What Is The Difference Between Flora And Fauna
Juapaving
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
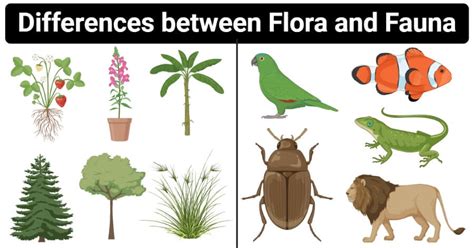
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Flora and Fauna? A Deep Dive into the Plant and Animal Kingdoms
The natural world is a breathtaking tapestry woven from countless threads of life. Two fundamental categories within this intricate design are flora and fauna. While often used interchangeably in casual conversation, understanding the distinct differences between flora and fauna is crucial for appreciating the complexity and interconnectedness of ecosystems. This article will delve deep into the definitions, characteristics, and ecological roles of flora and fauna, highlighting their unique contributions to the planet's biodiversity.
Defining Flora and Fauna: More Than Just Plants and Animals
At its simplest, flora refers to the plant life of a particular region or time period. This encompasses all forms of plant life, from the tiniest algae and mosses to the tallest redwood trees and the most vibrant flowering plants. Flora isn't just about the individual plants themselves; it also includes the study of their distribution, classification, and interactions with their environment. Think of flora as a collective noun representing the entire plant kingdom within a specific context.
Fauna, on the other hand, refers to the animal life of a particular region or time period. This broad term encompasses all animals, from microscopic invertebrates to gigantic whales, from crawling insects to soaring birds. Just like with flora, the study of fauna includes the classification, distribution, and ecological relationships of these animals. It's the complete animal kingdom in a specific setting.
Beyond the Basic Definitions: Exploring the Nuances
The distinctions between flora and fauna might seem straightforward, but there are subtle complexities to consider. For example:
-
Microorganisms: Where do bacteria, fungi, and protists fit in? While traditionally associated with the plant or animal kingdoms, many microorganisms don't neatly fit into either flora or fauna. Fungi, for instance, have characteristics of both plants and animals, yet they represent a kingdom of their own. Similarly, certain protists blur the line between plant and animal classifications.
-
Viruses: These are considered non-living entities by many scientists and are not typically included under either flora or fauna. Their unique nature places them outside the traditional classifications of living organisms.
-
Extinct species: Both flora and fauna encompass species that no longer exist, providing valuable insights into past ecosystems and evolutionary history. Paleobotany (the study of fossil plants) and paleozoology (the study of fossil animals) are crucial fields dedicated to understanding these extinct components of flora and fauna.
The Interdependence of Flora and Fauna: A Delicate Balance
Flora and fauna are not isolated entities; they are intricately interwoven in a complex web of life. Their interdependence is fundamental to the health and stability of ecosystems. Here's how they relate:
-
Food Webs: Plants (flora) form the base of most food webs, serving as primary producers that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores (plant-eating animals – fauna) consume these plants, and carnivores (meat-eating animals – fauna) consume herbivores, creating a cascade of energy transfer.
-
Habitat Provision: Plants provide habitats for countless animals. Forests offer shelter and food for birds, mammals, insects, and many more. Coral reefs, which are a form of flora (albeit marine), support incredibly diverse fauna communities.
-
Pollination and Seed Dispersal: Animals play a critical role in the reproduction of plants. Bees, butterflies, birds, and other fauna pollinate flowers, facilitating the production of seeds. Animals also contribute to seed dispersal, carrying seeds to new locations.
-
Nutrient Cycling: Both flora and fauna are involved in nutrient cycling. Plants absorb nutrients from the soil, and when they die and decompose, these nutrients are released back into the environment. Animals also contribute to nutrient cycling through their waste and decomposition.
-
Climate Regulation: Forests (flora) play a vital role in regulating climate by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This effect is intricately linked with the fauna that inhabit these forests, as their presence influences the forest's overall health and ability to sequester carbon.
Exploring the Diversity of Flora and Fauna: A Global Perspective
The diversity of flora and fauna varies significantly across the globe, influenced by factors such as climate, geography, and human activity.
Biomes and Ecosystems: Habitats Shaping Flora and Fauna
Different biomes, such as forests, grasslands, deserts, and aquatic ecosystems, support distinct flora and fauna communities. Each biome has unique environmental conditions that shape the types of plants and animals that can thrive there.
-
Tropical Rainforests: Boast incredibly high biodiversity, with a vast array of plants and animals adapted to the warm, humid climate.
-
Temperate Forests: Experience distinct seasons, supporting a mix of deciduous and coniferous trees, along with a diverse range of fauna.
-
Deserts: Characterized by arid conditions, supporting specialized flora and fauna adapted to water scarcity.
-
Marine Ecosystems: Encompass oceans, seas, and coral reefs, harboring an immense diversity of marine flora and fauna.
Endemic Species: Unique to Specific Regions
Many species are endemic, meaning they are found only in a specific geographical region. These species are particularly vulnerable to habitat loss and other environmental threats. The unique flora and fauna of islands, for example, often demonstrate high levels of endemism.
Threats to Flora and Fauna: The Impact of Human Activity
Human activities are causing significant threats to global biodiversity, impacting both flora and fauna. Habitat loss, climate change, pollution, and overexploitation are major drivers of species extinction and ecosystem degradation. Conservation efforts are crucial to mitigating these threats and preserving the planet's rich biodiversity.
The Scientific Study of Flora and Fauna: Key Disciplines
Understanding flora and fauna requires a multidisciplinary approach, drawing from various scientific fields:
-
Botany: The scientific study of plants (flora). It encompasses diverse aspects such as plant physiology, taxonomy, ecology, and genetics.
-
Zoology: The scientific study of animals (fauna). Similar to botany, it explores diverse aspects such as animal behavior, physiology, evolution, and conservation.
-
Ecology: The study of the relationships between organisms and their environment, encompassing the interactions between flora and fauna and their physical surroundings.
-
Taxonomy: The science of classifying and naming organisms, crucial for understanding the relationships between different species of flora and fauna.
-
Conservation Biology: A field dedicated to protecting biodiversity and preventing species extinctions, dealing with both flora and fauna conservation strategies.
Conclusion: The Vital Importance of Understanding Flora and Fauna
The distinction between flora and fauna, while seemingly simple, opens a window into the incredible complexity and interconnectedness of life on Earth. Understanding the unique characteristics, roles, and interdependence of plants and animals is fundamental to appreciating the beauty and fragility of our planet's ecosystems. The continued study and conservation of both flora and fauna are essential for maintaining the health of our planet and ensuring the survival of countless species, including our own. As we continue to learn more about the intricacies of the natural world, the critical need for responsible stewardship and environmental protection becomes ever more apparent. The future of our planet relies on our collective understanding and appreciation of the magnificent world of flora and fauna.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
All Important Equations Of Chemistry Class 10
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 27
Apr 01, 2025
-
The Innermost Layer Of The Root Cortex Is The
Apr 01, 2025
-
Full Form Of Sho In Police
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 72 And 120
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Flora And Fauna . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
