How Many Symmetrical Lines Does A Square Have
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
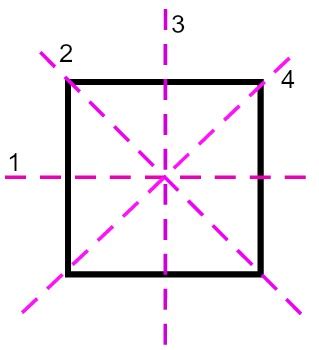
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Square Have? A Comprehensive Exploration
Symmetry, a concept fundamental to geometry and art, refers to a balanced and proportionate arrangement of parts. Understanding lines of symmetry is crucial in various fields, from designing aesthetically pleasing logos to constructing stable structures in engineering. This article delves deep into the fascinating world of symmetry, focusing specifically on the number of lines of symmetry a square possesses. We'll explore the definition of symmetry, different types of symmetry, and the unique properties of a square that determine its lines of symmetry. We will also touch upon how understanding lines of symmetry applies to other shapes and broader mathematical concepts.
Defining Symmetry and Lines of Symmetry
Before we tackle the question of a square's symmetry, let's establish a clear understanding of the terms involved. Symmetry, in a geometrical context, means that a shape can be folded or rotated in such a way that one half exactly matches the other. A line of symmetry (also known as an axis of symmetry) is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along this line, both halves would perfectly overlap.
There are two primary types of symmetry we'll consider:
1. Line Symmetry (Reflectional Symmetry)
Line symmetry, or reflectional symmetry, is the type of symmetry we primarily focus on when discussing lines of symmetry. This is the symmetry exhibited when a shape can be divided into two congruent halves by a line. These halves are mirror images of each other – a reflection across the line of symmetry.
2. Rotational Symmetry
Rotational symmetry, while not directly related to the number of lines of symmetry, is an important related concept. A shape has rotational symmetry if it can be rotated about a central point by less than 360 degrees and still look exactly the same. The order of rotational symmetry indicates how many times the shape looks identical during a 360-degree rotation.
Unpacking the Symmetry of a Square
A square, a fundamental geometric shape, possesses a high degree of symmetry. Let's systematically explore its lines of symmetry:
The Two Lines of Symmetry Through Opposite Vertices (Diagonal Symmetry)
A square has two diagonals. Each diagonal connects two opposite vertices (corners) of the square. If you fold a square along either diagonal, you'll find that the two halves perfectly overlap. This confirms that each diagonal acts as a line of symmetry. These are often referred to as diagonal lines of symmetry.
Visualizing this: Imagine a square ABCD, where A is the top left vertex, B is the top right, C is the bottom right, and D is the bottom left. The diagonal AC is one line of symmetry, and the diagonal BD is the other.
The Two Lines of Symmetry Through the Midpoints of Opposite Sides (Horizontal and Vertical Symmetry)
Beyond the diagonals, a square also possesses two additional lines of symmetry. One is a horizontal line passing through the midpoints of the top and bottom sides of the square. The other is a vertical line passing through the midpoints of the left and right sides. Folding the square along either of these lines will also result in perfectly overlapping halves.
Visualizing this: Using the same square ABCD, a horizontal line passes through the midpoints of AB and CD, while a vertical line passes through the midpoints of AD and BC.
Total Lines of Symmetry in a Square
By combining the two diagonal lines of symmetry and the two lines of symmetry through the midpoints of opposite sides, we arrive at the final answer: A square has four lines of symmetry.
Comparing Symmetry in Other Shapes
Understanding the symmetry of a square provides a valuable foundation for analyzing the symmetry of other shapes. Let’s compare:
-
Rectangle: A rectangle (excluding squares) only has two lines of symmetry, one horizontal and one vertical, passing through the midpoints of opposite sides. It lacks diagonal symmetry.
-
Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry, each line connecting a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
-
Circle: A circle has infinite lines of symmetry, as any line passing through its center acts as a line of symmetry.
-
Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon has five lines of symmetry, each connecting a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
-
Irregular Shapes: Irregular shapes, by definition, do not possess lines of symmetry.
Applications of Lines of Symmetry
The concept of lines of symmetry extends far beyond the realm of theoretical geometry. Its applications are widespread:
-
Art and Design: Artists and designers extensively utilize symmetry to create aesthetically pleasing and balanced compositions in paintings, sculptures, architecture, and graphic design. Logos often incorporate symmetry for memorability and visual appeal.
-
Nature: Many natural phenomena exhibit symmetry. Snowflakes, certain flowers, and even the human body display varying degrees of symmetry. Understanding symmetry helps us appreciate and analyze the patterns found in nature.
-
Engineering and Construction: Symmetrical designs often lead to more stable and efficient structures in engineering. Bridges, buildings, and other constructions often incorporate symmetrical elements to ensure structural integrity.
-
Computer Graphics and Animation: Symmetry plays a crucial role in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer animation. Efficient algorithms leverage symmetry to reduce computational load and improve rendering speed.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
The study of symmetry extends beyond basic geometric shapes. Concepts like group theory in mathematics provide a powerful framework for understanding and classifying symmetries in more complex structures. Furthermore, exploring different types of symmetries in higher dimensions provides a rich area of research.
Conclusion: The Beauty and Importance of Symmetry
The seemingly simple question of how many lines of symmetry a square possesses leads us down a fascinating path exploring the nature of symmetry itself. Understanding symmetry is not just a matter of geometrical knowledge; it's a key concept that underpins numerous aspects of art, science, engineering, and design. A square, with its four lines of symmetry, stands as a testament to the beauty and mathematical elegance of this fundamental concept. The ability to accurately identify and quantify lines of symmetry is a valuable skill applicable across diverse fields, highlighting the importance of this seemingly simple concept in a broader context. The exploration continues beyond the square, opening up vast realms of mathematical and artistic discovery.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Scattering Of Light By Colloids Is Called
Mar 18, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 2 4 And 8
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Equal Sides Does An Isosceles Triangle Have
Mar 18, 2025
-
Full Form Of S I T
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Number Is A Multiple Of 5
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Symmetrical Lines Does A Square Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
