How To Find Square Root Of Fraction
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
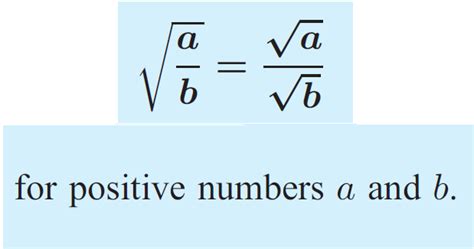
Table of Contents
How to Find the Square Root of a Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the square root of a fraction might seem daunting at first, but it's a straightforward process once you understand the underlying principles. This comprehensive guide breaks down the process step-by-step, providing you with multiple methods and examples to solidify your understanding. Whether you're a student brushing up on your math skills or an adult looking to refresh your knowledge, this guide will equip you with the tools to confidently tackle square roots of fractions.
Understanding Square Roots and Fractions
Before diving into the methods, let's review the basics. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. A fraction, on the other hand, represents a part of a whole and is expressed as a ratio of two numbers – the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number).
Understanding these concepts is crucial for tackling the square root of a fraction. The core principle is that we can find the square root of the numerator and the denominator separately.
Method 1: Finding the Square Root of the Numerator and Denominator Individually
This is the most straightforward method. It involves calculating the square root of the numerator and the square root of the denominator separately. This method works best when both the numerator and the denominator are perfect squares (numbers that have exact square roots, like 4, 9, 16, 25, etc.).
Steps:
- Find the square root of the numerator: Determine the number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the numerator.
- Find the square root of the denominator: Determine the number that, when multiplied by itself, equals the denominator.
- Simplify the fraction: Write the square roots you found as a new fraction. Often, this new fraction can be further simplified by reducing it to its lowest terms.
Example:
Let's find the square root of 16/25:
- Square root of the numerator (16): √16 = 4
- Square root of the denominator (25): √25 = 5
- Simplified fraction: The square root of 16/25 is 4/5.
Example with Simplification:
Find the square root of 36/100:
- Square root of the numerator (36): √36 = 6
- Square root of the denominator (100): √100 = 10
- Simplified fraction: The square root is 6/10. This can be simplified further by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor (GCD), which is 2. Therefore, 6/10 simplifies to 3/5.
Method 2: Simplifying the Fraction First
If the numerator and denominator aren't perfect squares, simplifying the fraction before taking the square root can often make the calculation easier. This involves finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the numerator and denominator and dividing both by it.
Steps:
- Find the GCD of the numerator and denominator: This is the largest number that divides both the numerator and the denominator evenly.
- Simplify the fraction: Divide both the numerator and the denominator by the GCD.
- Find the square root of the simplified fraction: Use Method 1 to find the square root of the simplified fraction.
Example:
Let's find the square root of 4/16:
- GCD of 4 and 16: The GCD is 4.
- Simplified fraction: Dividing both numerator and denominator by 4 gives 1/4.
- Square root of the simplified fraction: √1/4 = √1/√4 = 1/2
Method 3: Using the Property of Square Roots
This method utilizes the property that the square root of a fraction is equal to the square root of the numerator divided by the square root of the denominator. This is mathematically expressed as: √(a/b) = √a/√b
This method works for any fraction, regardless of whether the numerator and denominator are perfect squares. However, you might end up with an irrational number (a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal) as your answer if the numerator or denominator (or both) are not perfect squares.
Steps:
- Separate the square root: Rewrite the square root of the fraction as the square root of the numerator divided by the square root of the denominator.
- Simplify if possible: Simplify the individual square roots if they are perfect squares.
- Approximate if necessary: If you have irrational numbers, you can use a calculator to approximate the decimal values.
Example with Perfect Squares:
Find the square root of 25/49:
- Separate the square root: √(25/49) = √25/√49
- Simplify: √25 = 5 and √49 = 7
- Result: 5/7
Example with Non-Perfect Squares:
Find the square root of 2/3:
- Separate the square root: √(2/3) = √2/√3
- Approximate: Using a calculator, √2 ≈ 1.414 and √3 ≈ 1.732
- Approximate result: 1.414/1.732 ≈ 0.816
Dealing with Mixed Numbers
A mixed number (like 2 1/2) needs to be converted into an improper fraction before you can find its square root.
Steps:
- Convert to an improper fraction: Multiply the whole number by the denominator and add the numerator. Keep the same denominator. For example, 2 1/2 becomes (2*2 + 1)/2 = 5/2.
- Find the square root using any of the methods above: Apply the chosen method to the improper fraction.
Example:
Find the square root of 2 1/4:
- Convert to an improper fraction: 2 1/4 = (2*4 + 1)/4 = 9/4
- Find the square root: √(9/4) = √9/√4 = 3/2 or 1.5
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Understanding how to find the square root of a fraction isn't just an academic exercise. It has practical applications in various fields, including:
- Geometry: Calculating the lengths of sides in triangles and other geometric shapes often involves dealing with fractions.
- Physics: Many physics formulas utilize fractions and square roots, especially in areas like mechanics and optics.
- Engineering: Engineering designs often involve calculations with fractions and square roots for accurate measurements and proportions.
- Statistics: Standard deviations and other statistical calculations frequently utilize square roots and fractions.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While this guide covers the fundamental methods, there are more advanced concepts you can explore:
- Complex Numbers: Square roots of negative numbers involve complex numbers, which extend the number system beyond real numbers.
- Nth Roots: The concept of square roots can be generalized to nth roots, where you find a number that, when multiplied by itself n times, gives the original number.
- Rationalizing the Denominator: This technique is used to eliminate radicals (square roots) from the denominator of a fraction, making it easier to work with.
Conclusion
Finding the square root of a fraction might initially seem complicated, but with a systematic approach and a strong understanding of the underlying principles, it becomes a manageable task. Mastering this skill opens doors to a wider range of mathematical problems and enhances your ability to apply mathematical concepts in various fields. Remember to practice regularly using different methods and examples to build your confidence and improve your accuracy. By following the steps outlined in this guide and practicing regularly, you'll become proficient in finding the square root of any fraction, paving your way for more advanced mathematical explorations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Are Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cells
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Molecular Mass Of Iron
Mar 09, 2025
-
How Do You Spell 12 In English
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Magnitude Of The Displacement
Mar 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Would Be Considered A Nonrenewable Resource
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find Square Root Of Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
