Riemann Sum Calculator For Each Cross-section
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
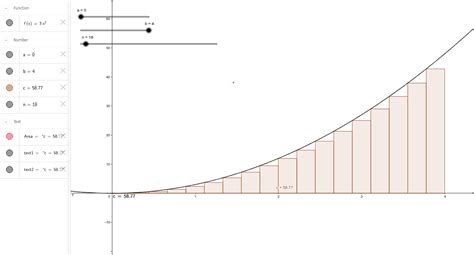
Table of Contents
Riemann Sum Calculator for Each Cross-Section: A Deep Dive
The Riemann sum is a fundamental concept in calculus used to approximate the definite integral of a function. It's a powerful tool for estimating areas under curves, volumes of solids, and other important quantities. While many calculators offer a general Riemann sum calculation, understanding how to apply this technique to individual cross-sections allows for a much more nuanced and insightful analysis, especially when dealing with complex shapes and functions. This article will delve deep into the Riemann sum, focusing on its application to individual cross-sections and exploring practical methods for calculation.
Understanding the Riemann Sum
Before we dive into cross-sections, let's solidify our understanding of the Riemann sum itself. Essentially, it's a method of approximating the area under a curve by dividing the area into a series of rectangles. The height of each rectangle is determined by the function's value at a specific point within the subinterval, and the width is determined by the subinterval's length.
There are three main types of Riemann sums:
-
Left Riemann Sum: The height of each rectangle is determined by the function's value at the left endpoint of each subinterval.
-
Right Riemann Sum: The height of each rectangle is determined by the function's value at the right endpoint of each subinterval.
-
Midpoint Riemann Sum: The height of each rectangle is determined by the function's value at the midpoint of each subinterval.
Formula for Riemann Sums
The general formula for a Riemann sum is:
∑<sub>i=1</sub><sup>n</sup> f(x<sub>i</sub><sup>*</sup>)Δx
Where:
- n is the number of rectangles (subintervals).
- Δx is the width of each rectangle ( (b-a)/n, where 'a' and 'b' are the limits of integration).
- x<sub>i</sub><sup>*</sup> is a point within the i-th subinterval. The choice of this point determines the type of Riemann sum (left, right, or midpoint).
- f(x<sub>i</sub><sup>*</sup>) is the height of the i-th rectangle.
Riemann Sums and Cross-Sections: A Powerful Combination
The true power of the Riemann sum becomes apparent when we apply it to problems involving cross-sections. Imagine you have a three-dimensional solid whose cross-sectional area is given by a function A(x). To find the volume of this solid, we can use a Riemann sum to approximate the volume by summing the volumes of a series of thin "slices" or cylinders.
Each slice has a volume approximately equal to:
A(x<sub>i</sub><sup>*</sup>)Δx
Where:
- A(x<sub>i</sub><sup>*</sup>) is the cross-sectional area at a particular point x<sub>i</sub><sup>*</sup> within the i-th subinterval.
- Δx is the thickness of each slice.
The total volume is then approximated by the sum:
∑<sub>i=1</sub><sup>n</sup> A(x<sub>i</sub><sup>*</sup>)Δx
This is essentially a Riemann sum, where the function we are integrating is the cross-sectional area function A(x). As the number of slices (n) increases, the approximation becomes increasingly accurate, converging to the true volume of the solid as n approaches infinity.
Calculating Riemann Sums for Cross-Sections: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let's walk through a practical example to illustrate the process. Consider a solid whose cross-sectional area at position x is given by the function:
A(x) = x² + 1 for 0 ≤ x ≤ 2
We want to approximate the volume of this solid using a right Riemann sum with n = 4 subintervals.
Step 1: Determine Δx
Δx = (b - a) / n = (2 - 0) / 4 = 0.5
Step 2: Define the Subintervals
Our subintervals are: [0, 0.5], [0.5, 1], [1, 1.5], [1.5, 2]
Step 3: Evaluate A(x) at the Right Endpoints
For a right Riemann sum, we evaluate A(x) at the right endpoint of each subinterval:
- A(0.5) = (0.5)² + 1 = 1.25
- A(1) = (1)² + 1 = 2
- A(1.5) = (1.5)² + 1 = 3.25
- A(2) = (2)² + 1 = 5
Step 4: Calculate the Riemann Sum
The approximate volume is:
∑<sub>i=1</sub><sup>4</sup> A(x<sub>i</sub><sup>*</sup>)Δx = (1.25 + 2 + 3.25 + 5) * 0.5 = 5.75
Therefore, using a right Riemann sum with 4 subintervals, the approximate volume of the solid is 5.75 cubic units.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
The accuracy of the Riemann sum approximation improves as the number of subintervals (n) increases. However, calculating the sum manually for large values of n can be tedious. This is where computational tools, including dedicated Riemann sum calculators or programming languages like Python, become invaluable. These tools can automate the process, allowing for rapid and accurate calculations even with a high number of subintervals.
Error Analysis and Convergence
Understanding the error inherent in Riemann sum approximations is crucial. The error decreases as n increases, but the rate of convergence depends on the function's smoothness and the type of Riemann sum used. Midpoint Riemann sums generally exhibit faster convergence than left or right sums.
Applications Beyond Volume Calculation
The Riemann sum technique, applied to cross-sections, isn't limited to volume calculations. It can also be used to approximate:
- Surface area: If the function provides the circumference of a cross-section, the Riemann sum can approximate the surface area of a solid of revolution.
- Mass: If the function represents the density of a solid, the Riemann sum can be used to estimate the total mass.
- Work: In physics, the Riemann sum can approximate the work done by a variable force.
Choosing the Right Riemann Sum and Number of Subintervals
The choice of Riemann sum (left, right, or midpoint) and the number of subintervals (n) influences the accuracy of the approximation. For monotonic functions (always increasing or always decreasing), the error is bounded, and the approximation is relatively straightforward. For oscillating functions, however, choosing the appropriate number of subintervals becomes crucial to minimize error. Experimentation and iterative refinement are often necessary to achieve a desired level of accuracy.
Utilizing Computational Tools
While manual calculation is valuable for understanding the fundamental principles, using computational tools is essential for real-world applications. Many software packages and online calculators are available, specifically designed for Riemann sum calculations. These tools often allow for adjustments to the number of subintervals and the type of Riemann sum used, providing a flexible and efficient approach to solving complex problems involving cross-sections.
Conclusion: Mastering Riemann Sums for Cross-Section Analysis
The Riemann sum, applied to cross-sections, is a powerful technique for approximating various quantities related to three-dimensional solids. Understanding the fundamental principles, mastering the step-by-step calculation process, and leveraging computational tools are key to accurately and efficiently analyzing these problems. This comprehensive understanding empowers you to tackle complex geometric and physical problems with confidence, providing insights that would be difficult to obtain through other means. By combining theoretical knowledge with practical application, you unlock the full potential of the Riemann sum as a valuable tool in calculus and beyond. Remember to always consider the limitations of the approximation and strive for accuracy through iterative refinement and careful consideration of the chosen method and number of subintervals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Riemann Sum Calculator For Each Cross-section . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
