What's The Square Root Of 128
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
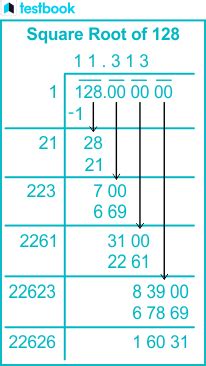
Table of Contents
What's the Square Root of 128? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Simplification
The question, "What's the square root of 128?" might seem simple at first glance. While a calculator will readily provide a decimal approximation, a deeper understanding involves exploring the concept of square roots, prime factorization, and simplifying radical expressions. This comprehensive guide will delve into these concepts, providing you not only with the answer but also with a thorough understanding of the underlying mathematical principles.
Understanding Square Roots
Before tackling the square root of 128, let's solidify our understanding of what a square root actually represents. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself (squared), results in the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 x 3 = 9. This is represented mathematically as √9 = 3.
Key Concepts:
- Perfect Squares: These are numbers that result from squaring an integer (whole number). Examples include 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, and so on.
- Radical Sign (√): This symbol denotes the square root operation.
- Radicand: The number inside the radical sign is called the radicand. In √128, 128 is the radicand.
Finding the Square Root of 128: A Step-by-Step Approach
The square root of 128 is not a whole number; it's an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. However, we can simplify it to its most concise radical form. This simplification involves the process of prime factorization.
1. Prime Factorization of 128:
Prime factorization involves breaking down a number into its prime factors—numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves. Let's factorize 128:
128 = 2 x 64 128 = 2 x 2 x 32 128 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 16 128 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 8 128 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 4 128 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2⁷
Therefore, 128 can be expressed as 2 raised to the power of 7 (2⁷).
2. Simplifying the Radical Expression:
Now, let's substitute the prime factorization back into the square root:
√128 = √(2⁷)
Remember, a square root essentially means finding a pair of identical factors. We can rewrite 2⁷ as 2⁶ x 2¹. This allows us to simplify:
√(2⁷) = √(2⁶ x 2¹) = √(2⁶) x √2 = 2³√2
Since √(2⁶) = (2⁶)^(1/2) = 2³ = 8, our simplified expression becomes:
√128 = 8√2
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 128 is 8√2.
Decimal Approximation
While 8√2 is the simplified radical form, you might need a decimal approximation for practical applications. Using a calculator, you'll find that:
√128 ≈ 11.3137
Keep in mind that this is an approximation; the decimal representation of √128 goes on infinitely without repeating.
Understanding Irrational Numbers
The square root of 128, like many square roots of non-perfect squares, is an irrational number. Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a simple fraction (a ratio of two integers). Their decimal representations are non-terminating and non-repeating, meaning they continue infinitely without ever settling into a repeating pattern. This is in contrast to rational numbers, which can be expressed as fractions.
Applications of Square Roots
Understanding square roots is crucial in various fields, including:
- Geometry: Calculating the length of the diagonal of a square or the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle using the Pythagorean theorem (a² + b² = c²).
- Physics: Solving problems related to velocity, acceleration, and energy.
- Engineering: Designing structures and calculating distances and forces.
- Computer Graphics: Creating realistic images and animations.
- Statistics: Calculating standard deviation and variance.
Further Exploration of Radical Expressions
Beyond the simple square root of 128, let's explore more complex radical expressions and their simplification. Consider the following example:
√72
Following the same steps as before:
- Prime Factorization: 72 = 2³ x 3²
- Simplification: √72 = √(2³ x 3²) = √(2² x 2 x 3²) = √(2²) x √(3²) x √2 = 2 x 3 x √2 = 6√2
Therefore, √72 simplifies to 6√2.
This demonstrates the consistent application of prime factorization in simplifying radical expressions. The ability to identify perfect square factors within the radicand is key to efficient simplification.
Advanced Concepts: Nth Roots
While we've focused on square roots (2nd roots), the concept extends to nth roots. An nth root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself n times, results in the original number. For instance:
- The cube root (3rd root) of 8 is 2 (because 2 x 2 x 2 = 8), denoted as ³√8 = 2.
- The fourth root of 16 is 2 (because 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16), denoted as ⁴√16 = 2.
Similar simplification techniques using prime factorization can be applied to nth roots.
Conclusion: Mastering Square Roots and Beyond
Understanding the square root of 128, and the broader concept of square roots, involves a combination of fundamental mathematical principles. By mastering prime factorization and the simplification of radical expressions, you gain a powerful tool applicable in diverse mathematical and scientific contexts. This goes beyond simply obtaining a numerical answer; it’s about developing a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical structures. Whether you're dealing with simple square roots or more complex nth roots, the consistent application of these principles will lead you to accurate and efficient solutions. Remember to practice regularly to build your confidence and proficiency in simplifying radical expressions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Determine The Equation Of The Circle Graphed Below
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Percent Is 50 Of 60
Mar 15, 2025
-
Unit Of Temperature In Si System
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Sum X X 3 3 X 3 2 X 3
Mar 15, 2025
-
Riemann Sum Calculator For Each Cross Section
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Square Root Of 128 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
