Which Of The Following Is The Final Product Of Spermiogenesis
Juapaving
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
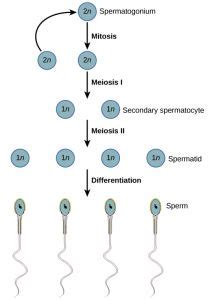
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is the Final Product of Spermiogenesis? A Deep Dive into Sperm Cell Maturation
Spermiogenesis, the final stage of spermatogenesis, is a fascinating and complex process that transforms spermatids into fully functional spermatozoa (sperm cells). Understanding this process is crucial for comprehending male fertility and reproductive health. This article will delve deep into spermiogenesis, exploring its intricate steps and ultimately answering the question: which of the following is the final product of spermiogenesis? We will examine the transformations that occur, the key players involved, and the significance of this remarkable cellular metamorphosis.
Understanding Spermatogenesis: The Bigger Picture
Before focusing on spermiogenesis, it's important to understand its place within the broader context of spermatogenesis. Spermatogenesis is the entire process of sperm cell production, occurring within the seminiferous tubules of the testes. It's a continuous process divided into three main phases:
1. Spermatocytogenesis: From Spermatogonia to Spermatids
This phase involves the mitotic divisions of spermatogonia (diploid stem cells) to produce primary spermatocytes. These primary spermatocytes then undergo meiosis I, a reductional division, resulting in secondary spermatocytes (haploid). Meiosis II follows, producing haploid spermatids. This phase establishes the genetic basis for the future sperm cells.
2. Meiosis: The Key to Genetic Diversity
Meiosis is a critical component of spermatogenesis, ensuring genetic diversity in offspring. The two meiotic divisions shuffle genetic material through recombination (crossing over) and independent assortment of chromosomes. This ensures that each resulting spermatid carries a unique genetic combination.
3. Spermiogenesis: The Transformation into Mature Sperm
This is the final stage and the focus of our discussion. Spermiogenesis is a complex differentiation process, transforming the round, immature spermatids into highly specialized, motile spermatozoa. This transformation involves dramatic morphological changes, preparing the sperm cell for its journey to fertilize an egg.
The Final Product of Spermiogenesis: The Mature Spermatozoon
The answer to the question, "Which of the following is the final product of spermiogenesis?" is unequivocally the mature spermatozoon (sperm cell). This highly specialized cell is uniquely designed for its role in fertilization. Let's break down its key features:
1. Head: The Genetic Cargo
The head of the spermatozoon is comprised primarily of the nucleus, containing the compacted haploid genome. This genetic material is crucial for fertilization and the creation of a new zygote. Covering the nucleus is the acrosome, a cap-like structure containing enzymes crucial for penetrating the protective layers surrounding the ovum (egg cell). These enzymes are vital for fertilization; without them, the sperm cell cannot penetrate the egg.
2. Midpiece: The Powerhouse
The midpiece is packed with mitochondria, the cell's powerhouses. These mitochondria generate the ATP (adenosine triphosphate) necessary for the flagellum's movement, propelling the sperm cell toward the egg. The energy supplied by the mitochondria is crucial for the long journey of the sperm cell to reach its destination. The higher the mitochondrial activity, the faster and more efficient the sperm cell's movement.
3. Tail (Flagellum): The Propulsion System
The tail, or flagellum, is a long, whip-like structure that enables the sperm cell's motility. The rhythmic beating of the flagellum propels the spermatozoon through the female reproductive tract, a journey that can take several days. The structure of the flagellum is complex, consisting of microtubules arranged in a specific pattern that allows for coordinated movement.
The Steps of Spermiogenesis: A Detailed Look
Spermiogenesis is a carefully orchestrated process involving several distinct steps:
1. Golgi Phase: Acrosome Formation
This initial phase focuses on the formation of the acrosome. Golgi apparatus vesicles containing acrosomal enzymes fuse to form the acrosomal cap, covering the anterior portion of the nucleus. This phase is crucial as the acrosome contains essential enzymes necessary for fertilization.
2. Cap Phase: Acrosome Growth and Nuclear Condensation
The acrosome continues to grow and mature, while the nucleus undergoes significant condensation. This condensation compacts the DNA, making the head smaller and more streamlined for efficient movement. The nucleus's compaction is an essential step to protect the genetic material during its journey through the female reproductive tract.
3. Acrosome Phase: Acrosome Maturation and Cytoplasmic Reduction
The acrosome reaches its final form, and excess cytoplasm is gradually eliminated. This cytoplasmic reduction is critical for optimizing the sperm cell's efficiency and streamlining its movement.
4. Maturation Phase: Flagellum Development and Cytoplasmic Residual Bodies
The flagellum develops from the centrioles, and the remaining cytoplasm is shed as residual bodies, which are eventually phagocytosed (engulfed) by Sertoli cells. The Sertoli cells play a supportive role during spermatogenesis, providing nutrients and protecting the developing sperm cells.
Clinical Significance and Disorders of Spermiogenesis
Disruptions in spermiogenesis can lead to male infertility. Various factors, including genetic mutations, hormonal imbalances, environmental toxins, and infections, can interfere with the intricate steps of sperm maturation. Understanding the mechanisms of spermiogenesis is crucial for diagnosing and treating male infertility. Many conditions impacting spermatogenesis ultimately manifest as defects in spermiogenesis, impacting the final mature sperm morphology and function.
Conclusion: The Mature Spermatozoon – A Marvel of Cellular Engineering
Spermiogenesis culminates in the production of the mature spermatozoon, a highly specialized cell perfectly adapted for its role in fertilization. This intricate process involves dramatic morphological changes and precise regulation of gene expression. The final product, the mature sperm cell, with its streamlined head, energy-packed midpiece, and powerful flagellum, stands as a testament to the remarkable efficiency of biological processes. Understanding the complexities of spermiogenesis enhances our appreciation of reproductive biology and the challenges associated with male infertility. Further research into the intricacies of spermiogenesis continues to unveil new insights and potential avenues for therapeutic intervention in cases of male infertility. The mature spermatozoon, therefore, represents not only the final product of spermiogenesis but also a critical component in the continuation of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Medical Problem Afflicts Mrs Mallard
Mar 31, 2025
-
2 Over 5 As A Percent
Mar 31, 2025
-
35 Inches Is How Many Feet
Mar 31, 2025
-
3 Cm Is How Many Mm
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Are In A Star
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is The Final Product Of Spermiogenesis . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
