88 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
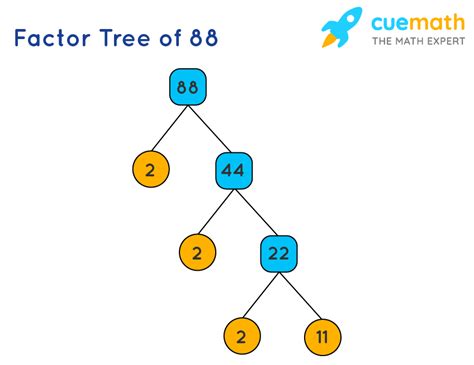
Table of Contents
88 as a Product of Prime Factors: A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors, is a fundamental concept in number theory with wide-ranging applications in mathematics and computer science. This article delves into the prime factorization of the number 88, exploring the methods involved, its significance, and its connections to other mathematical concepts.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before we embark on the factorization of 88, let's solidify our understanding of the core concepts:
What are Prime Numbers?
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 2 is the only even prime number; all other even numbers are composite (not prime).
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal the original number. This factorization is unique for every number (except for the order of the factors). This uniqueness is a cornerstone of number theory and is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Finding the Prime Factors of 88
Now, let's tackle the prime factorization of 88. We'll employ a systematic approach using the method of successive division by prime numbers:
-
Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 88 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. Dividing 88 by 2, we get 44.
-
Continue dividing by 2: 44 is also even, so we divide it by 2, resulting in 22.
-
Repeat the process: 22 is even, and dividing by 2 yields 11.
-
Identify the final prime factor: 11 is a prime number. We've reached a prime number, indicating the end of our factorization process.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 88 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 11, which can be written more concisely as 2³ x 11.
Visualizing the Prime Factorization
A factor tree is a helpful visual tool to represent the prime factorization process. For 88, the factor tree would look like this:
88
/ \
2 44
/ \
2 22
/ \
2 11
Each branch of the tree terminates at a prime number, and the product of these terminal prime numbers gives us the original number, 88.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has surprisingly profound applications across various mathematical fields and beyond:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM):**
Prime factorization is crucial for efficiently calculating the GCD and LCM of two or more numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder, while the LCM is the smallest number that is divisible by both numbers. By comparing the prime factorizations, we can easily find the GCD and LCM. For example, let's find the GCD and LCM of 88 and 132.
- 88 = 2³ x 11
- 132 = 2² x 3 x 11
The GCD is found by taking the minimum power of each common prime factor: 2² x 11 = 44
The LCM is found by taking the maximum power of each prime factor present in either number: 2³ x 3 x 11 = 264
2. Cryptography:**
Prime factorization lies at the heart of many modern cryptographic systems, such as RSA encryption. RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors. The security of these systems depends on this computational challenge. While factoring small numbers like 88 is trivial, factoring extremely large numbers (hundreds or thousands of digits) is computationally infeasible with current technology, making RSA secure.
3. Modular Arithmetic:**
Prime factorization plays a significant role in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory that deals with remainders after division. Many theorems and applications in modular arithmetic rely on the properties of prime numbers and their factorizations.
4. Algebra:**
Prime factorization is essential for simplifying algebraic expressions and solving equations. Being able to factor expressions into prime factors allows for simplification and helps reveal underlying structure and patterns.
5. Number Theory Research:**
Prime factorization is a central theme in number theory research, with ongoing exploration into the distribution of prime numbers, the efficiency of factorization algorithms, and the relationship between prime numbers and other mathematical structures. Unraveling the mysteries of prime numbers is a significant focus of ongoing mathematical research.
Beyond 88: Exploring Other Factorizations
While we've focused on 88, the principles of prime factorization apply universally to all integers. Let's briefly explore the factorization of some related numbers:
-
880: Since 880 = 88 x 10, we can build upon the factorization of 88. 10 = 2 x 5, so 880 = 2³ x 11 x 2 x 5 = 2⁴ x 5 x 11.
-
176: 176 = 88 x 2, so its prime factorization is 2⁴ x 11.
-
44: As shown in the factorization of 88, 44 = 2² x 11.
These examples highlight how understanding the prime factorization of one number can assist in finding the prime factorization of related numbers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple concept of prime factorization of a number like 88 underpins a vast array of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From efficiently calculating GCDs and LCMs to securing sensitive data through cryptography, the power of prime factorization is undeniable. The seemingly straightforward task of breaking down a number into its prime constituents unlocks a deeper understanding of number theory and its wide-ranging implications in various fields. The continuing exploration and refinement of factorization algorithms highlight its enduring importance in mathematics and computer science. Understanding prime factorization is not just about finding the prime factors of a number; it's about unlocking the fundamental building blocks of arithmetic and appreciating its profound impact on our mathematical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Net For A Triangular Prism
Mar 23, 2025
-
Real Life Applications Of Linear Equations In Two Variables
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is Gold A Pure Substance Or A Mixture
Mar 23, 2025
-
Select Three Components That Make Up A Nucleotide
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between A Nucleotide And A Nucleoside
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 88 As A Product Of Prime Factors . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
