How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
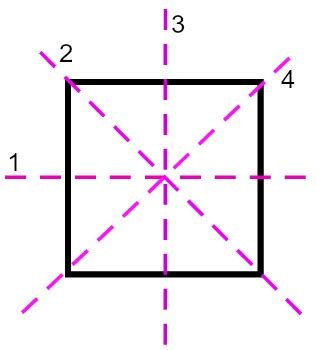
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Square Have? A Comprehensive Exploration
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in mathematics and art, refers to a balanced and proportionate arrangement of elements within a shape or design. Understanding lines of symmetry is crucial in various fields, from geometry and art to architecture and design. This article delves deep into the question: how many lines of symmetry does a square possess? We’ll explore the concept of symmetry, different types of symmetry, and then specifically examine the lines of symmetry present in a square, providing clear explanations and visual aids to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection or an axis of symmetry, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, both halves would perfectly overlap. This means that every point on one side of the line has a corresponding point on the other side at an equal distance from the line.
There are various types of symmetry, but the one relevant to our discussion of a square is reflectional symmetry (also known as bilateral symmetry). This is the type of symmetry where a shape can be reflected across a line to produce a mirror image. Other types of symmetry include rotational symmetry (where a shape can be rotated around a point and still look the same) and translational symmetry (where a shape can be repeated across a plane).
Exploring Symmetry in Different Shapes
Before focusing on the square, let's briefly look at the lines of symmetry in other simple shapes:
-
Circle: A circle has infinite lines of symmetry. Any line passing through the center of the circle will divide it into two identical halves.
-
Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry. Each line connects a vertex (corner) to the midpoint of the opposite side.
-
Rectangle (non-square): A rectangle has two lines of symmetry. These lines run horizontally and vertically through the center of the rectangle.
-
Isosceles Triangle: An isosceles triangle has one line of symmetry. This line bisects the angle formed by the two equal sides and also bisects the opposite side.
The Square: A Geometric Masterpiece of Symmetry
Now, let's turn our attention to the square. A square is a quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles. Its unique properties contribute to a relatively high number of lines of symmetry.
To visualize the lines of symmetry in a square, consider a perfect square. Draw lines that bisect the shape. You will discover that a square possesses a total of four lines of symmetry.
The Four Lines of Symmetry in a Square: A Detailed Breakdown
-
Horizontal Line of Symmetry: This line runs horizontally through the midpoint of the top and bottom sides of the square. Folding the square along this line perfectly overlaps the top and bottom halves.
-
Vertical Line of Symmetry: This line runs vertically through the midpoint of the left and right sides of the square. Folding along this line superimposes the left and right halves.
-
Diagonal Line of Symmetry 1: This line runs diagonally from one corner of the square to the opposite corner. This divides the square into two congruent right-angled triangles.
-
Diagonal Line of Symmetry 2: The second diagonal line of symmetry runs from the remaining corner to the opposite corner, perpendicular to the first diagonal line. This also divides the square into two congruent right-angled triangles.
Visualizing the Lines of Symmetry: Practical Examples
Imagine a square piece of paper. You can easily demonstrate the four lines of symmetry by folding it:
- Fold it in half horizontally. The top and bottom halves should perfectly match.
- Fold it in half vertically. The left and right halves should perfectly match.
- Fold it diagonally from one corner to the opposite corner. The two resulting triangles are congruent.
- Fold it along the other diagonal. Again, the two resulting triangles are congruent.
This hands-on approach provides a clear understanding of how the four lines of symmetry divide the square into identical halves.
Beyond the Basic: Exploring Rotational Symmetry in Squares
While we've primarily focused on lines of symmetry (reflectional symmetry), it's important to note that squares also possess rotational symmetry. A square has rotational symmetry of order 4. This means that it can be rotated about its center by 90°, 180°, and 270°, and it will still appear unchanged. Each of these rotations is equivalent to a reflection about a line of symmetry.
Applications of Symmetry in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of symmetry, and particularly the lines of symmetry in a square, finds numerous applications in various fields:
-
Architecture and Design: Many buildings and structures incorporate square elements, leveraging symmetry for aesthetic appeal and structural stability. Think about the symmetrical design of windows, doors, or even the overall layout of a house.
-
Art and Design: Artists and designers use symmetry to create visually balanced and pleasing compositions. From paintings and sculptures to logos and patterns, symmetry plays a significant role in creating aesthetically appealing designs.
-
Engineering: Symmetrical designs in engineering often lead to increased stability and efficiency. Consider the symmetrical design of bridges, cars, or aircraft.
-
Nature: Symmetry is prevalent in nature, appearing in snowflakes, flowers, and many other natural formations. The understanding of symmetry helps us understand the underlying principles governing natural patterns.
-
Computer Graphics and Programming: Understanding symmetry is crucial in computer graphics and game development for efficient rendering and animation of symmetrical objects.
Common Misconceptions about Lines of Symmetry
A common misunderstanding revolves around confusing the lines of symmetry with lines that simply bisect a square. While all lines of symmetry bisect a square, not all lines that bisect a square are lines of symmetry. Only the four lines described above meet the criteria of reflectional symmetry.
Conclusion: The Square's Symmetrical Elegance
In conclusion, a square possesses four lines of symmetry: two lines of symmetry through the center horizontally and vertically, and two diagonal lines of symmetry. Understanding these lines of symmetry is not only important for geometrical purposes but also has far-reaching implications in various fields, from art and design to engineering and nature. This comprehensive exploration should solidify your understanding of the symmetrical elegance inherent in the seemingly simple square. The concept of symmetry extends far beyond simple shapes, influencing the design and function of numerous elements in our world. The square serves as an excellent introduction to the fascinating world of symmetry, showcasing its fundamental principles and multifaceted applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Food Is Digested Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Are The Factor Pairs Of 56
Mar 17, 2025
-
Are Lysosomes Only In Animal Cells
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Are The Prime Factors Of 47
Mar 17, 2025
-
Electronic Configuration Of Cr And Cu
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
