What's The Lcm Of 12 And 18
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
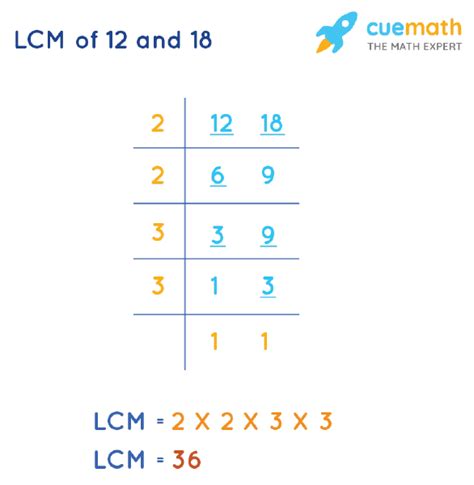
Table of Contents
What's the LCM of 12 and 18? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, but understanding the underlying concepts and various methods for calculating it provides a strong foundation in number theory and has practical applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "What's the LCM of 12 and 18?" but will also explore the concept of LCM in detail, providing multiple methods for calculation, real-world examples, and a deeper understanding of its significance in mathematics.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors. This concept is crucial in various mathematical operations and problem-solving scenarios.
Key Concepts Related to LCM
- Factors: Numbers that divide another number completely without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
- Multiples: Numbers obtained by multiplying a given number by integers (1, 2, 3, and so on). For example, multiples of 12 are 12, 24, 36, 48, and so on.
- Divisibility: The ability of one number to divide another without leaving a remainder.
- Prime Factorization: Expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11).
Calculating the LCM of 12 and 18: Multiple Methods
There are several ways to calculate the LCM of 12 and 18. Let's explore the most common methods:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. List the multiples of each number until you find the smallest multiple common to both.
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, ...
- Multiples of 18: 18, 36, 54, 72, 90, ...
The smallest common multiple is 36. Therefore, the LCM of 12 and 18 is 36.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 x 3²
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 3: 3² = 9
LCM(12, 18) = 2² x 3² = 4 x 9 = 36
Method 3: Using the Formula
The LCM can be calculated using the following formula, which relates the LCM and the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of two numbers:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where:
- a and b are the two numbers.
- GCD(a, b) is the greatest common divisor of a and b.
First, we need to find the GCD of 12 and 18. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide the larger number (18) by the smaller number (12): 18 ÷ 12 = 1 with a remainder of 6.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (12) and the smaller number with the remainder (6): 12 ÷ 6 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
- The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 6.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(12, 18) = (12 x 18) / 6 = 216 / 6 = 36
Real-World Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
- Scheduling: Imagine two buses depart from a station at different intervals. The LCM helps determine when both buses will depart simultaneously again.
- Fraction Operations: Finding the LCM of the denominators is essential when adding or subtracting fractions.
- Project Management: Determining the timing of tasks with different completion cycles.
- Engineering: Synchronization of mechanical systems with different cyclical operations.
- Music: Determining when two musical notes with different frequencies will harmonize.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods discussed above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method is particularly useful in this case. For example, to find the LCM of 12, 18, and 24:
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 x 3²
- Prime factorization of 24: 2³ x 3
LCM(12, 18, 24) = 2³ x 3² = 8 x 9 = 72
The Importance of Understanding LCM in Mathematics
Understanding LCM is crucial for building a solid foundation in mathematics. It connects to other fundamental concepts like GCD, prime factorization, and divisibility, all essential for advanced mathematical studies. Proficiency in calculating LCM and understanding its applications allows for efficient problem-solving in various mathematical contexts.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Mathematical Proficiency
This comprehensive guide has explored the concept of LCM, demonstrating multiple methods for calculating it, illustrating its real-world applications, and highlighting its importance in mathematics. Whether you use the listing method, prime factorization, or the formula, understanding the underlying principles will enable you to confidently tackle LCM problems and appreciate its significance in various fields. Remember, the LCM of 12 and 18 is 36, and mastering this seemingly simple concept unlocks a deeper understanding of number theory and its practical relevance. The ability to efficiently and accurately compute LCM is a valuable skill applicable across many areas of study and problem-solving. Therefore, solidifying your understanding of LCM is a worthwhile investment in your mathematical proficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Reaction Of Ammonium Nitrate With Water
Mar 18, 2025
-
Through Which Medium Will Sound Travel Most Rapidly
Mar 18, 2025
-
A Random Variable Is Said To Be Continuous If It
Mar 18, 2025
-
Is Sodium Chloride A Covalent Compound
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 9 12 And 15
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What's The Lcm Of 12 And 18 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
