Which Of The Following Is A Function Of A Nucleus
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
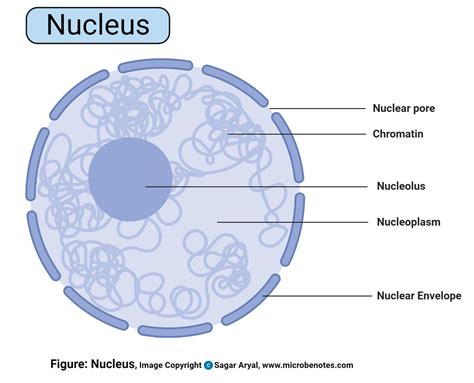
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is a Function of a Nucleus? Unveiling the Control Center of the Cell
The nucleus, often described as the cell's "control center," is a vital organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Understanding its functions is crucial to comprehending the intricacies of cellular biology and the processes that underpin life itself. This comprehensive article delves into the multifaceted roles of the nucleus, exploring its structure and explaining how it orchestrates various cellular activities. We'll examine the nucleus's functions in detail, clarifying its importance in genetic information storage, processing, and regulation.
The Nucleus: Structure and Organization
Before diving into the functions, let's briefly review the nucleus's structure. Encased within a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, the nucleus houses the cell's genetic material, chromatin, which consists of DNA and associated proteins. This DNA isn't simply a jumbled mess; it's meticulously organized into chromosomes, ensuring efficient storage and access.
The nuclear envelope isn't impenetrable; it's punctuated by nuclear pores, which act as selective gateways, regulating the transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. This controlled transport is vital for maintaining the nucleus's unique environment and coordinating cellular processes. The nucleolus, a dense region within the nucleus, plays a critical role in ribosome biogenesis, the synthesis of ribosomes—the protein factories of the cell.
Key Functions of the Nucleus: A Detailed Exploration
The nucleus's functions are not isolated events but rather intertwined processes that work in concert to ensure the cell's proper functioning. Let's dissect these functions in detail:
1. Storage and Protection of Genetic Information (DNA)
The most fundamental function of the nucleus is the storage and protection of the cell's DNA. DNA, the blueprint of life, contains the instructions for building and maintaining the organism. The nuclear envelope provides a protective barrier, shielding the DNA from damaging agents in the cytoplasm, ensuring the integrity of the genetic code. This protection is crucial for preventing mutations and maintaining the cell's identity. The organized structure of chromatin further enhances protection and facilitates efficient access to specific genetic regions.
2. DNA Replication and Repair
The nucleus is not merely a passive storage unit; it's also the site of DNA replication. Before a cell divides, its DNA must be precisely duplicated to ensure each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic instructions. This intricate process, occurring during the S phase of the cell cycle, is meticulously controlled within the nucleus to minimize errors. Furthermore, the nucleus houses the machinery for DNA repair, correcting errors that may arise from various sources like radiation or replication mistakes. This repair mechanism safeguards the genetic integrity and prevents the propagation of harmful mutations.
3. Transcription: RNA Synthesis
The nucleus is where transcription takes place—the process of copying DNA into RNA. DNA contains the genetic code, but it's RNA that carries the instructions to the ribosomes for protein synthesis. Specific regions of DNA, called genes, are transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), each playing a crucial role in protein synthesis. The precise regulation of transcription, controlled by various transcription factors, ensures that only the necessary genes are expressed at the appropriate times and in the correct amounts.
4. RNA Processing and Modification
The RNA transcripts produced during transcription undergo significant processing within the nucleus before they can be exported to the cytoplasm. This processing includes capping, splicing, and polyadenylation. Capping protects the mRNA from degradation, splicing removes non-coding regions (introns), and polyadenylation adds a tail that helps regulate mRNA stability and translation. These modifications are crucial for ensuring the efficient translation of mRNA into proteins.
5. Ribosome Biogenesis: The Nucleolus's Role
The nucleolus, a prominent structure within the nucleus, is the site of ribosome biogenesis. Ribosomes are essential cellular components responsible for protein synthesis. The nucleolus orchestrates the transcription and processing of rRNA, along with the assembly of ribosomal proteins, forming functional ribosomes. These ribosomes are then transported to the cytoplasm, where they perform their protein synthesis function. The efficiency of ribosome production in the nucleolus significantly impacts the cell's capacity for protein synthesis and overall function.
6. Regulation of Gene Expression
The nucleus isn't just a passive player; it actively regulates gene expression. This precise control ensures that only the appropriate genes are expressed at the right time and in the right amounts. Various mechanisms, including chromatin remodeling, DNA methylation, and the binding of transcription factors, determine which genes are transcribed and at what level. This intricate regulatory system is crucial for cellular differentiation, development, and response to environmental changes. Dysregulation of gene expression can lead to various diseases, highlighting the significance of the nucleus's role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
7. Cellular Signaling and Communication
The nucleus acts as a central hub for cellular signaling and communication. It receives signals from the cytoplasm and integrates them with the cell's genetic information to orchestrate a response. These signals can trigger changes in gene expression, leading to alterations in cellular behavior. The nucleus's ability to process and respond to signals is essential for the cell's adaptation to its environment and its communication with other cells. This communication involves the import and export of signaling molecules through the nuclear pores, highlighting the dynamic nature of the nucleus.
The Nucleus and Human Health: Implications of Nuclear Dysfunction
The nucleus plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular health. Dysfunction in nuclear processes can have far-reaching consequences, leading to various diseases. For example:
- Cancer: Many cancers are linked to mutations in genes located within the nucleus, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and division.
- Genetic disorders: Errors in DNA replication or repair within the nucleus can cause genetic disorders, characterized by abnormalities in various cellular processes.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: The accumulation of misfolded proteins or DNA damage within the nucleus can contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
- Aging: Aging is associated with the accumulation of damage to the nucleus and its contents, affecting cellular function and overall health.
Conclusion: The Nucleus – A Dynamic Orchestrator of Cellular Life
The nucleus, far from being a simple storage compartment, is a highly dynamic and complex organelle that orchestrates a multitude of cellular processes. Its multifaceted functions, from safeguarding genetic information to regulating gene expression, are crucial for maintaining cellular health and overall organismal function. Understanding the complexities of the nucleus provides insights into the fundamental processes of life, and unraveling its secrets holds the key to advancing our knowledge of health and disease. Future research continues to explore the intricacies of the nucleus, promising a deeper understanding of its vital role in cellular biology and the development of novel therapeutic approaches for various diseases. The nucleus, in essence, remains a fascinating and vital area of ongoing scientific exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is An Operator In Biology
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is A Function Of A Nucleus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
