Unit Of Temperature In Si System
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
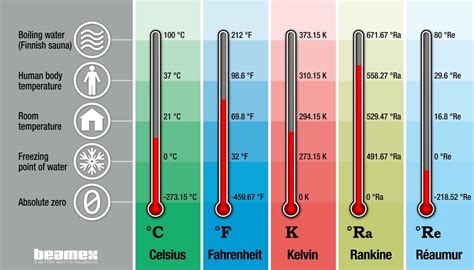
Table of Contents
The Kelvin: Understanding the SI Unit of Temperature
The International System of Units (SI), the modern metric system, provides a standardized framework for measurement across various scientific disciplines. Within this framework, temperature plays a crucial role, governing numerous physical phenomena and influencing countless processes. The fundamental unit of thermodynamic temperature within the SI system is the kelvin (K), a cornerstone for accurate scientific measurements and calculations. This article will delve deep into the nature of the kelvin, exploring its definition, history, applications, and importance across various fields.
The History and Definition of the Kelvin
The kelvin's story is inextricably linked to the development of thermodynamics and the quest to define an absolute temperature scale. Unlike Celsius or Fahrenheit, which are relative scales based on arbitrary reference points (the freezing and boiling points of water), the kelvin scale is absolute. This means its zero point corresponds to absolute zero, the theoretical temperature at which all molecular motion ceases.
Prior to the formal adoption of the kelvin, several scientists contributed to the understanding of absolute temperature. Lord Kelvin (William Thomson), after whom the unit is named, played a pivotal role in formulating the concept of absolute zero and establishing a thermodynamic temperature scale. His work built upon the discoveries of earlier scientists like Gay-Lussac and Charles, who observed the relationship between temperature and gas volume.
The current definition of the kelvin, adopted in 2018, anchors it to the Boltzmann constant (k<sub>B</sub>), a fundamental physical constant relating the average kinetic energy of particles in a gas to its absolute temperature. Specifically, one kelvin is defined as the change in thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy equal to k<sub>B</sub> multiplied by one joule (J). This definition provides exceptional precision and stability, independent of any specific substance or physical process.
The Boltzmann Constant and its Role
The Boltzmann constant (k<sub>B</sub> ≈ 1.380649 × 10<sup>-23</sup> J⋅K<sup>-1</sup>) acts as a bridge between the microscopic world of atoms and molecules and the macroscopic world of thermodynamics. It quantifies the relationship between temperature and the average kinetic energy of particles. A higher temperature implies a greater average kinetic energy, and vice-versa. The precise definition of the kelvin through the Boltzmann constant ensures a highly accurate and reproducible unit of temperature.
Distinguishing Kelvin from Celsius and Fahrenheit
While the kelvin is the SI unit, other temperature scales, notably Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F), are frequently encountered in daily life and specific applications. Understanding their relationships with the kelvin is crucial.
-
Celsius: The Celsius scale is defined by assigning 0 °C to the freezing point of water and 100 °C to its boiling point at standard atmospheric pressure. The relationship between Celsius and kelvin is straightforward: K = °C + 273.15. This means that 0 °C is equivalent to 273.15 K.
-
Fahrenheit: The Fahrenheit scale is less commonly used in scientific contexts but remains prevalent in some parts of the world. Its reference points are different, assigning 32 °F to the freezing point of water and 212 °F to its boiling point. The conversion between Fahrenheit and kelvin is more complex, requiring a two-step process: first converting to Celsius and then to kelvin, or vice versa.
Applications of the Kelvin Scale in Science and Engineering
The kelvin's significance extends across a vast array of scientific and engineering disciplines. Its absolute nature and high precision are crucial for:
1. Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics
Thermodynamics, the study of energy and its transformations, relies heavily on the kelvin scale. Concepts like entropy, Gibbs free energy, and enthalpy are all defined in terms of absolute temperature. Statistical mechanics, which connects macroscopic properties to microscopic behavior, uses the kelvin to quantify the average kinetic energy of particles and predict system behavior.
2. Material Science and Engineering
Material properties often exhibit significant temperature dependence. Understanding how materials behave at various temperatures, from cryogenic levels (close to absolute zero) to extremely high temperatures, is critical for designing and manufacturing advanced materials. The kelvin provides the necessary precision for characterizing these temperature-dependent properties.
3. Astrophysics and Cosmology
Astronomers and cosmologists use the kelvin to describe the temperatures of celestial objects, ranging from the extremely hot cores of stars to the frigid expanse of interstellar space. Precise temperature measurements are vital for understanding stellar evolution, galactic formation, and the cosmic microwave background radiation.
4. Chemistry and Chemical Engineering
Chemical reactions and processes are profoundly affected by temperature. Reaction rates, equilibrium constants, and phase transitions are all described using the kelvin, providing a quantitative understanding of chemical phenomena. Chemical engineers use this knowledge for process optimization and control.
5. Meteorology and Climatology
While Celsius is commonly used in weather reports, the kelvin plays a role in understanding atmospheric processes and climate modeling. Global climate models, which predict future climate change, use temperature data expressed in kelvins to accurately simulate atmospheric dynamics and predict the Earth's temperature response to various factors.
6. Cryogenics and Low-Temperature Physics
Cryogenics, the science of extremely low temperatures, explores the unique properties of matter at temperatures approaching absolute zero. The kelvin is indispensable for this field, allowing for accurate temperature control and characterization of phenomena like superconductivity and superfluidity.
The Significance of the Redefinition of the Kelvin
The 2018 redefinition of the kelvin, based on the Boltzmann constant, represents a significant advancement in metrology. This change moved away from reliance on the triple point of water, a temperature-specific physical property of water, and towards a more fundamental constant. This offers several key advantages:
-
Improved Accuracy and Precision: The new definition significantly enhances the accuracy and reproducibility of temperature measurements across various laboratories globally.
-
Greater Stability: The Boltzmann constant is a fundamental physical constant, making the definition of the kelvin inherently more stable and less susceptible to variations caused by changing physical properties of water.
-
Enhanced International Collaboration: The new definition ensures a consistent and universally accepted standard for temperature measurement, fostering greater collaboration and data comparability across scientific communities worldwide.
Conclusion: The Kelvin's Enduring Importance
The kelvin, the SI unit of thermodynamic temperature, is far more than just a unit of measurement. It's a cornerstone of modern science and engineering, providing a precise and reliable standard for quantifying temperature across a vast range of applications. Its redefinition in 2018 further cemented its importance, ensuring that temperature measurements remain accurate, reliable, and consistent across disciplines and nations. As scientific research and technological advancements continue, the kelvin will remain a crucial tool for understanding the universe and the world around us. Its absolute nature and connection to fundamental physical constants ensure its enduring relevance in the ongoing quest for scientific knowledge and technological progress. The understanding and precise use of the Kelvin scale are vital for anyone working in fields where accurate temperature measurement is paramount.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Unit Of Temperature In Si System . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
