Is Nitrogen Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
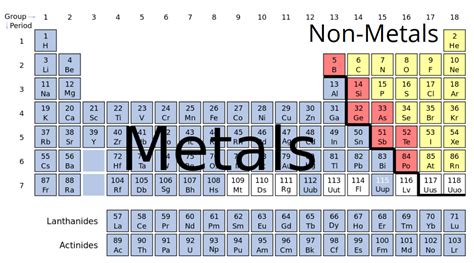
Table of Contents
Is Nitrogen a Metal, Nonmetal, or Metalloid? A Deep Dive into its Properties
Nitrogen, a ubiquitous element crucial to life as we know it, often sparks curiosity regarding its classification within the periodic table. Is it a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid? The answer, as we will explore in detail, is unequivocally nonmetal. However, understanding why requires a closer look at its atomic structure, chemical behavior, and physical properties. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics, dispelling any ambiguity surrounding nitrogen's classification.
Understanding the Periodic Table Classifications
Before diving into nitrogen's specifics, let's establish the fundamental differences between metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic structure and resulting properties, grouping them into these three broad categories:
Metals
Metals, typically located on the left side of the periodic table, are characterized by:
- Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity: They readily conduct electricity and heat.
- Malleability and ductility: They can be hammered into sheets (malleability) and drawn into wires (ductility).
- Metallic luster: They have a shiny appearance.
- High density: They are generally dense materials.
- Low electronegativity: They tend to lose electrons easily.
Nonmetals
Nonmetals, largely situated on the right side of the periodic table, exhibit contrasting properties:
- Poor electrical and thermal conductivity: They are generally poor conductors of electricity and heat.
- Brittle solids: They are often brittle and shatter easily.
- Lack of metallic luster: They typically lack the shiny appearance of metals.
- Low density: They tend to have lower densities compared to metals.
- High electronegativity: They readily attract electrons.
Metalloids (Semimetals)
Metalloids, forming a zigzag line separating metals and nonmetals, demonstrate intermediate properties:
- Semiconductivity: They exhibit properties between conductors and insulators, meaning their conductivity can be influenced by factors like temperature or the addition of impurities.
- Variable physical properties: Their properties can vary depending on the specific metalloid and its conditions.
Nitrogen: A Definitive Nonmetal
Nitrogen's position on the periodic table, in Group 15 (formerly Group VA) and Period 2, immediately suggests its nonmetallic nature. Let's examine its characteristics to solidify this classification:
Atomic Structure and Chemical Behavior
Nitrogen's atomic number is 7, meaning it possesses 7 protons and 7 electrons. Its electronic configuration is 1s²2s²2p³. This configuration dictates its chemical behavior:
- High Electronegativity: Nitrogen has a relatively high electronegativity, meaning it strongly attracts electrons in chemical bonds. This is a hallmark characteristic of nonmetals.
- Covalent Bonding: To achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outermost shell), nitrogen forms covalent bonds, sharing electrons with other atoms. This is typical of nonmetals, contrasting with the ionic bonding frequently observed in metals.
- Formation of Molecular Gases: Nitrogen exists primarily as a diatomic gas (N₂), held together by a strong triple covalent bond. This molecular structure contributes to its low boiling point and gaseous state at standard conditions – another nonmetal trait.
- Oxidation States: Nitrogen exhibits multiple oxidation states, ranging from -3 to +5, reflecting its ability to both gain and lose electrons, although gaining is more common. While some metals also exhibit variable oxidation states, the range and context differ significantly.
Physical Properties Reinforcing Nonmetallic Nature
The physical properties of nitrogen further confirm its classification as a nonmetal:
- Gaseous State at Room Temperature: Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas at standard temperature and pressure. This is atypical of metals, which are generally solid at room temperature.
- Poor Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Nitrogen is a very poor conductor of both electricity and heat. This is consistent with the nonmetal pattern.
- Low Density: Nitrogen has a significantly lower density than most metals.
- Brittle (in Solid State): Solid nitrogen, under extremely low temperatures, is brittle and lacks metallic luster.
Contrasting Nitrogen with Metals and Metalloids
To emphasize nitrogen's nonmetallic nature, let's compare it to a typical metal (like sodium) and a metalloid (like silicon):
| Property | Nitrogen (Nonmetal) | Sodium (Metal) | Silicon (Metalloid) |
|---|---|---|---|
| State at 25°C | Gas | Solid | Solid |
| Electrical Conductivity | Poor | Excellent | Semiconductor |
| Thermal Conductivity | Poor | Excellent | Moderate |
| Malleability | N/A (Gas) | High | Brittle |
| Ductility | N/A (Gas) | High | Brittle |
| Luster | None | High | Dull |
| Electronegativity | High | Low | Moderate |
| Bonding | Covalent | Ionic/Metallic | Covalent |
This table clearly highlights the significant differences between nitrogen and typical metals and metalloids, solidifying its classification as a nonmetal.
Addressing Potential Misconceptions
Some might mistakenly consider nitrogen's role in biological molecules (like amino acids and proteins) as evidence for it possessing metallic characteristics. However, this is a misconception. Nitrogen's importance in biological systems stems from its ability to form strong covalent bonds, facilitating the intricate structures of organic molecules. This ability is a direct consequence of its nonmetallic properties.
Conclusion: Nitrogen Remains a Nonmetal
In conclusion, overwhelming evidence firmly places nitrogen within the nonmetal category of the periodic table. Its atomic structure, chemical behavior, and physical properties consistently align with the characteristics of nonmetals and diverge significantly from those of metals and metalloids. While its role in biological processes is critical, it doesn't alter its fundamental chemical classification. Understanding this distinction is crucial for comprehending the vast range of applications and importance of nitrogen in chemistry, biology, and various industrial processes. The information presented here provides a comprehensive and scientifically accurate overview of nitrogen's nature and dispels any lingering doubts regarding its classification.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Push Or A Pull
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Part Of Speech Is Did
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Color Is The Animal Cell
Mar 09, 2025
-
The Final Electron Acceptor Of Aerobic Cellular Respiration Is
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Are The Prime Numbers Of 24
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Nitrogen Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
