How Many Valence Electrons In Br
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
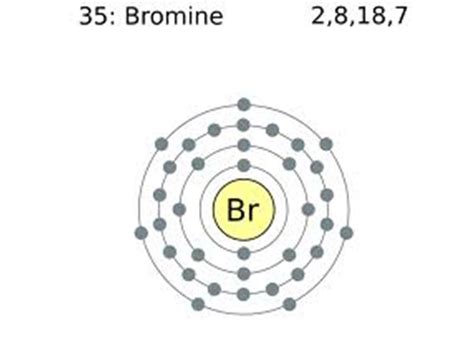
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does Bromine (Br) Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure and Chemical Behavior
Bromine (Br), a fascinating halogen element, plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and industrial processes. Understanding its electronic structure, specifically the number of valence electrons, is key to grasping its chemical behavior and reactivity. This article delves deep into the atomic structure of bromine, explaining in detail why it possesses the specific number of valence electrons it does, and how this influences its bonding characteristics and chemical properties. We'll explore this topic comprehensively, incorporating relevant concepts and examples to ensure a clear and thorough understanding.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Reactivity
Before we pinpoint the number of valence electrons in bromine, let's define what valence electrons are and why they're so important. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are crucial because they determine an atom's ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms. They're the primary participants in chemical reactions, influencing an element's reactivity and the types of compounds it can form. Atoms tend to react in ways that achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling the noble gases with their filled outermost shells.
Determining Bromine's Valence Electrons: Electron Configuration
To determine the number of valence electrons in bromine, we need to examine its electron configuration. The electron configuration describes how electrons are distributed among the different energy levels (shells) and sublevels (orbitals) within an atom. Bromine's atomic number is 35, meaning it has 35 protons and 35 electrons in a neutral atom.
The electron configuration of bromine is: 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵.
Let's break this down:
-
1s², 2s², 2p⁶, 3s², 3p⁶: These represent the filled inner shells. These electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus and don't typically participate in chemical bonding.
-
4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁵: This is where the action is! This is bromine's outermost shell, also known as the valence shell. The electrons in this shell are the valence electrons.
Counting the electrons in the outermost shell (4s and 4p): 2 (from 4s) + 5 (from 4p) = 7 valence electrons.
Therefore, bromine (Br) has 7 valence electrons.
The Significance of 7 Valence Electrons: Chemical Behavior of Bromine
Having seven valence electrons profoundly influences bromine's chemical behavior. Bromine is a halogen, a group of highly reactive nonmetals located in Group 17 (or VIIA) of the periodic table. All halogens have seven valence electrons. This electron configuration drives their reactivity.
To achieve a stable electron configuration, similar to the noble gases, bromine atoms tend to gain one electron to complete their outermost shell (achieving an octet). This results in a bromide ion (Br⁻) with a stable configuration of 8 valence electrons. This strong tendency to gain an electron makes bromine a powerful oxidizing agent, readily accepting electrons from other atoms or molecules.
Bromine's Bonding Characteristics:
-
Ionic Bonding: The most common type of bonding for bromine involves the transfer of an electron to form an ionic bond. This is especially true when reacting with metals, which tend to lose electrons. For instance, in the formation of sodium bromide (NaBr), sodium (Na) loses one electron to bromine (Br), creating Na⁺ and Br⁻ ions, which are held together by electrostatic attraction.
-
Covalent Bonding: Bromine can also form covalent bonds by sharing electrons with other nonmetals. This sharing allows both atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration. For example, in bromine gas (Br₂), two bromine atoms share one pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. This sharing completes their outer shell and creates a stable diatomic molecule.
-
Polar Covalent Bonding: When bromine forms covalent bonds with other elements that have different electronegativities (ability to attract electrons), the bond becomes polar. The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, resulting in a partial positive charge (δ⁺) on the less electronegative atom and a partial negative charge (δ⁻) on the more electronegative atom. This is common in bromine-containing organic molecules.
Examples of Bromine's Reactivity and Applications
Bromine's seven valence electrons and resulting reactivity manifest in various important applications:
-
Flame Retardants: Organobromine compounds are used extensively as flame retardants in plastics, textiles, and electronics. Their effectiveness arises from their ability to interfere with the combustion process.
-
Disinfectants and Sanitizers: Bromine compounds are powerful disinfectants and sanitizers, used in swimming pools, hot tubs, and water treatment facilities. They effectively kill bacteria and other microorganisms.
-
Agricultural Chemicals: Certain bromine-containing compounds are employed as pesticides and fumigants in agriculture.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Bromine is incorporated into some pharmaceuticals, playing diverse roles in drug formulation and therapeutic activity.
-
Photography: Silver bromide (AgBr) is a critical component in photographic films and papers, crucial for light sensitivity and image development.
Further Exploring Bromine's Chemistry
The understanding of bromine's seven valence electrons is fundamental to comprehending its diverse chemical reactions and applications. Further exploration into its redox reactions, its behavior in different solvents, and its interactions with organic compounds would enhance our knowledge of its role in numerous chemical processes. Advanced studies involve analyzing reaction kinetics, mechanisms, and thermodynamic parameters. The field of organobromine chemistry, which explores the synthesis and properties of organic compounds containing bromine, represents a vast area of ongoing research and discovery.
Conclusion: Valence Electrons as the Foundation of Chemical Understanding
The number of valence electrons an atom possesses is paramount in predicting its chemical behavior. Bromine, with its seven valence electrons, embodies this principle, displaying a high degree of reactivity, readily forming ionic and covalent bonds, and finding applications across many diverse fields. This detailed analysis reinforces the importance of understanding fundamental atomic structure in interpreting the chemical properties and reactivity of elements, particularly in the context of its valence electrons. This knowledge forms the bedrock for numerous scientific advancements and technological applications utilizing bromine and its compounds.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Spell The Number 30
Mar 09, 2025
-
Is Nitrogen Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 09, 2025
-
How To Find Square Root Of Fraction
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Are The Factors Of 53
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is A Factor Of 38
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons In Br . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
