Whats The Lcm Of 5 And 15
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
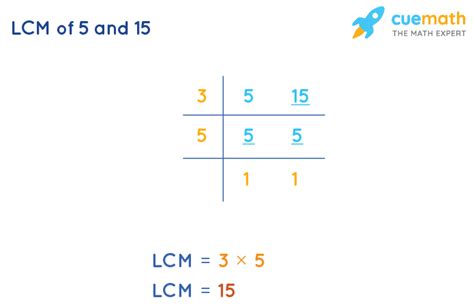
Table of Contents
What's the LCM of 5 and 15? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and exploring different methods to solve it provides a valuable foundation in mathematics and its applications. This article will delve into determining the LCM of 5 and 15, explaining the process in detail and exploring various approaches. We'll also touch upon the broader significance of LCMs in various fields, from scheduling to music theory.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we jump into calculating the LCM of 5 and 15, let's clarify what an LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers in the set as factors.
Example: Let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16... The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The least common multiple is 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers like 5 and 15, is to list the multiples of each number and identify the smallest common multiple.
Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30...
Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60...
By comparing the lists, we can readily see that the smallest number appearing in both lists is 15. Therefore, the LCM of 5 and 15 is 15.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers or when dealing with multiple numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor.
-
Find the prime factorization of each number:
- 5 = 5 (5 is a prime number)
- 15 = 3 x 5
-
Identify the highest power of each prime factor:
- The prime factors are 3 and 5.
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ = 5
-
Multiply the highest powers together:
- LCM(5, 15) = 3 x 5 = 15
Therefore, using prime factorization, we again confirm that the LCM of 5 and 15 is 15.
Method 3: Using the Formula (for two numbers)
For two numbers, a and b, there's a handy formula that relates the LCM and the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD):
LCM(a, b) = (| a x b |) / GCD(a, b)
-
Find the GCD of 5 and 15: The greatest common divisor is the largest number that divides both 5 and 15 without leaving a remainder. In this case, the GCD(5, 15) = 5.
-
Apply the formula: LCM(5, 15) = (5 x 15) / 5 = 15
This method efficiently calculates the LCM using the GCD, demonstrating the interconnectedness of these two concepts.
Why is Understanding LCM Important?
The concept of the least common multiple extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. Its applications are diverse and span various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management:
Imagine you have two tasks: one that repeats every 5 days and another that repeats every 15 days. To find when both tasks coincide, you need to find the LCM of 5 and 15. The LCM, 15, tells us that both tasks will coincide every 15 days. This principle is crucial in scheduling appointments, production cycles, and other time-dependent processes.
2. Fractions and Arithmetic Operations:
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is essential for finding a common denominator. This allows you to perform the addition or subtraction seamlessly.
3. Music Theory:
Musical intervals and harmonies are often based on the relationships between frequencies. The LCM helps determine when different musical notes or chords will coincide, producing specific harmonic effects.
4. Computer Science and Algorithms:
LCMs play a vital role in various algorithms and computations. They are used in tasks such as synchronization of processes, resource allocation, and efficient data management.
Exploring Further: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For prime factorization, you simply include all the prime factors of all the numbers and take the highest power of each. For the listing method, the process becomes more cumbersome as the number of numbers increases.
Example: Finding the LCM of 5, 15, and 20
-
Prime Factorization:
- 5 = 5
- 15 = 3 x 5
- 20 = 2² x 5
-
Highest Powers:
- 2² = 4
- 3¹ = 3
- 5¹ = 5
-
Multiply:
- LCM(5, 15, 20) = 2² x 3 x 5 = 60
Therefore, the LCM of 5, 15, and 20 is 60.
Conclusion: The Power of Simple Concepts
While determining the LCM of 5 and 15 might seem trivial, understanding the various methods and their underlying principles highlights the broader importance of LCMs in numerous applications. Mastering this concept provides a strong foundation in mathematics and enhances your ability to tackle more complex problems in diverse fields. Whether you're managing schedules, working with fractions, or exploring the nuances of music theory, the LCM remains a powerful tool in your mathematical arsenal. The seemingly simple calculation underscores the elegance and power of fundamental mathematical concepts. By grasping the essence of LCMs, you unlock a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships and their real-world implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write 70 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 2 And 8
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Name Of Mg No3 2
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is True About Hiv
Mar 28, 2025
-
In Which Situation Is The Distance Traveled Proportional To Time
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Whats The Lcm Of 5 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
