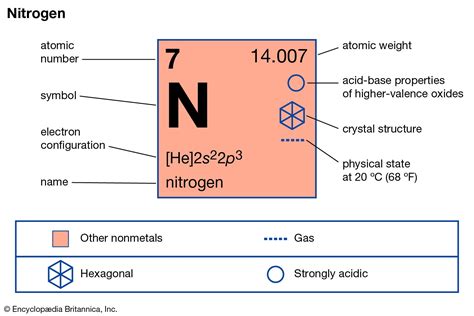
Table of Contents
Is Nitrogen a Metal, Metalloid, or Nonmetal? A Deep Dive into its Properties
Nitrogen, a ubiquitous element crucial to life on Earth, often sparks curiosity regarding its classification within the periodic table. Is it a metal, a metalloid, or a nonmetal? The answer, unequivocally, is nonmetal. However, understanding why requires a deeper exploration of its physical and chemical properties, its position within the periodic table, and how it contrasts with metals and metalloids. This article will delve into these aspects to provide a comprehensive understanding of nitrogen's classification.
Understanding the Three Categories: Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals
Before classifying nitrogen, let's establish clear distinctions between metals, metalloids, and nonmetals. These classifications are based on several key properties:
Metals
Metals generally exhibit the following characteristics:
- High electrical conductivity: They readily conduct electricity.
- High thermal conductivity: They efficiently transfer heat.
- Malleability: They can be hammered into thin sheets.
- Ductility: They can be drawn into wires.
- Luster: They have a shiny appearance.
- High density: They are relatively heavy for their size.
- Low electronegativity: They tend to lose electrons easily.
- High melting and boiling points: Generally require significant energy to change states.
Examples of metals include iron, copper, gold, and aluminum.
Metalloids (Semimetals)
Metalloids possess properties intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. Their characteristics are less definitive, often showing variability depending on conditions:
- Variable electrical conductivity: Their conductivity can be affected by factors like temperature and light. They are often semiconductors.
- Variable thermal conductivity: Similar to electrical conductivity, their thermal conductivity varies.
- Brittle: They tend to be fragile and break easily.
- Moderate luster: Their shine is less pronounced than that of metals.
- Intermediate density: Their density falls between metals and nonmetals.
- Variable electronegativity: Their tendency to gain or lose electrons is less predictable.
- Variable melting and boiling points: These properties can vary widely among metalloids.
Silicon, germanium, arsenic, and tellurium are examples of metalloids.
Nonmetals
Nonmetals, in contrast to metals, generally show:
- Low electrical conductivity: They are poor conductors of electricity.
- Low thermal conductivity: They poorly transfer heat.
- Brittle: They are often solid and break easily. (Exceptions exist for those that are gaseous).
- Dull appearance: They lack the characteristic shine of metals.
- Low density: They are relatively light for their size.
- High electronegativity: They tend to gain electrons readily.
- Low melting and boiling points: They typically have lower melting and boiling points than metals.
Examples of nonmetals include oxygen, sulfur, chlorine, and nitrogen.
Nitrogen's Properties and its Nonmetal Classification
Now, let's examine nitrogen's properties to definitively place it within the nonmetal category:
- Electrical Conductivity: Nitrogen is an extremely poor conductor of electricity in its gaseous and liquid states. It doesn't readily allow the flow of electrons.
- Thermal Conductivity: Similarly, nitrogen has low thermal conductivity, meaning it doesn't efficiently transfer heat.
- Physical State: At room temperature and pressure, nitrogen exists as a colorless, odorless, and tasteless diatomic gas (N₂). This gaseous nature contrasts sharply with the solid nature of most metals.
- Appearance: Nitrogen gas is transparent and lacks the metallic luster.
- Electronegativity: Nitrogen possesses a relatively high electronegativity (3.04 on the Pauling scale), indicating its strong tendency to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. This characteristic is typical of nonmetals.
- Chemical Reactivity: Nitrogen's chemical reactivity is relatively low under normal conditions due to the strong triple bond in the N₂ molecule. However, it can react with other elements under specific conditions, forming various compounds crucial for life (like amino acids and nucleic acids). This moderate reactivity is another indicator of its non-metallic nature; highly reactive elements are often found among the halogens (nonmetals).
- Melting and Boiling Points: Nitrogen has a very low melting point (-210°C) and boiling point (-196°C), further supporting its classification as a nonmetal.
All of these properties strongly support the classification of nitrogen as a nonmetal. There is no significant evidence suggesting metallic or metalloid behavior.
Nitrogen's Position in the Periodic Table
Nitrogen's position in the periodic table further reinforces its nonmetal status. It resides in Group 15 (also known as Group VA or the pnictogens), which contains both nonmetals (nitrogen, phosphorus) and metalloids (arsenic, antimony, bismuth). While the group shows a trend of increasing metallic character down the group (from nitrogen to bismuth), nitrogen itself displays distinctly nonmetallic properties. The trend across the period (from left to right) is also crucial; electronegativity generally increases and metallic character decreases. Therefore, given its position in the upper right portion of the periodic table, nitrogen's nonmetal classification is expected.
Distinguishing Nitrogen from Metals and Metalloids
The differences between nitrogen and metals are profound. Metals are characterized by their ability to conduct electricity and heat, their malleability and ductility, and their metallic luster. Nitrogen exhibits none of these properties.
The distinction between nitrogen and metalloids is also clear. While some metalloids exhibit variable conductivity, nitrogen is a consistently poor conductor. Metalloids often possess a somewhat metallic luster, which nitrogen lacks. The chemical reactivity of metalloids is also generally higher than that of nitrogen.
Conclusion: Nitrogen is Definitely a Nonmetal
The overwhelming evidence from its physical and chemical properties and its position in the periodic table conclusively categorizes nitrogen as a nonmetal. Its low electrical and thermal conductivity, its gaseous nature at room temperature, its high electronegativity, and its relatively low reactivity all align perfectly with the characteristics of nonmetals. While the heavier elements in its group exhibit increasing metallic properties, nitrogen remains firmly within the nonmetal realm, playing a pivotal role in biological and industrial processes worldwide. Its importance in life's building blocks and industrial applications underscores its significance despite its non-metallic nature. Understanding its nonmetal properties is key to grasping its fundamental role in chemistry and biology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Multiplication Chart From 1 To 20
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Are 3 Fractions Equivalent To 3 8
Mar 21, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 40 And 25
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 42 C In Fahrenheit
Mar 21, 2025
-
Intermediate Value Theorem Vs Mean Value Theorem
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Nitrogen A Metal Metalloid Or Nonmetal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
