What Is The Roman Number Of 5000
Juapaving
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
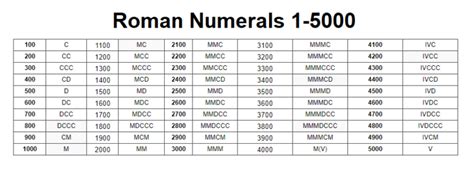
Table of Contents
What is the Roman Numeral for 5000? Unlocking the Secrets of Roman Numeration
Roman numerals, a system of numerical notation originating in ancient Rome, continue to fascinate and intrigue us today. While commonly used for things like clock faces, chapter headings, and copyright dates, the system presents a unique challenge when dealing with larger numbers. This article delves deep into the intricacies of Roman numerals, focusing specifically on the representation of 5000 and exploring the historical context and evolution of this fascinating system.
Understanding the Basics of Roman Numerals
Before we tackle the representation of 5000, let's establish a foundational understanding of Roman numerals. The system utilizes seven basic symbols:
- I: 1
- V: 5
- X: 10
- L: 50
- C: 100
- D: 500
- M: 1000
These symbols are combined to create larger numbers. The key principle is that smaller values placed before larger values are subtracted, while smaller values placed after larger values are added. For example:
- IV: 4 (5 - 1)
- IX: 9 (10 - 1)
- XL: 40 (50 - 10)
- XC: 90 (100 - 10)
- CD: 400 (500 - 100)
- CM: 900 (1000 - 100)
- VI: 6 (5 + 1)
- XI: 11 (10 + 1)
- LX: 60 (50 + 10)
- CX: 110 (100 + 10)
The Challenge of Representing Larger Numbers in Roman Numerals
The standard Roman numeral system, as outlined above, doesn't inherently provide a single symbol for numbers beyond 1000 (M). Historically, the Romans themselves didn't frequently encounter or record numbers exceeding a few thousand. Therefore, a standardized system for expressing much larger numbers wasn't strictly necessary for everyday life or record-keeping.
However, as the need arose to represent larger numbers, particularly in later periods and scholarly contexts, various conventions and extensions of the basic system evolved. These extensions weren't universally consistent, contributing to some ambiguity in historical texts.
The Roman Numeral for 5000: Exploring the Options
There's no single universally accepted Roman numeral for 5000 within the classical system. However, several conventions have emerged over time:
1. Using a Vinculum (Overline):
The most common and generally accepted method for representing 5000 in Roman numerals is to place a vinculum (a horizontal line or bar) above the symbol for 1000 (M). This notation signifies multiplication by 1000.
Therefore, $\overline{V}$ is commonly understood to represent 5000. This method extends logically to represent even larger numbers: $\overline{X}$ for 10,000, $\overline{L}$ for 50,000, and so on.
2. Alternative Notations:
While the vinculum method is the most prevalent, other less common notations have been used historically, often depending on the context or the preferences of the scribe or author. These may include variations like:
- V̅: A single bar above the V.
- MMMMM: While functionally correct (five 1000s), it’s lengthy and less elegant than the vinculum method.
3. The Importance of Context:
Understanding the context in which a Roman numeral is used is crucial, especially when encountering larger numbers. The method of representation might vary based on the era, the specific field (e.g., mathematics, astronomy, history), and the individual writing the numeral.
The Historical Context and Evolution of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system did not emerge fully formed but evolved over centuries. Its early forms were likely simpler, potentially lacking some of the subtractive notation we see in later examples. The standardization of the system we recognize today was a gradual process.
The lack of a systematic way to easily handle very large numbers within the standard system reflects the practical limitations of Roman society. While large-scale projects existed (e.g., the construction of aqueducts and public buildings), the need for precise numerical representation of extremely large numbers simply wasn't as pervasive as it is in our modern quantitative world.
The later adoption of the vinculum method for representing multiples of 1000 showcases the system's adaptability and response to the growing need for representing increasingly larger numbers in various applications.
Beyond 5000: Extending Roman Numeration
Once you grasp the concept of the vinculum, representing numbers significantly larger than 5000 becomes straightforward. Simply combine the vinculum notation with the basic symbols, adhering to the standard additive and subtractive principles:
- $\overline{X}$: 10,000
- $\overline{X} \overline{X}$: 20,000
- $\overline{L}$: 50,000
- $\overline{C}$: 100,000
- $\overline{D}$: 500,000
- $\overline{M}$: 1,000,000
Practical Applications of Roman Numerals Today
While the Arabic numeral system has replaced Roman numerals in most everyday calculations and numerical representations, Roman numerals still hold significance and are employed in various contexts, including:
- Clock faces: Many clocks and watches continue to utilize Roman numerals, primarily for aesthetic reasons.
- Chapter headings: Books often use Roman numerals for outlining chapters and sections.
- Copyright dates: Copyright years are sometimes represented using Roman numerals.
- Outlines and lists: Roman numerals can add a touch of formality and visual distinction to outlines and numbered lists.
- Monuments and historical inscriptions: Roman numerals can be found on many historical structures and inscriptions.
Conclusion: 5000 and the Enduring Legacy of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral for 5000, typically represented as $\overline{V}$, highlights the evolution and flexibility of this ancient system. While not initially designed for representing such large numbers, the addition of the vinculum allowed for expansion and adaptation to meet changing needs. Roman numerals continue to maintain their presence in modern society, serving both functional and aesthetic purposes, underscoring their enduring legacy and timeless appeal. Understanding the system, including methods for representing large numbers like 5000, allows us to appreciate the ingenuity of the Roman system and its enduring influence on our methods of numerical representation. The adaptability demonstrated by the use of the vinculum to easily extend the system beyond 1000 is a testament to its enduring value and efficiency. While the Arabic numeral system prevails for most mathematical operations, the Roman numeral system remains a captivating system that continues to hold its unique place in history and culture.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Matter Is Anything That Has And Occupies
Mar 30, 2025
-
When Ice Cream Melts A Chemical Change Occurs
Mar 30, 2025
-
How To Tell Time On A Watch Without Numbers
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Many Km Are In 230 M
Mar 30, 2025
-
Definition Of Word Form In Math
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Roman Number Of 5000 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
