Which Of The Following Is True About Fungi
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
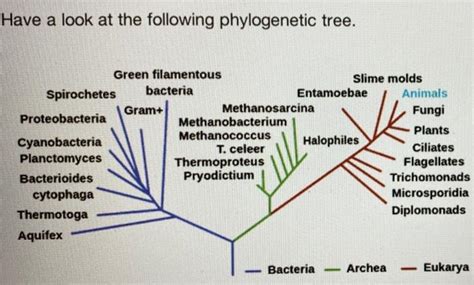
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is True About Fungi? Decoding the Kingdom of Mycelium
The kingdom Fungi, a diverse and often misunderstood group of organisms, plays a crucial role in our ecosystems and even our daily lives. From the delicious mushrooms adorning our plates to the microscopic yeasts responsible for bread-making, fungi are ubiquitous. However, many misconceptions surround their nature and function. This comprehensive guide aims to clarify these misconceptions and delve deep into the fascinating world of fungi, answering the question: which of the following is true about fungi? We'll explore their characteristics, ecological roles, and economic importance, dispelling common myths and highlighting the amazing complexity of this kingdom.
Fungi: A Kingdom Apart
To understand what is true about fungi, we must first establish their unique characteristics. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms, meaning their cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. This distinguishes them from bacteria, which are prokaryotic. However, they are distinct from plants and animals. Unlike plants, fungi are heterotrophic, meaning they cannot produce their own food through photosynthesis. Instead, they obtain nutrients by absorbing organic matter from their environment. Unlike animals, fungi digest their food externally, secreting enzymes to break down complex organic molecules before absorbing the simpler products.
Key Characteristics Distinguishing Fungi:
-
Heterotrophic Nutrition: Fungi are consumers, not producers. They rely on other organisms, living or dead, for their sustenance. This mode of nutrition can be saprophytic (decomposing dead organic matter), parasitic (living off a host organism), or symbiotic (forming mutually beneficial relationships with other organisms).
-
Chitinous Cell Walls: Unlike plant cells with cellulose cell walls, fungal cells are encased in chitin, a strong, flexible polysaccharide also found in the exoskeletons of insects. This provides structural support and protection.
-
Filamentous Structure (Hyphae): The bodies of most fungi are composed of thread-like filaments called hyphae. These hyphae intertwine to form a network called mycelium, which is the main body of the fungus. This extensive network allows for efficient absorption of nutrients from the surrounding environment. Some fungi, like yeasts, are unicellular.
-
Spore Reproduction: Fungi reproduce primarily through spores, which are tiny, lightweight reproductive units that can be dispersed by wind, water, or animals. This method of reproduction allows fungi to colonize new habitats effectively. Spores can be produced sexually or asexually, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
Debunking Common Myths About Fungi
Many misconceptions surround the fungal kingdom. Let's address some of the most prevalent inaccuracies:
Myth 1: All Fungi are Mushrooms
This is perhaps the most common misconception. Mushrooms are merely the fruiting bodies of certain fungi, analogous to the apple on an apple tree. The vast majority of the fungal organism, the mycelium, remains hidden beneath the surface of the soil or substrate. Many fungi don't even produce macroscopic fruiting bodies.
Myth 2: All Fungi are Harmful
While some fungi are indeed parasitic and can cause diseases in plants, animals, and humans, many others are beneficial. Many are essential decomposers, recycling nutrients in ecosystems. Others form symbiotic relationships with plants, enhancing their growth and nutrient uptake (mycorrhizae). Still others are used in food production (yeasts, mushrooms), medicine (penicillin), and various industrial processes.
Myth 3: Fungi are Plants
Fungi were once classified as plants, but they are now recognized as a separate kingdom. Their heterotrophic nutrition, chitinous cell walls, and unique reproductive strategies clearly distinguish them from plants.
The Ecological Importance of Fungi
Fungi play a vital role in maintaining the health and balance of our ecosystems. Their importance cannot be overstated:
1. Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling:
Fungi are the primary decomposers in most terrestrial ecosystems. They break down dead plants and animals, releasing essential nutrients back into the environment. Without fungi, the accumulation of dead organic matter would severely disrupt nutrient cycles and ecosystem function.
2. Symbiotic Relationships:
Many fungi form symbiotic relationships with other organisms. Mycorrhizae, for example, are symbiotic associations between fungi and plant roots. The fungus enhances the plant's ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil, while the plant provides the fungus with carbohydrates produced during photosynthesis. This mutually beneficial relationship is crucial for the growth and survival of many plants. Lichens are another example of symbiotic relationships, involving a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium.
3. Disease Control:
Some fungi are used as biological control agents to combat pests and diseases. Certain fungi are parasitic to insects or other harmful organisms, effectively controlling their populations and reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
The Economic Importance of Fungi
Beyond their ecological roles, fungi have significant economic importance:
1. Food Production:
Mushrooms are a popular and nutritious food source worldwide, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and protein. Yeasts are crucial in baking and brewing, contributing to the texture and flavor of bread, beer, and wine.
2. Medicine:
Penicillin, the first antibiotic, was derived from a fungus, Penicillium. Many other antibiotics and other pharmaceuticals are derived from fungal sources or are produced with the help of fungal enzymes.
3. Industrial Applications:
Fungi are used in various industrial processes, including the production of enzymes, organic acids, and other valuable compounds. They are also used in bioremediation, breaking down pollutants in contaminated environments.
Answering the Question: Which of the Following is True About Fungi?
Now, let's address the initial question directly. Without knowing the specific "following" statements, we can definitively say the following are true about fungi:
- They are heterotrophic organisms.
- They have chitinous cell walls.
- They reproduce primarily through spores.
- They play a crucial role in nutrient cycling.
- They can form symbiotic relationships with other organisms.
- They have both beneficial and harmful species.
- They are not plants.
- Many are essential decomposers in ecosystems.
- They are a diverse kingdom with a wide range of ecological and economic importance.
Depending on the specific options provided in the original question, you can select the statements that align with these truths.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Fungal Kingdom
The kingdom Fungi is a fascinating and complex group of organisms with a profound impact on our planet and our lives. By understanding their characteristics, ecological roles, and economic importance, we can appreciate their crucial contribution to the health of our ecosystems and the well-being of humanity. Dispelling the myths and misconceptions surrounding fungi allows for a deeper understanding and appreciation of their remarkable diversity and significance. Further research and exploration continue to reveal new and exciting discoveries about this often-overlooked kingdom, highlighting the enduring mystery and wonder of the fungal world. From the microscopic to the macroscopic, the kingdom of mycelium continues to surprise and inspire.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Full Stop In Writing
Mar 24, 2025
-
Substances That Are Formed During A Chemical Reaction Are Called
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is 4 9 As A Percent
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Highest Common Factor Of 28 And 36
Mar 24, 2025
-
Acetic Acid Vs Glacial Acetic Acid
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is True About Fungi . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
