How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does This Equilateral Triangle Have
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
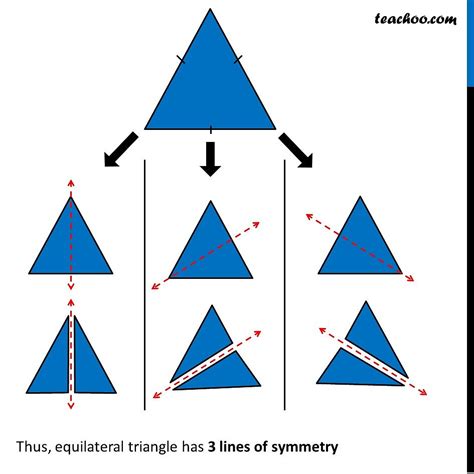
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does an Equilateral Triangle Have? A Deep Dive into Geometric Symmetry
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in mathematics and art, describes the harmonious arrangement of parts within a whole. It's a captivating topic that extends beyond simple visual appeal, impacting fields from crystallography to computer graphics. This article will delve into the fascinating world of symmetry, focusing specifically on the equilateral triangle and its lines of symmetry. We’ll explore the concept in detail, illustrating it with examples and providing practical applications. By the end, you'll not only know the answer to the central question – how many lines of symmetry does an equilateral triangle have? – but you'll also have a deeper understanding of geometric symmetry itself.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
Before we tackle the equilateral triangle, let's establish a clear definition of a line of symmetry. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection or axis of symmetry, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This means every point on one side of the line has a corresponding point on the other side, equidistant from the line. Not all shapes possess lines of symmetry; some may have none, while others may have many.
Identifying Lines of Symmetry: A Practical Approach
Identifying lines of symmetry can be done visually or through more rigorous mathematical methods. Visually inspecting a shape is often sufficient for simple figures. Imagine folding the shape along a potential line of symmetry. If the two halves match perfectly, you've found a line of symmetry. This simple method works well for many shapes, including the equilateral triangle, as we'll see later.
The Equilateral Triangle: A Symmetrical Shape
An equilateral triangle is a polygon with three sides of equal length and three angles of equal measure (60° each). This inherent equality creates a high degree of symmetry. Let's explore why and how many lines of symmetry it possesses.
Visualizing the Lines of Symmetry
Imagine an equilateral triangle. You can draw three lines, each connecting a vertex (corner) to the midpoint of the opposite side. These lines are not arbitrary; they are precisely the lines of symmetry for an equilateral triangle. Let's break this down:
-
Line 1: Draw a line from the top vertex straight down to the midpoint of the base. Fold the triangle along this line. The two halves perfectly overlap. This is a line of symmetry.
-
Line 2: Now, draw a line from the bottom-left vertex to the midpoint of the right side. Again, fold the triangle along this line. Perfect overlap confirms this is another line of symmetry.
-
Line 3: Finally, draw a line from the bottom-right vertex to the midpoint of the left side. One more perfect fold confirms the presence of a third line of symmetry.
Therefore, an equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry.
Mathematical Proof: A Deeper Understanding
While visual inspection provides a clear demonstration, a more rigorous mathematical approach can solidify our understanding. We can use coordinate geometry to prove the existence of these three lines of symmetry. For simplicity, let's place the equilateral triangle on a coordinate plane.
Coordinate Geometry Approach
Let's consider an equilateral triangle with vertices at coordinates A(0, √3), B(-1, 0), and C(1, 0). The three lines connecting a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side can be represented by equations:
-
Line 1 (Altitude from A): x = 0. This line passes through the midpoint of BC, which is (0,0).
-
Line 2 (Altitude from B): y = (√3/2)x + (√3/2). This line passes through the midpoint of AC, which is (0,√3/2).
-
Line 3 (Altitude from C): y = (-√3/2)x + (√3/2). This line passes through the midpoint of AB, which is (-1/2, √3/2).
These lines divide the triangle into two congruent halves, reflecting each point across the line onto its corresponding point. This proves mathematically that the equilateral triangle possesses three lines of symmetry.
Comparing to Other Shapes: Expanding the Concept
Understanding the symmetry of an equilateral triangle helps us appreciate the variety of symmetries found in other geometric shapes.
Isosceles Triangle: Fewer Lines of Symmetry
An isosceles triangle, with two equal sides, generally has only one line of symmetry. This line bisects the angle formed by the two equal sides and also bisects the unequal side.
Scalene Triangle: No Lines of Symmetry
A scalene triangle, with no equal sides, has no lines of symmetry. There's no line that can divide it into two congruent mirror images.
Square: Multiple Lines of Symmetry
A square possesses four lines of symmetry: two diagonals and two lines passing through the midpoints of opposite sides.
Circle: Infinite Lines of Symmetry
A circle has an infinite number of lines of symmetry. Any line passing through the center of the circle will divide it into two identical halves.
Applications of Symmetry: Real-World Examples
The concept of symmetry extends far beyond theoretical geometry; it has significant applications in various fields:
Art and Design
Symmetry is a fundamental principle in art and design. From ancient architecture to modern logos, symmetrical designs create a sense of balance, harmony, and visual appeal.
Nature
Symmetry is prevalent in nature. Flowers, snowflakes, and many other natural forms exhibit various types of symmetry, reflecting underlying mathematical patterns.
Science and Engineering
Symmetry plays a crucial role in physics, chemistry, and engineering. Understanding the symmetry of molecules, for instance, is essential in chemistry for predicting their properties.
Computer Graphics
Symmetry is utilized in computer graphics for efficient rendering and modeling. Symmetrical objects can be defined using fewer data points, reducing computational resources.
Conclusion: The Significance of Symmetry
This exploration of the equilateral triangle's symmetry highlights the beauty and utility of this fundamental geometric concept. The simple answer – an equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry – opens the door to a much wider understanding of symmetry's presence in mathematics, nature, and design. By understanding the principles of symmetry, we can better appreciate the intricate relationships within shapes and their broader implications in the world around us. From visual appeal to complex scientific applications, symmetry continues to be a compelling and significant area of study. Through visual inspection, mathematical proofs, and real-world applications, we've established a robust understanding of why an equilateral triangle possesses its unique and elegant three lines of symmetry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Symmetrical Lines Does A Square Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Spell The Word 60
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Light And Electron Microscopes
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Particles Account For The Mass Of The Atom
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Sides On A Heptagon
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does This Equilateral Triangle Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
