How Many Valence Electrons In Bromine
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
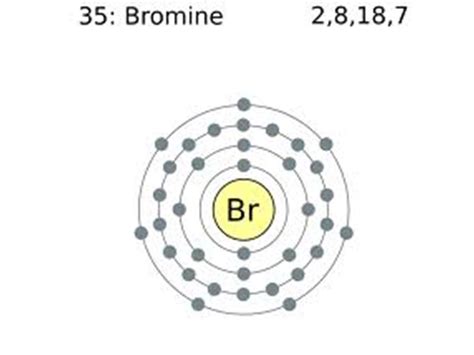
Table of Contents
- How Many Valence Electrons In Bromine
- Table of Contents
- How Many Valence Electrons Does Bromine Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
- Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Bonding
- The Significance of the Outermost Shell
- Determining Bromine's Valence Electrons: Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
- Bromine's Electron Configuration
- The Role of the Periodic Table: A Quick Shortcut
- Bromine's Chemical Behavior: Implications of Seven Valence Electrons
- Formation of Ionic Compounds: Gaining an Electron
- Formation of Covalent Compounds: Sharing Electrons
- Bromine's Applications: A Versatile Element
- Conclusion: Valence Electrons Define Bromine's Chemistry
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Many Valence Electrons Does Bromine Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Bromine, a fascinating element with a rich reddish-brown hue and a pungent odor, holds a unique place in the periodic table. Understanding its properties, particularly its valence electrons, is crucial to comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This in-depth article explores the number of valence electrons in bromine, delving into the underlying atomic structure and its implications for bromine's role in various chemical compounds and reactions.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Bonding
Before diving into bromine specifically, let's establish a foundational understanding of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. These electrons are the primary players in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form. They are the architects of chemical interactions, dictating how atoms interact to form molecules and compounds. The number of valence electrons directly influences an element's position within the periodic table and its chemical properties.
The Significance of the Outermost Shell
The outermost electron shell, often called the valence shell, is crucial because it's where atoms interact most readily with other atoms. Electrons in inner shells are tightly bound to the nucleus and are generally not involved in chemical bonding. Atoms strive for stability, often achieved by filling their valence shell with the maximum number of electrons it can accommodate. This stability is often associated with the noble gases, which have full valence shells and are exceptionally unreactive.
Determining Bromine's Valence Electrons: Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
Bromine (Br) is located in Group 17 (also known as Group VIIA or the halogens) of the periodic table. The periodic table's structure provides a powerful tool for quickly determining the number of valence electrons for most elements. Group 17 elements consistently have seven valence electrons.
Bromine's Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of bromine helps to confirm this. Bromine's atomic number is 35, meaning it has 35 electrons. Its electron configuration is written as: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁵.
Let's break down this electron configuration:
- 1s², 2s², 2p⁶, 3s², 3p⁶: These electrons fill the inner shells and are not valence electrons.
- 4s²: These two electrons are in the fourth energy level, but they are not valence electrons in the context of chemical bonding for bromine.
- 3d¹⁰: These ten electrons fill the 3d subshell; however, they are also considered core electrons and do not directly participate in typical bromine chemical bonding.
- 4p⁵: These five electrons are located in the outermost energy level (n=4), making them the valence electrons.
Therefore, bromine possesses seven valence electrons.
The Role of the Periodic Table: A Quick Shortcut
The periodic table provides a quick method to determine the number of valence electrons. The group number (for main group elements like bromine) corresponds to the number of valence electrons. Group 17, where bromine resides, indicates seven valence electrons. This convenient shortcut eliminates the need for writing out the full electron configuration each time.
Bromine's Chemical Behavior: Implications of Seven Valence Electrons
The presence of seven valence electrons profoundly influences bromine's chemical behavior. Atoms tend to react in ways that lead to a stable, full valence shell (usually eight electrons, the octet rule). Bromine readily achieves this stability by gaining one electron, forming a bromide ion (Br⁻) with a stable octet.
Formation of Ionic Compounds: Gaining an Electron
Bromine's high electronegativity (its tendency to attract electrons) contributes to its ability to gain an electron easily. This leads to the formation of ionic compounds with metals, where bromine accepts an electron from the metal, creating a positively charged metal cation and a negatively charged bromide anion. For example, in sodium bromide (NaBr), sodium (Na) donates one electron to bromine, forming Na⁺ and Br⁻ ions. The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions holds the compound together.
Formation of Covalent Compounds: Sharing Electrons
Bromine can also form covalent bonds by sharing electrons with other nonmetals. In these bonds, bromine shares one electron to complete its octet. For instance, in bromine gas (Br₂), two bromine atoms share one pair of electrons to achieve a full valence shell for each atom. This sharing forms a stable diatomic molecule.
Bromine's Applications: A Versatile Element
Bromine's unique chemical properties, stemming directly from its seven valence electrons, make it a versatile element with numerous applications. Here are a few examples:
- Flame Retardants: Brominated flame retardants are used in various materials to prevent or slow the spread of fire. The bromine atoms disrupt the combustion process.
- Agricultural Chemicals: Bromine compounds are used as fumigants and pesticides to control pests and weeds.
- Water Purification: Bromine is used as a disinfectant in water treatment due to its effectiveness in killing bacteria and other microorganisms.
- Medical Applications: Some bromine compounds possess medicinal properties, finding use in certain pharmaceuticals.
- Photography: Bromide salts were historically used in photography, contributing to the formation of photographic images.
Conclusion: Valence Electrons Define Bromine's Chemistry
The number of valence electrons an atom possesses fundamentally determines its chemical behavior. Bromine, with its seven valence electrons, exhibits a strong tendency to gain an electron to achieve a stable octet. This characteristic leads to the formation of ionic and covalent compounds, explaining its reactivity and diverse applications across various fields. Understanding the concept of valence electrons, and the specific case of bromine's seven valence electrons, provides a key to comprehending the element's fundamental role in chemistry and its impact on modern technology and everyday life. The interplay between atomic structure and chemical properties highlights the power of fundamental scientific principles in explaining the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Is 15 Of 50
Mar 27, 2025
-
Nh4 3po4 Pb No3 4 Pb3 Po4 4 Nh4no3
Mar 27, 2025
-
In Which Figure Is Point G A Centroid
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is The Charge Of Beryllium
Mar 27, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Diseases Is Not Caused By Virus
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons In Bromine . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
