Difference Between Area And Surface Area
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
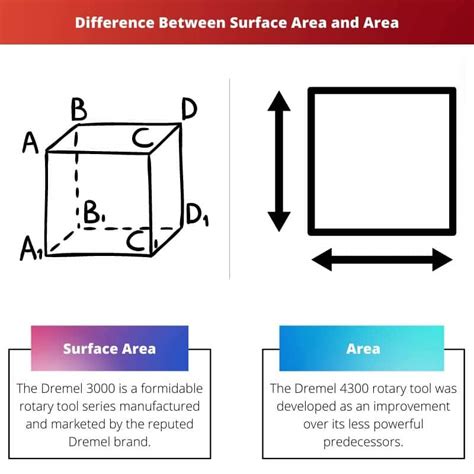
Table of Contents
Delving Deep: Understanding the Difference Between Area and Surface Area
The terms "area" and "surface area" are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion, especially in geometry and related fields. While seemingly similar, they represent distinct concepts with crucial differences in their application and calculation. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the nuances between area and surface area, providing a clear understanding of their definitions, formulas, and practical applications. We will explore various shapes and delve into real-world examples to solidify your grasp of these fundamental geometrical concepts.
What is Area?
Area, in its simplest form, measures the two-dimensional space occupied by a flat shape or figure. Think of it as the amount of surface covered by a shape on a plane. It's a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude (size) and no direction. The standard unit for area is square units, such as square meters (m²), square centimeters (cm²), square feet (ft²), or square inches (in²).
Calculating Area: A Shape-by-Shape Guide
The method for calculating the area depends entirely on the shape's characteristics. Here's a breakdown for some common shapes:
- Rectangle: Area = length × width. This is arguably the most fundamental area calculation.
- Square: Area = side × side = side². A square is simply a special case of a rectangle where all sides are equal.
- Triangle: Area = ½ × base × height. The height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
- Circle: Area = π × radius². Here, π (pi) is approximately 3.14159. The radius is the distance from the center to any point on the circle.
- Parallelogram: Area = base × height. Similar to a rectangle, but the sides are not necessarily perpendicular.
- Trapezoid: Area = ½ × (base₁ + base₂) × height. A trapezoid has two parallel bases.
Example: A rectangular garden measuring 10 meters in length and 5 meters in width has an area of 10 m × 5 m = 50 m².
What is Surface Area?
Surface area, on the other hand, measures the total area of all the faces of a three-dimensional object (a solid). It's the sum of the areas of all the surfaces that enclose a solid. Like area, it's a scalar quantity expressed in square units. Understanding surface area is crucial in various applications, from packaging design to calculating the amount of paint needed to cover a wall.
Calculating Surface Area: Navigating Three Dimensions
The calculation of surface area becomes more complex due to the object's three-dimensional nature. The formulas vary significantly depending on the solid's shape. Let's examine some common three-dimensional shapes:
- Cube: Surface Area = 6 × side². A cube has six identical square faces.
- Cuboid (Rectangular Prism): Surface Area = 2(length × width + width × height + height × length). A cuboid has six rectangular faces.
- Sphere: Surface Area = 4 × π × radius².
- Cylinder: Surface Area = 2 × π × radius × height + 2 × π × radius². This includes the area of the circular top and bottom, as well as the curved side.
- Cone: Surface Area = π × radius × slant height + π × radius². The slant height is the distance from the apex to the edge of the circular base.
- Pyramid: The surface area of a pyramid depends on the shape of its base. It's the sum of the area of the base and the areas of all the triangular faces.
Example: A cube with sides of 2 meters each has a surface area of 6 × 2² m² = 24 m².
Key Differences Between Area and Surface Area: A Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Area | Surface Area |
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Two-dimensional | Three-dimensional |
| Object Type | Flat shapes (2D) | Solid objects (3D) |
| Measurement | Space enclosed by a 2D shape | Total area of all external surfaces of a 3D object |
| Units | Square units (m², cm², ft², in²) | Square units (m², cm², ft², in²) |
| Calculation | Varies by shape (length x width, etc.) | Varies significantly by solid's shape |
| Real-world use | Measuring floor space, land plots, etc. | Painting a wall, wrapping a present, etc. |
Practical Applications: Where Area and Surface Area Shine
Both area and surface area are indispensable in various fields:
Area:
- Construction: Calculating the amount of flooring, tiling, or carpeting needed.
- Agriculture: Determining the size of fields for planting or calculating irrigation needs.
- Real Estate: Measuring the size of land parcels or buildings.
- Cartography: Representing geographical regions on maps.
- Graphic Design: Determining the size of images or printed materials.
Surface Area:
- Manufacturing: Designing packaging, calculating the amount of material needed, or determining heat transfer rates.
- Architecture: Calculating the amount of paint or materials needed for building exteriors.
- Medicine: Determining the dosage of topical medications based on body surface area.
- Engineering: Calculating heat loss or gain in structures or components.
- Environmental Science: Estimating the surface area of lakes or forests to assess their ecological role.
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
For more complex shapes or situations, calculus becomes necessary. The concept of surface integrals allows for the calculation of surface area for irregularly shaped objects. Similarly, using double integrals, we can calculate the area of irregular two-dimensional shapes.
Furthermore, understanding the relationship between area and volume is crucial. While area measures the surface, volume measures the space enclosed within a three-dimensional object. There is no direct mathematical relationship between area and volume that applies universally across all shapes.
Conclusion: Mastering Area and Surface Area
Understanding the difference between area and surface area is fundamental to grasping many concepts in geometry and various applied fields. While seemingly simple at first glance, the subtleties of their definitions and calculations become crucial as we tackle increasingly complex shapes and real-world problems. By mastering these concepts, you'll be better equipped to solve practical problems and enhance your understanding of the spatial world around us. Remember that diligent practice with various shapes and formulas is key to solidifying your understanding and applying these concepts effectively. This comprehensive guide has provided a strong foundation; now, it's your turn to build upon it!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats The Difference Between Alternator And Generator
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Does Xlv Mean In Roman Numbers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Melting Ice Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Strontium
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Gold A Mixture Or Pure Substance
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Area And Surface Area . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
