Is Benzoic Acid A Weak Acid
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
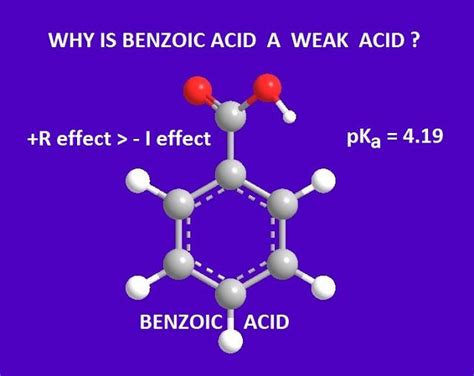
Table of Contents
- Is Benzoic Acid A Weak Acid
- Table of Contents
- Is Benzoic Acid a Weak Acid? A Comprehensive Exploration
- Understanding Acid Strength: A Quick Refresher
- Benzoic Acid's Dissociation and pKa
- Factors Influencing Benzoic Acid's Weak Acidity
- 1. Resonance Stabilization of the Benzoate Ion:
- 2. Inductive Effect of the Benzene Ring:
- 3. Electronegativity of Oxygen Atoms:
- Comparison with Other Acids: Strong vs. Weak
- Applications of Benzoic Acid: Leveraging its Weak Acidity
- 1. Food Preservation:
- 2. Pharmaceutical Applications:
- 3. Industrial Chemical Synthesis:
- 4. Other Applications:
- Conclusion: Understanding Benzoic Acid's Role
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Is Benzoic Acid a Weak Acid? A Comprehensive Exploration
Benzoic acid, a simple aromatic carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C₇H₆O₂, is frequently encountered in various fields, from food preservation to industrial chemical synthesis. A common question that arises regarding benzoic acid is its acidity. Is it a strong acid or a weak acid? The answer, unequivocally, is benzoic acid is a weak acid. This article will delve deep into the reasons behind this classification, exploring its dissociation behavior, pKa value, applications, and comparisons with other acids.
Understanding Acid Strength: A Quick Refresher
Before diving into the specifics of benzoic acid, let's establish a fundamental understanding of acid strength. Acids, by definition, donate protons (H⁺ ions) in aqueous solutions. Strong acids completely dissociate in water, meaning all their molecules donate a proton, resulting in a high concentration of H⁺ ions. Conversely, weak acids only partially dissociate, meaning only a small fraction of their molecules donate a proton, leading to a lower concentration of H⁺ ions. This partial dissociation is an equilibrium process.
The strength of an acid is quantified using its acid dissociation constant (Ka), or more commonly, its negative logarithm, the pKa. A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid, meaning it readily donates protons. A higher pKa value indicates a weaker acid.
Benzoic Acid's Dissociation and pKa
Benzoic acid, upon dissolving in water, undergoes partial dissociation according to the following equilibrium:
C₇H₆O₂(aq) + H₂O(l) ⇌ C₇H₅O₂⁻(aq) + H₃O⁺(aq)
Where:
- C₇H₆O₂ represents the undissociated benzoic acid molecule.
- C₇H₅O₂⁻ represents the benzoate ion, the conjugate base.
- H₃O⁺ represents the hydronium ion, formed by the proton donated by benzoic acid.
The equilibrium constant for this reaction is Ka, and for benzoic acid, its pKa is approximately 4.2 at 25°C. This value clearly places benzoic acid in the weak acid category. The pKa of 4.2 indicates that only a small percentage of benzoic acid molecules dissociate into benzoate ions and hydronium ions in water at equilibrium. Most of the benzoic acid remains in its undissociated form.
Factors Influencing Benzoic Acid's Weak Acidity
Several factors contribute to benzoic acid's relatively weak acidity:
1. Resonance Stabilization of the Benzoate Ion:
The conjugate base of benzoic acid, the benzoate ion (C₇H₅O₂⁻), is significantly stabilized by resonance. The negative charge on the carboxylate group (COO⁻) can be delocalized across the benzene ring through resonance structures. This delocalization distributes the negative charge, making the benzoate ion more stable. A more stable conjugate base implies a weaker acid.
2. Inductive Effect of the Benzene Ring:
The benzene ring's electron-withdrawing inductive effect slightly pulls electron density away from the carboxyl group. This effect makes it slightly more difficult for the carboxyl group to donate a proton, thereby contributing to benzoic acid's weak acidity. However, this effect is less significant compared to the resonance stabilization of the benzoate ion.
3. Electronegativity of Oxygen Atoms:
The oxygen atoms in the carboxyl group are highly electronegative. This electronegativity helps stabilize the negative charge on the carboxylate ion after proton donation, but it also makes it relatively difficult for the carboxyl group to release a proton in the first place. This partially contributes to benzoic acid's weak acidity.
Comparison with Other Acids: Strong vs. Weak
To further understand benzoic acid's weak acidity, let's compare it to some strong and weak acids:
Strong Acids (pKa < 0): Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), and nitric acid (HNO₃) are examples of strong acids. They completely dissociate in water, exhibiting pKa values far below zero.
Weak Acids (pKa > 0): Acetic acid (CH₃COOH, pKa ≈ 4.76), lactic acid (CH₃CH(OH)COOH, pKa ≈ 3.86), and formic acid (HCOOH, pKa ≈ 3.75) are examples of weak acids, like benzoic acid. Their pKa values are positive, indicating partial dissociation in water. Note that the pKa values of these weak acids are relatively close to that of benzoic acid, highlighting that the strength of weakness is a relative scale.
Applications of Benzoic Acid: Leveraging its Weak Acidity
Benzoic acid's weak acidity plays a crucial role in its various applications:
1. Food Preservation:
Benzoic acid and its salts (benzoates) are widely used as food preservatives. Their weak acidity makes them effective against a broad range of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and molds. The low pH created by benzoic acid inhibits the growth of these organisms, preserving the food's quality and extending its shelf life.
2. Pharmaceutical Applications:
Benzoic acid is a precursor in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals. Its properties, including its weak acidity and aromatic nature, make it a valuable building block for various drug molecules.
3. Industrial Chemical Synthesis:
Benzoic acid serves as an intermediate in the production of various industrial chemicals, including plasticizers, dyes, and resins. Its chemical reactivity stemming from its carboxylic acid functional group is exploited in diverse synthetic routes.
4. Other Applications:
Beyond food preservation and industrial synthesis, benzoic acid has niche applications in agriculture as a fungicide and in the production of certain polymers.
Conclusion: Understanding Benzoic Acid's Role
Benzoic acid's classification as a weak acid is not just an academic detail; it has profound implications for its properties, reactivity, and applications. Its partial dissociation in water, governed by its pKa of approximately 4.2, underpins its effectiveness as a food preservative and its suitability for various chemical syntheses. The factors contributing to its weak acidity—resonance stabilization, inductive effects, and electronegativity—provide a deeper understanding of its chemical behavior. By comprehending the nuances of its weak acidity, we can better appreciate benzoic acid's diverse roles across various industries and scientific disciplines. It is this delicate balance between strength and weakness that defines the versatility of this important organic compound. Further research continually refines our understanding of benzoic acid's behavior and potential applications. The study of this seemingly simple molecule provides a valuable insight into the broader realm of organic chemistry and its practical implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lowest Common Multiple Of 6 And 18
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is The Factor Of 180
Mar 27, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 46 Inches
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is The Roman Number Of 5000
Mar 27, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between A Rhombus And A Parallelogram
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Benzoic Acid A Weak Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
