Which State Of Matter Undergoes Changes In Volume Most Easily
Juapaving
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
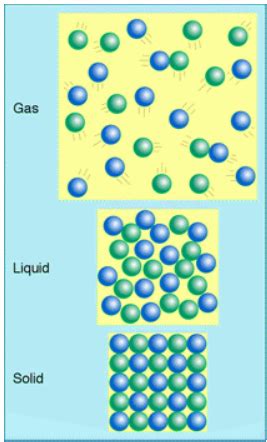
Table of Contents
Which State of Matter Undergoes Changes in Volume Most Easily?
The answer to this question is straightforward: gases. Gases are far more compressible and expansible than liquids and solids, meaning they undergo changes in volume far more easily. This fundamental difference stems from the unique characteristics of the particles that make up each state of matter. Let's delve deeper into the reasons behind this, examining the properties of gases, liquids, and solids and exploring the implications of this easy volume change.
Understanding the States of Matter
Before we can answer which state of matter is most easily compressed, we need to understand the fundamental differences between solids, liquids, and gases. These differences are primarily dictated by the intermolecular forces holding the constituent particles (atoms or molecules) together and the kinetic energy of these particles.
Solids: Fixed Shape and Volume
In solids, the intermolecular forces are very strong. The particles are tightly packed in a fixed arrangement, with little freedom to move around. This strong attraction and fixed arrangement are why solids maintain a definite shape and volume. Applying pressure to a solid might slightly reduce its volume, but the change is negligible compared to the changes experienced by gases or, to a lesser extent, liquids. The particles simply cannot move significantly closer together to accommodate the pressure.
Liquids: Definite Volume, Indefinite Shape
Liquids have weaker intermolecular forces than solids. While the particles are still relatively close together, they have enough kinetic energy to overcome some of the attraction, allowing them to move past each other. This is why liquids take the shape of their container but maintain a constant volume. Liquids are slightly compressible, but the change in volume is minimal due to the relatively close packing of particles. Applying external pressure will only cause a very small reduction in volume.
Gases: Indefinite Shape and Volume
Gases exhibit the weakest intermolecular forces. The particles in a gas are far apart and move randomly at high speeds. This large distance between particles and their significant kinetic energy explain why gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume. They readily fill any container they occupy and are easily compressed or expanded. This is the key difference: the large spaces between gas particles allow them to move significantly closer together under pressure, resulting in a substantial reduction in volume. Conversely, an increase in temperature or reduction in pressure leads to significant expansion.
Why Gases Change Volume Most Easily: A Deeper Look
The ease with which gases change volume comes down to several factors:
-
Weak Intermolecular Forces: The negligible attractive forces between gas particles mean there's minimal resistance to compression or expansion. The particles are largely independent of each other, readily moving closer or farther apart.
-
Large Interparticle Distances: The significant distance between gas particles means there's considerable empty space. This empty space allows for significant compression; the particles can simply move closer to fill the reduced volume.
-
High Kinetic Energy: Gas particles possess high kinetic energy, meaning they are constantly in motion and colliding with each other and the walls of their container. This constant movement makes them highly responsive to changes in pressure and temperature, leading to volume changes.
-
Compressibility and Expansibility: Gases are both highly compressible and expansible. Applying pressure reduces the volume significantly, while reducing pressure or increasing temperature increases the volume significantly. This responsiveness to external factors is unique to gases.
Real-World Examples of Gas Volume Changes
The easy changeability of gas volume is evident in many everyday occurrences:
-
Inflating a balloon: Blowing air (a gas) into a balloon increases the volume dramatically. The gas particles expand to fill the available space within the balloon.
-
Using a bicycle pump: A bicycle pump compresses air into a smaller volume. The pressure applied forces the air particles closer together.
-
Weather balloons: Weather balloons expand as they rise to higher altitudes, where the atmospheric pressure is lower. The gas inside expands to fill the larger volume created by the decrease in pressure.
-
Scuba diving: Scuba divers experience the effects of gas compression as they descend to greater depths. The increased pressure at depth reduces the volume of the air in their tanks.
-
Aerosol cans: Aerosol cans contain gases under pressure. When the valve is opened, the gas expands rapidly to fill the surrounding space.
The Ideal Gas Law and Volume Changes
The behavior of gases is well-described by the Ideal Gas Law: PV = nRT. This equation demonstrates the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), the number of moles of gas (n), the ideal gas constant (R), and temperature (T). This equation beautifully shows how volume is directly related to temperature and inversely related to pressure, highlighting the easy changeability of gas volume. A change in any of these parameters (pressure or temperature) leads to a predictable change in volume.
Contrasting Gas Volume Changes with Liquids and Solids
While liquids and solids can exhibit some minor volume changes, the magnitude of these changes is considerably smaller than those observed in gases. Liquids are slightly compressible, but the effect is much less pronounced. Solids are even less compressible, demonstrating minimal volume changes under even extreme pressures.
Conclusion: Gases Reign Supreme in Volume Changeability
In summary, gases undergo changes in volume most easily due to their weak intermolecular forces, large interparticle distances, and high kinetic energy. This unique combination allows for significant compression and expansion in response to changes in pressure and temperature. This property underlies numerous everyday phenomena and is described accurately by the Ideal Gas Law. While liquids and solids can experience slight volume changes, these are negligible compared to the dramatic variations observed in gases. The ability of gases to readily adapt their volume makes them distinct and uniquely responsive to environmental changes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 27
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Innermost Layer Of The Root Cortex Is The
Apr 01, 2025
-
Full Form Of Sho In Police
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 72 And 120
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Do You Spell 20 In Word Form
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which State Of Matter Undergoes Changes In Volume Most Easily . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
