How Many Protons And Neutrons Does Sodium Have
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 4 min read
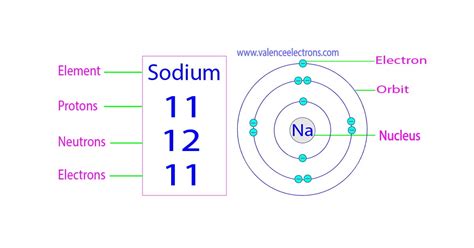
Table of Contents
- How Many Protons And Neutrons Does Sodium Have
- Table of Contents
- How Many Protons and Neutrons Does Sodium Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
- Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
- Sodium's Atomic Structure: Unveiling the Numbers
- Isotopes of Sodium: Variations on a Theme
- The Significance of Sodium in Biological Systems and Beyond
- Applications and Importance of Isotopes
- Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Atomic Structure
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Many Protons and Neutrons Does Sodium Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Sodium, a ubiquitous element essential for life, holds a fascinating place in the periodic table. Understanding its atomic structure, specifically the number of protons and neutrons it possesses, is key to grasping its chemical properties and behavior. This comprehensive article will delve into the intricacies of sodium's atomic composition, exploring its isotopes, applications, and the broader implications of understanding nuclear structure.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we pinpoint the number of protons and neutrons in sodium, let's establish a fundamental understanding of atomic structure. An atom is the basic building block of matter, composed of three subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; it's the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also residing in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The atomic number of an element is crucial; it uniquely identifies the element on the periodic table. The mass number represents the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
Sodium's Atomic Structure: Unveiling the Numbers
Sodium (Na), element number 11 on the periodic table, has an atomic number of 11. This means that every sodium atom possesses 11 protons in its nucleus. This defining characteristic is what makes it sodium, differentiating it from all other elements.
However, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. The most common isotope of sodium, Sodium-23 (²³Na), has 12 neutrons (23 - 11 = 12). This is the predominant form of sodium found in nature.
Isotopes of Sodium: Variations on a Theme
While ²³Na is the most abundant isotope, other isotopes of sodium exist, albeit in much smaller quantities. These isotopes have the same number of protons (11) but differ in their neutron count. Some examples include:
- Sodium-22 (²²Na): This radioactive isotope has 11 protons and 11 neutrons. It's used in various medical and industrial applications, including positron emission tomography (PET) scans.
- Sodium-24 (²⁴Na): Another radioactive isotope with 11 protons and 13 neutrons, it has a relatively short half-life and finds applications in certain research areas.
The different isotopes of sodium exhibit similar chemical behavior due to the identical number of protons and electrons. However, their physical properties, such as mass and radioactive decay characteristics, can differ significantly.
The Significance of Sodium in Biological Systems and Beyond
Sodium's role extends far beyond its atomic structure. It's a vital element for all living organisms:
- Nerve Impulse Transmission: Sodium ions (Na⁺) play a crucial role in transmitting nerve impulses throughout the body. The movement of sodium ions across cell membranes generates the electrical signals that enable communication between nerve cells.
- Muscle Contraction: Sodium ions are also involved in muscle contraction. The influx of sodium ions into muscle cells triggers the process of muscle contraction, enabling movement.
- Fluid Balance: Sodium helps regulate the body's fluid balance, maintaining the proper amount of water in and around cells.
- Industrial Applications: Beyond biological systems, sodium is used extensively in various industrial processes, including the production of sodium hydroxide (lye), sodium chloride (table salt), and sodium lamps.
Applications and Importance of Isotopes
The radioactive isotopes of sodium, like ²²Na and ²⁴Na, find specialized applications:
- Medical Imaging: ²²Na is employed in PET scans to visualize metabolic activity in the body. It emits positrons, which interact with electrons, producing gamma rays that can be detected by imaging equipment.
- Industrial Tracers: Radioactive sodium isotopes are used as tracers in industrial processes to monitor flow rates, identify leaks, and study various materials' behavior.
- Research Applications: These isotopes are valuable tools in various scientific research areas, including nuclear chemistry, environmental science, and material science.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Atomic Structure
Understanding the number of protons and neutrons in sodium, including its isotopic variations, is fundamental to comprehending its chemical and physical properties, its biological significance, and its applications in diverse fields. The atomic structure provides the framework for interpreting the element's behavior, from its role in maintaining life to its uses in technology and research. The concept of isotopes further highlights the complexity and versatility inherent in even seemingly simple elements like sodium. This knowledge forms a cornerstone of our understanding of chemistry, physics, and biology. The study of elements like sodium demonstrates the interconnectedness of scientific principles and their practical implications in our world.
The exploration of sodium’s atomic structure, including the precise count of protons and neutrons and the variations presented by its isotopes, serves as a microcosm of the broader significance of understanding atomic composition. This comprehension lays the foundation for advancements in medicine, industry, and scientific research, continuously shaping our world in profound ways. From the vital role sodium plays in biological processes to its application in various technologies, the study of its atomic structure remains both foundational and ever-evolving. Future research will undoubtedly continue to unravel more intricate details about this essential element and its impact on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Only Movable Bone In The Skull
Mar 30, 2025
-
How Do You Do Expanded Notation
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Flora And Fauna
Mar 30, 2025
-
Is 23 A Multiple Of 3
Mar 30, 2025
-
Which State Of Matter Undergoes Changes In Volume Most Easily
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons And Neutrons Does Sodium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
