How Do You Write 19 In Roman Numerals
Juapaving
Apr 01, 2025 · 5 min read
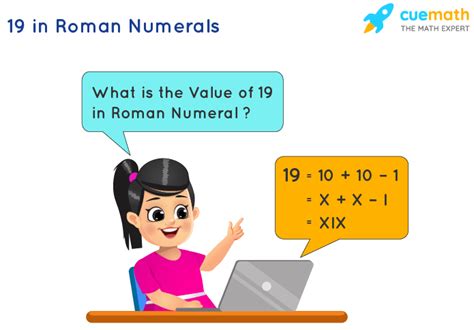
Table of Contents
- How Do You Write 19 In Roman Numerals
- Table of Contents
- How Do You Write 19 in Roman Numerals? A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Roman Numeral System
- Deconstructing the Number 19
- Writing 19 in Roman Numerals: The Solution
- Advanced Roman Numeral Concepts
- 1. Additive Principle in Action
- 2. Subtractive Principle: More Examples
- 3. Limitations of the Subtractive Principle
- 4. Numbers Beyond 1000
- 5. Absence of Zero
- Roman Numerals in Modern Usage
- Practicing with Roman Numerals
- Why Roman Numerals Still Matter
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Do You Write 19 in Roman Numerals? A Comprehensive Guide
Roman numerals, a system of numerical notation originating in ancient Rome, continue to hold relevance in various contexts today. From chapter numbering in books to clock faces and copyright dates, understanding Roman numerals remains valuable. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of writing numbers in Roman numerals, focusing specifically on how to represent the number 19, and exploring the underlying principles of the system.
Understanding the Roman Numeral System
Before tackling the representation of 19, let's establish a foundational understanding of the Roman numeral system. This system uses combinations of seven basic symbols to represent numbers:
- I: 1
- V: 5
- X: 10
- L: 50
- C: 100
- D: 500
- M: 1000
The core principle of the system lies in the additive and subtractive properties of these symbols. Additive means that when a smaller symbol appears before a larger symbol, it is subtracted from the larger symbol. Subtractive means that when a smaller symbol appears after a larger symbol, it is added to the larger symbol.
Deconstructing the Number 19
To represent 19 in Roman numerals, we need to break down the number into its constituent parts. 19 can be thought of as 10 + 9. We know that 10 is represented by X. Now we need to figure out how to represent 9.
While we could write 9 as IIIIIIIII, this is cumbersome and not the standard practice. The Roman numeral system efficiently uses a subtractive principle: a smaller numeral placed before a larger numeral indicates subtraction. Therefore, 9 is represented as IX, where I (1) is subtracted from X (10).
Writing 19 in Roman Numerals: The Solution
Combining the representation of 10 and 9, we arrive at the Roman numeral representation of 19: XIX. This concisely represents 10 + (10 - 1) = 19.
Advanced Roman Numeral Concepts
Mastering the representation of 19 is a crucial stepping stone to understanding more complex Roman numerals. Let's explore some further concepts:
1. Additive Principle in Action
Consider the number 28. We can break this down as 10 + 10 + 8. 10 is X, and 8 can be represented as VIII (5 + 1 + 1 + 1). Therefore, 28 is XXVIII. Notice how the smaller symbols are consistently added to the larger symbols.
2. Subtractive Principle: More Examples
The subtractive principle extends beyond representing 9. Consider the number 4 (IV), 40 (XL), 90 (XC), 400 (CD), and 900 (CM). In each instance, a smaller numeral is placed before a larger numeral to signify subtraction, creating a more efficient representation than simply adding smaller numerals.
3. Limitations of the Subtractive Principle
While the subtractive principle enhances efficiency, it's not without limitations. Only certain subtractions are allowed. For example, you cannot write 99 as IC (100 - 1), although it might seem logical. The correct representation is XCIX (100 - 10 + 10 - 1). The standard rules dictate that only one smaller numeral can be subtracted from a larger numeral, and the smaller numeral must be one or two orders of magnitude smaller (I can subtract from V and X; X can subtract from L and C; C can subtract from D and M).
4. Numbers Beyond 1000
Numbers exceeding 1000 are represented by placing a bar above a Roman numeral, effectively multiplying it by 1000. For example, \(\bar{V}\) represents 5000, and \(\bar{X}\) represents 10,000. This notation extends the system's capacity to represent much larger numbers. This is less frequently used in modern applications but remains an important historical aspect of the system.
5. Absence of Zero
A notable characteristic of the Roman numeral system is the absence of a symbol for zero. The concept of zero as a number wasn't established until much later in mathematical history. This absence influenced the system's limitations in performing arithmetic operations compared to positional number systems like the decimal system.
Roman Numerals in Modern Usage
Despite its limitations in arithmetic, the Roman numeral system continues to find practical applications:
- Clock Faces: Many analog clocks utilize Roman numerals to indicate hours.
- Chapter Numbering: Books often employ Roman numerals for chapter numbering.
- Copyright Dates: Copyright notices sometimes use Roman numerals.
- Outlines and Lists: They are used to create structured lists and outlines.
- Monuments and Buildings: Architectural features and monuments often feature Roman numerals.
- Formal Documents: Some formal documents might use Roman numerals for numbering sections or pages.
Practicing with Roman Numerals
To solidify your understanding, here's a practice exercise:
Try converting the following numbers into Roman numerals:
- 27
- 39
- 64
- 88
- 149
- 499
- 999
And convert these Roman numerals into Arabic numbers:
- LXXV
- CXIV
- CCXLIX
- CDXCIX
- CMXCIX
(Answers provided at the end of the article)
Why Roman Numerals Still Matter
Despite the prevalence of the decimal system, Roman numerals maintain their presence. Their continued usage stems from several factors:
- Aesthetic Appeal: The elegant appearance of Roman numerals lends a classical or formal touch to various applications.
- Historical Significance: They provide a link to history and classical antiquity.
- Conciseness (in certain cases): For certain numbers, Roman numerals offer a more concise representation than their Arabic counterparts.
Conclusion
Learning to write 19 in Roman numerals (XIX) is not merely about memorizing a single representation. It's about grasping the fundamental principles of an ancient number system that continues to hold cultural and practical relevance. By understanding the additive and subtractive principles, and the limitations of the system, you unlock a deeper appreciation for this unique and enduring method of numerical notation.
Answers to Practice Exercise:
Arabic to Roman:
- XXVII
- XXXIX
- LXIV
- LXXXVIII
- CXLIX
- CDXCIX
- CMXCIX
Roman to Arabic:
- 75
- 114
- 249
- 499
- 999
This comprehensive guide provides a strong foundation for understanding and utilizing Roman numerals, going beyond the simple representation of 19 and delving into the nuances and applications of this historic number system. Remember to practice regularly to solidify your skills!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 9 15
Apr 06, 2025
-
Why Activation Energy Is Not Affected By Temperature
Apr 06, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 196
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 2 And 9
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Numerator
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Write 19 In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
