Which Of The Following Statements About Vaccines Is True
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
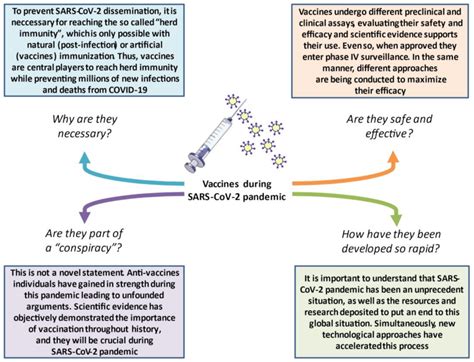
Table of Contents
Which of the Following Statements About Vaccines is True? Debunking Myths and Understanding the Science
Vaccines are one of the most significant achievements in modern medicine, saving millions of lives and eradicating diseases that once ravaged communities. However, despite their proven efficacy and safety, numerous misconceptions surround vaccines. This article aims to address common questions and clarify which statements about vaccines are true, backed by scientific evidence and reputable sources. We will explore the science behind vaccines, their safety profile, and address common concerns and myths.
Understanding How Vaccines Work: A Deep Dive into Immunity
Before we delve into the truth behind specific statements, let's establish a foundational understanding of how vaccines work. Vaccines train your immune system to recognize and fight off specific viruses or bacteria. They do this by introducing a weakened or inactive form of the germ, or even just a piece of it (like a protein), into your body. This doesn't cause illness, but it triggers your body's natural defenses to produce antibodies and memory cells. These memory cells remain in your system, ready to quickly recognize and neutralize the actual pathogen if you encounter it in the future. This is the basis of immunity, preventing or minimizing the severity of the disease.
Types of Vaccines and Their Mechanisms:
Several vaccine types exist, each employing different strategies to elicit an immune response. These include:
-
Live-attenuated vaccines: These use a weakened version of the germ. Because the germ is alive, it replicates in the body, leading to a robust immune response. Examples include the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and the oral polio vaccine.
-
Inactivated vaccines: These use a killed version of the germ. They're generally safer than live vaccines but may require multiple doses for full protection. Examples include the polio (IPV) vaccine and the influenza vaccine (shot).
-
Subunit, recombinant, polysaccharide, and conjugate vaccines: These vaccines use only specific parts of the germ, like a surface protein, to stimulate an immune response. They are particularly helpful for individuals who might have a weakened immune system. Examples include the hepatitis B vaccine and the HPV vaccine.
-
Toxoid vaccines: These vaccines introduce a toxin produced by a bacterium. The immune system learns to neutralize the toxin, protecting against the disease's harmful effects. Examples include tetanus and diphtheria vaccines.
-
mRNA vaccines: These vaccines use messenger RNA (mRNA) to instruct the body's cells to produce a harmless piece of the virus, triggering an immune response. The mRNA itself is quickly broken down by the body. The COVID-19 vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna are examples of mRNA vaccines.
Debunking Common Myths: Separating Fact from Fiction
Now, let's tackle some common statements about vaccines and determine whether they're true or false, based on overwhelming scientific consensus.
Statement 1: Vaccines cause autism.
FALSE. This statement is unequivocally false and has been thoroughly debunked by numerous large-scale studies. The original study that sparked this myth was retracted due to fraudulent data and unethical conduct. Major health organizations worldwide, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO), have confirmed the lack of any link between vaccines and autism.
Statement 2: Vaccines contain harmful preservatives like mercury.
PARTIALLY TRUE (but misleading). Thimerosal, an organomercury compound, was used as a preservative in some vaccines in the past. However, due to concerns (largely unfounded), it has been largely removed from most childhood vaccines in developed countries. The amount previously present was considered safe by regulatory agencies, but the removal was a precautionary measure. It's crucial to note that the amount of thimerosal in vaccines was far less than the amount considered harmful through other routes of exposure.
Statement 3: Vaccines weaken the immune system.
FALSE. Vaccines actually strengthen the immune system. They train it to recognize and fight specific pathogens, making it more robust overall. While some minor, temporary side effects like soreness or fever might occur, these are signs of a working immune system, not a weakened one. These side effects are typically mild and short-lived.
Statement 4: It's better to get sick naturally to build immunity.
FALSE. Getting sick naturally can lead to severe complications, long-term health problems, and even death, especially for vulnerable populations like infants, the elderly, and those with compromised immune systems. Vaccines offer safe and effective protection without the risks associated with natural infection. Furthermore, some diseases may cause permanent damage even after recovery.
Statement 5: Vaccines contain aborted fetal cells.
PARTIALLY TRUE (but requires nuance). Some vaccines use cell lines originally derived from aborted fetal tissue decades ago. These cell lines are not derived from newly aborted fetuses. They are used in the manufacturing process to grow viruses, not as a component of the vaccine itself. Many people find this ethically problematic, leading to the development of alternative vaccine production methods. The use of these cell lines is a complex ethical issue, and understanding the process and the reasons behind its continued use is important.
Statement 6: Vaccine side effects are common and severe.
FALSE. While some mild side effects like soreness, redness at the injection site, fever, and fatigue are possible, serious side effects are extremely rare. The benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks of these rare side effects. Extensive monitoring and reporting systems track vaccine safety, allowing for quick identification and response to any serious adverse events.
Statement 7: Herd immunity is not important.
FALSE. Herd immunity refers to the indirect protection conferred to unvaccinated individuals when a sufficient percentage of the population is vaccinated. This protection helps prevent outbreaks and protects vulnerable individuals who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. A high vaccination rate is crucial for maintaining herd immunity and protecting public health.
Statement 8: Vaccines are only effective for a short period.
PARTIALLY TRUE (depending on the vaccine). Some vaccines provide lifelong immunity, while others require booster shots to maintain protection. The duration of immunity varies depending on the vaccine and the individual's immune response. Booster shots are essential to reinforce immunity and maintain protection, especially against diseases with changing strains, like influenza.
Statement 9: Natural immunity is always better than vaccine-induced immunity.
FALSE. Natural immunity acquired through infection offers no guarantee of protection against future infections and can vary widely in effectiveness. Vaccine-induced immunity, on the other hand, is typically more consistent and predictable, offering safer and more reliable protection. Furthermore, acquiring natural immunity often comes at the cost of serious illness and potential long-term complications.
Statement 10: Vaccines are a conspiracy to control the population.
FALSE. This is a harmful and baseless conspiracy theory. The development and deployment of vaccines are driven by scientific research and public health goals, aimed at preventing and controlling infectious diseases. The extensive research, testing, and regulatory processes involved in vaccine development and approval demonstrate the commitment to safety and efficacy.
The Importance of Vaccination: Protecting Yourself and the Community
Vaccination is a cornerstone of public health. The numerous benefits far outweigh the extremely rare risks. Vaccines have significantly reduced the incidence of preventable diseases, saving millions of lives. By understanding the science behind vaccines and debunking common myths, we can make informed decisions to protect ourselves, our families, and our communities. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice on vaccination schedules and any concerns you may have. Staying informed and engaging in critical thinking about vaccine information are crucial steps in making the best choices for your health and well-being. A healthy and vaccinated population is a stronger and more resilient community.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Do Atoms Want 8 Valence Electrons
Mar 28, 2025
-
Two Angles Whose Measures Have A Sum Of 180 Degrees
Mar 28, 2025
-
Select All Of The Following That Are Characteristics Of Plants
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Resistance And Impedance
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Structure Controls The Cells Activities
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Statements About Vaccines Is True . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
