Write The Prime Factorization Of 16
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
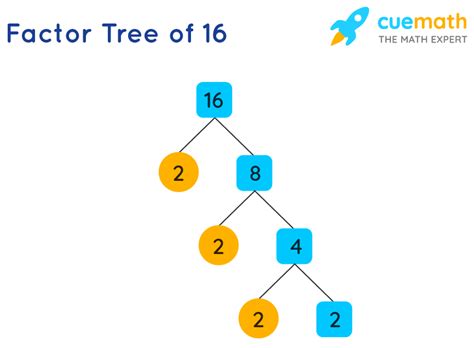
Table of Contents
Prime Factorization of 16: A Deep Dive into the Fundamentals of Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 16?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, exploring the underlying concepts reveals the fundamental building blocks of mathematics and the elegance of prime numbers. This article delves deep into the prime factorization of 16, explaining the process, exploring related concepts, and highlighting the significance of prime numbers in various mathematical fields.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 16, let's establish a clear understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. They are the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers.
Why are Prime Numbers Important?
Prime numbers are crucial in number theory and cryptography for several reasons:
-
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic: This theorem states that every whole number greater than 1 can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers. This uniqueness is what makes prime factorization so important. It's the "atomic structure" of numbers.
-
Cryptography: The difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components is the foundation of many modern encryption methods. RSA encryption, for example, relies on this difficulty to secure online transactions and communications.
-
Mathematical Structures: Prime numbers underpin many mathematical structures and concepts, including modular arithmetic, which has applications in computer science and coding theory.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 16
Now, let's determine the prime factorization of 16. The process involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number possible until we are left with 1.
-
Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 16 is divisible by 2. 16 ÷ 2 = 8.
-
Continue dividing by 2: 8 is also divisible by 2. 8 ÷ 2 = 4.
-
Divide by 2 again: 4 is divisible by 2. 4 ÷ 2 = 2.
-
The final division: 2 is a prime number. 2 ÷ 2 = 1.
We have reached 1, indicating we've fully factored the number. Therefore, the prime factorization of 16 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 2, which can be written more concisely as 2<sup>4</sup>.
Visualizing the Factorization
A factor tree can help visualize this process:
16
/ \
8 2
/ \
4 2
/ \
2 2
Each branch ends with a prime number, demonstrating that 16 is composed entirely of four factors of 2.
Exploring Related Concepts
The prime factorization of 16 provides a foundation for understanding several related mathematical concepts:
Composite Numbers
A composite number is a whole number greater than 1 that is not a prime number. This means it has more than two divisors. 16 is a composite number because it has divisors 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16. All composite numbers can be expressed as a product of prime numbers.
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides each of them without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD is simplified by using prime factorization. For example, to find the GCD of 16 and 24, we first find their prime factorizations:
- 16 = 2<sup>4</sup>
- 24 = 2<sup>3</sup> x 3
The GCD is found by taking the lowest power of the common prime factors: 2<sup>3</sup> = 8. Therefore, the GCD of 16 and 24 is 8.
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of each of the numbers. Again, prime factorization simplifies this calculation. To find the LCM of 16 and 24:
- 16 = 2<sup>4</sup>
- 24 = 2<sup>3</sup> x 3
The LCM is found by taking the highest power of all prime factors present in either number: 2<sup>4</sup> x 3 = 48. Therefore, the LCM of 16 and 24 is 48.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Beyond the fundamental concepts, prime factorization has significant applications in various fields:
Cryptography, as mentioned earlier, relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. The security of online transactions and sensitive data depends on this principle.
Computer Science: Algorithms for finding prime numbers and factoring large numbers are crucial in computer science research and development. Efficient algorithms are continually being developed to improve computational speed and security.
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a role in error-correcting codes, ensuring reliable data transmission in various applications.
Number Theory Research: Prime numbers are a central focus of number theory research, with many unsolved problems and ongoing investigations into their properties and distribution.
Beyond 16: Exploring Other Factorizations
While we've focused on the prime factorization of 16, the process is applicable to any whole number greater than 1. Let's consider a few examples:
- 20: 20 = 2<sup>2</sup> x 5
- 36: 36 = 2<sup>2</sup> x 3<sup>2</sup>
- 100: 100 = 2<sup>2</sup> x 5<sup>2</sup>
These examples demonstrate how prime factorization breaks down composite numbers into their fundamental prime components, revealing their unique structure.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 16, seemingly a simple calculation, unlocks a wealth of mathematical understanding. The concepts explored—prime numbers, composite numbers, GCD, LCM, and the applications in diverse fields—highlight the fundamental role of prime numbers in mathematics and beyond. The seemingly simple question serves as a gateway to a deeper appreciation of the elegance and power of number theory. Understanding prime factorization is not just an academic exercise; it's a key to understanding the fundamental building blocks of numbers and their influence on the world around us. From securing online transactions to advancing research in number theory, the significance of prime factorization is undeniable and enduring.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Square Root Of 125 In Simplest Radical Form
Mar 16, 2025
-
Is Melting Of Wax A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Is Carbon Tetrachloride Ionic Or Covalent
Mar 16, 2025
-
Write The Formula For Sulfurous Acid
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Prime Factorization Of 16 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
