What Are The Factors Of 53
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
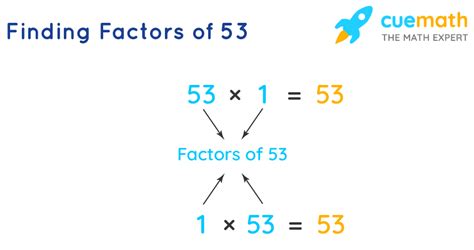
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 53? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 53?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime numbers, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the immediate answer might appear straightforward, understanding the concept thoroughly unlocks a deeper appreciation for the elegance and complexity of numbers. This article will explore the factors of 53, delve into the meaning of factors and prime numbers, and examine related mathematical concepts.
Understanding Factors
Before diving into the specifics of 53, let's define what we mean by "factors." In mathematics, a factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. For instance, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
We can express this relationship using the division operator: if a is a factor of b, then b ÷ a results in a whole number. This is equivalent to saying that b is a multiple of a.
Identifying the Factors of 53
Now, let's apply this understanding to the number 53. To find the factors of 53, we need to identify all the whole numbers that divide 53 without leaving a remainder. Let's systematically check:
- 1: 53 ÷ 1 = 53 (no remainder)
- 53: 53 ÷ 53 = 1 (no remainder)
That's it! The only whole numbers that divide 53 evenly are 1 and 53 itself.
Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks
The fact that 53 only has two factors – 1 and itself – classifies it as a prime number. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other numbers, as every composite number (a number that is not prime) can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers (this is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic).
Prime numbers hold a significant position in number theory and cryptography. Their seemingly random distribution across the number line has captivated mathematicians for centuries, leading to ongoing research and unsolved problems like the twin prime conjecture (which posits that there are infinitely many pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2).
Distinguishing Prime Numbers from Composite Numbers
It's crucial to differentiate between prime and composite numbers. Composite numbers are natural numbers greater than 1 that are not prime. This means they have more than two factors. For example, 12 is a composite number because its factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. The number 1 is neither prime nor composite; it's a unique case.
Understanding this distinction is vital for various mathematical operations, including factorization, simplification of fractions, and solving equations.
Methods for Identifying Prime Numbers
While simple for smaller numbers like 53, determining whether larger numbers are prime can be more challenging. Several methods exist to check for primality:
-
Trial division: This involves testing divisibility by all prime numbers up to the square root of the number in question. If none of these primes divide the number evenly, it's prime. This method is computationally expensive for very large numbers.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm efficiently identifies all prime numbers up to a specified limit. It works by iteratively marking multiples of each prime number as composite.
-
Probabilistic primality tests: For extremely large numbers, deterministic primality tests become computationally infeasible. Probabilistic tests, like the Miller-Rabin test, offer a high probability (but not certainty) of determining primality. These tests are widely used in cryptography.
The Significance of 53 as a Prime Number
53's status as a prime number is significant within the broader context of number theory. Its presence within sequences and patterns of numbers contributes to the overall structure of mathematics. Although it might seem like a small, isolated number, its prime nature makes it a fundamental building block in the construction of larger numbers and mathematical structures.
53 in Different Mathematical Contexts
Let's explore some ways 53 appears in various mathematical contexts:
-
Number Systems: 53 is a prime number in the decimal number system (base 10). Its representation and properties will change in different number systems (e.g., binary, hexadecimal).
-
Modular Arithmetic: 53 plays a role in modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus). For example, in modulo 53 arithmetic, 54 would be equivalent to 1 (54 mod 53 = 1).
-
Polynomials: 53 can be a coefficient or a root in polynomial equations. Understanding its properties as a prime number can influence the factorization and solving of these equations.
-
Sequences: 53 might appear in various number sequences, such as prime number sequences, Fibonacci-related sequences, or other mathematically defined sequences. Analyzing its position within such sequences can reveal patterns and connections.
Applications of Prime Numbers
The importance of prime numbers extends far beyond the realm of pure mathematics. They have crucial applications in:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers form the backbone of many modern cryptographic systems, such as RSA encryption, which is used to secure online transactions and communications. The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components ensures the security of these systems.
-
Hashing Algorithms: Prime numbers are frequently used in hashing algorithms, which are used to create unique digital fingerprints of data. This has applications in data storage, retrieval, and security.
-
Random Number Generation: Prime numbers play a vital role in generating pseudo-random numbers, which are used in simulations, statistical analysis, and other computational tasks.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers find application in various aspects of coding theory, especially error-correcting codes. These codes ensure reliable data transmission despite noise or interference.
Conclusion: The Unsung Importance of Prime Numbers like 53
While the immediate answer to "What are the factors of 53?" is simply 1 and 53, the question opens a gateway to the rich and fascinating world of prime numbers and their profound impact on mathematics and its applications. 53, as a prime number, is not merely a single number; it's a fundamental building block that contributes to the intricate structure of mathematics and plays a significant role in various fields, highlighting the unexpected depth and importance of seemingly simple numbers. The exploration of such seemingly simple numerical concepts serves as a constant reminder of the beauty and enduring mystery of mathematics. Further research into prime number theory will undoubtedly reveal even more intricate applications and properties of these fundamental building blocks of our number system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Vertices Rectangular Prism Have
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is A Push Or A Pull
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Part Of Speech Is Did
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Color Is The Animal Cell
Mar 09, 2025
-
The Final Electron Acceptor Of Aerobic Cellular Respiration Is
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 53 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
