How Many Angles Does Triangle Have
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
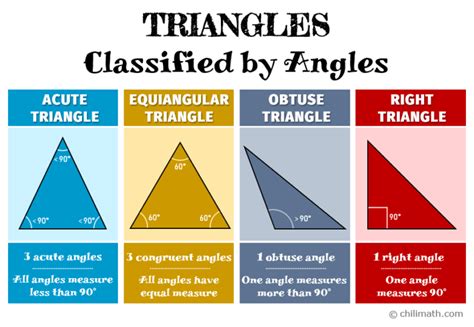
Table of Contents
How Many Angles Does a Triangle Have? A Deep Dive into Triangles and Their Properties
The seemingly simple question, "How many angles does a triangle have?" opens the door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, a fundamental branch of mathematics. While the answer itself is straightforward – three – understanding the properties of these angles is crucial for grasping a wide range of geometric concepts and applications. This article will delve deep into the world of triangles, exploring their angles, classifications, and the theorems that govern their behavior.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What is a Triangle?
Before diving into the specifics of angles, let's establish a solid foundation. A triangle is a two-dimensional geometric shape defined by three straight lines that intersect to form three angles and three vertices. These lines are called the sides of the triangle. The points where the sides meet are called vertices. The angles within the triangle are formed by the intersection of these sides. It's this very structure—three sides and three angles—that gives triangles their unique characteristics and makes them so important in geometry.
Key Terminology:
- Vertices: The points where two sides of the triangle meet. Triangles have three vertices, often labeled with capital letters (A, B, C).
- Sides: The three straight line segments that connect the vertices of the triangle. The lengths of these sides determine many of the triangle's properties.
- Angles: The three angles formed by the intersection of the sides at each vertex. These angles are crucial in classifying triangles and solving geometric problems. They are often denoted using lowercase letters (a, b, c) or angle notation (∠A, ∠B, ∠C).
- Interior Angles: The angles inside the triangle. The sum of the interior angles of any triangle always equals 180 degrees. This is a fundamental theorem in geometry.
- Exterior Angles: The angles formed by extending one side of the triangle. Each exterior angle is supplementary to its adjacent interior angle (meaning they add up to 180 degrees).
The Sum of Interior Angles: A Cornerstone Theorem
One of the most important theorems in geometry concerns the sum of the interior angles of a triangle. The sum of the interior angles of any triangle always equals 180 degrees. This holds true regardless of the size or shape of the triangle – whether it's a right-angled triangle, an equilateral triangle, or an obtuse triangle. This theorem is fundamental to solving a vast array of geometric problems.
Proving the 180-Degree Rule:
Several methods exist to prove this fundamental theorem. One common approach involves drawing a line parallel to one side of the triangle through the opposite vertex. By applying alternate interior angle theorems, it's possible to demonstrate that the sum of the angles equals 180 degrees. This proof underscores the interconnectedness of different geometric principles. Understanding this proof strengthens your overall grasp of geometric reasoning.
Classifying Triangles Based on Their Angles
Triangles can be classified based on the measure of their angles:
- Acute Triangles: All three angles are acute (less than 90 degrees).
- Right Triangles: One angle is a right angle (exactly 90 degrees). These triangles are particularly important in trigonometry and many practical applications. The relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle is governed by the Pythagorean Theorem (a² + b² = c², where a and b are the legs and c is the hypotenuse).
- Obtuse Triangles: One angle is obtuse (greater than 90 degrees).
Understanding these classifications is essential for solving problems that involve triangles because different types of triangles have different properties and relationships between their sides and angles.
Classifying Triangles Based on Their Sides
Triangles can also be classified based on the lengths of their sides:
- Equilateral Triangles: All three sides are of equal length. Consequently, all three angles are also equal (60 degrees each).
- Isosceles Triangles: Two sides are of equal length. The angles opposite these sides are also equal.
- Scalene Triangles: All three sides are of different lengths. All three angles are also different.
The Importance of Angles in Solving Problems
The angles of a triangle play a crucial role in solving various geometric problems. Here are some examples:
- Trigonometry: The angles of a right-angled triangle are fundamental to trigonometry, allowing us to calculate the lengths of sides and angles using trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent). This is essential in fields such as surveying, navigation, and engineering.
- Area Calculation: The area of a triangle can be calculated using the formula: Area = (1/2) * base * height. While the height is often needed, the angles can be used to determine the height if other side lengths are known.
- Congruence and Similarity: Angle measurements are crucial in determining whether two triangles are congruent (identical in shape and size) or similar (identical in shape but different in size). Congruence and similarity theorems heavily rely on angle comparisons.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts
The study of triangles extends far beyond the basic concepts of angles and their sum. More advanced concepts include:
- Inscribed and Circumscribed Circles: Understanding how circles relate to triangles – a circle inscribed within a triangle or a circle circumscribing a triangle – involves working with angles and their relationships to the sides and vertices.
- Triangle Centers: There are various points within a triangle that have specific geometric properties, such as the centroid, incenter, circumcenter, and orthocenter. The calculation of these centers often involves using angle properties.
- Trigonometric Identities: Advanced trigonometry involves numerous identities and relationships that are essential for solving complex geometric problems involving triangles.
Real-World Applications of Triangle Geometry
The seemingly simple geometry of triangles has far-reaching applications in various fields:
- Engineering and Architecture: Triangles are used extensively in construction due to their inherent strength and stability. The angles and side lengths are crucial in designing structures like bridges, roofs, and trusses.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: Triangles are the fundamental building blocks of computer graphics. Three-dimensional models are often composed of numerous interconnected triangles, and their angles and positions determine the final image.
- Navigation and Surveying: Trigonometric functions based on the angles of triangles are used for distance and position calculations in navigation and surveying.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use triangulation to determine the distances to celestial objects. This process relies heavily on angle measurements.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Triangles
The seemingly simple question of how many angles a triangle has – three – reveals a rich and complex world of geometry. Understanding the properties of these angles, their relationships to the sides, and the theorems that govern their behavior is crucial for grasping a wide range of mathematical concepts and applying them to real-world problems. From basic calculations to advanced engineering designs, triangles and their angles remain a cornerstone of mathematics and its many practical applications. This exploration underscores the enduring importance of this fundamental geometric shape and the power of its inherent properties. The next time you see a triangle, remember the wealth of knowledge embedded within its three angles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Examples Of Polar And Non Polar Solvents
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 8
Mar 26, 2025
-
Fundamental Building Blocks Of All Matter
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is Potassium A Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is It Called When A Gas Turns To Liquid
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Angles Does Triangle Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
