What Ocean Is Between North America And Europe
Juapaving
Mar 30, 2025 · 6 min read
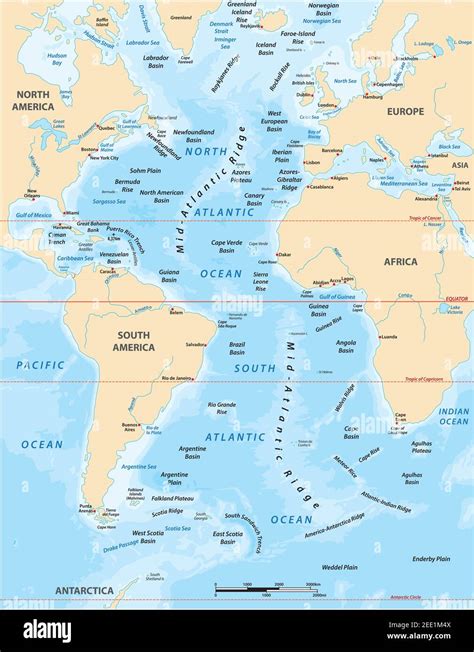
Table of Contents
What Ocean is Between North America and Europe? A Deep Dive into the Atlantic
The simple answer is the Atlantic Ocean. However, understanding the vastness and complexity of this body of water requires a deeper dive than just a one-word response. This article will explore the Atlantic Ocean, its geographical boundaries, its unique characteristics, and its significance in shaping the world we live in today.
The Atlantic Ocean: A Geographical Overview
The Atlantic Ocean, the second-largest of the world's five oceans, stretches from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, separating the continents of North America and South America from Europe and Africa. It's a crucial waterway, influencing global climate patterns, supporting diverse marine ecosystems, and playing a pivotal role in global trade and transportation.
Defining the Boundaries: More Than Just a Line on a Map
Pinpointing the exact boundaries of the Atlantic can be tricky. While generally understood as the expanse of water between the continents mentioned above, the lines are less clear-cut at its northern and southern extents.
-
Northern Boundary: The Arctic Ocean forms its northern boundary, although the exact demarcation point is a subject of ongoing geographical debate. Many sources use the line connecting Greenland, Iceland, and the northern coast of Norway as the dividing line.
-
Southern Boundary: The situation is similarly complex at the southern end. Traditionally, the boundary with the Indian Ocean was considered the 20° East meridian. However, the more modern view, accepted by many oceanographers, defines the southern boundary as the convergence zone with the Southern Ocean – a dynamic region where the colder waters of the Antarctic meet the warmer waters of the Atlantic. This boundary is not a fixed line but rather a fluctuating zone depending on ocean currents and seasonal variations.
-
Eastern and Western Boundaries: The eastern and western boundaries are more easily defined, largely following the coastlines of Europe, Africa, North America, and South America. However, even these can have nuances, particularly in considering islands and archipelagos within the Atlantic basin.
The Atlantic's Impact: Climate, Ecosystems, and Human Activity
The Atlantic Ocean isn't just a vast body of water; it's a powerful force shaping our planet and our lives.
Climate Regulation: A Global Thermostat
The Atlantic plays a crucial role in global climate regulation. Ocean currents, such as the Gulf Stream, act like massive conveyor belts, transporting warm water from the tropics towards the poles and cold water from the poles towards the tropics. This movement of water significantly influences temperature and weather patterns around the world. The Gulf Stream, for example, moderates the climate of Western Europe, making it significantly warmer than other regions at similar latitudes.
Changes in the Atlantic's currents can have significant global impacts, potentially leading to alterations in precipitation patterns, sea levels, and overall climate stability. Understanding these processes is crucial for predicting and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Biodiversity Hotspot: A Rich Tapestry of Life
The Atlantic Ocean boasts incredible biodiversity, harboring a wide array of marine life, from microscopic plankton to massive whales. Different regions of the Atlantic support unique ecosystems, reflecting variations in water temperature, salinity, and depth.
-
Coral Reefs: While not as extensive as in the Pacific, coral reefs exist in the warmer waters of the Atlantic, providing crucial habitat for a multitude of species.
-
Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents: These unique ecosystems, found along mid-ocean ridges, support life forms that thrive in the absence of sunlight, relying on chemosynthesis instead of photosynthesis.
-
Coastal Habitats: Coastal regions, including estuaries, mangroves, and salt marshes, are vital breeding grounds and nurseries for many commercially important fish species.
Threats to this biodiversity include overfishing, pollution, and climate change, all of which necessitate careful management and conservation efforts.
Human Impact: Trade, Transportation, and Resources
The Atlantic Ocean has been a vital artery for human activity for centuries. It has facilitated exploration, trade, and communication, shaping the course of history and connecting different cultures.
-
Trade Routes: The Atlantic has been a major conduit for global trade since the Age of Exploration. Transatlantic trade routes carry billions of dollars worth of goods each year, connecting continents and supporting global economies.
-
Transportation: The Atlantic Ocean supports extensive shipping networks, facilitating the transport of goods, people, and resources across continents. Major ports along the Atlantic coastlines serve as crucial hubs in the global transportation system.
-
Resource Extraction: The Atlantic is a source of various natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. Offshore drilling and mining operations extract these resources, but these activities must be carefully managed to minimize environmental impact.
Exploring the Atlantic's Diverse Regions
The Atlantic Ocean is not a uniform body of water; it comprises distinct regions with their own characteristics.
The North Atlantic: A Realm of Contrasts
The North Atlantic encompasses a vast area, ranging from the relatively warm waters near the equator to the icy conditions closer to the Arctic. The Gulf Stream dominates this region, significantly influencing climate and ecosystems. This area is also marked by significant fishing grounds and historically important shipping lanes.
The South Atlantic: A Realm of Subtropical Currents
The South Atlantic showcases the powerful Brazil and Benguela currents, influencing temperature and salinity patterns. This region is known for its upwelling zones, areas where nutrient-rich waters rise from the depths, fueling high biological productivity.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge: A Tectonic Marvel
Running through the entire length of the Atlantic Ocean is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a massive undersea mountain range formed by tectonic plate divergence. This ridge is volcanically active, and hydrothermal vents along its axis support unique ecosystems. The ridge significantly shapes the ocean's bathymetry and circulation patterns.
The Atlantic's Future: Challenges and Conservation
The Atlantic Ocean faces significant challenges in the 21st century. Climate change, pollution, and overfishing are major threats to its ecosystems and the services it provides.
Climate Change: A Looming Threat
Climate change is altering ocean temperatures, sea levels, and the frequency and intensity of storms. These changes have profound implications for marine ecosystems, coastal communities, and global climate patterns. Rising sea levels pose a direct threat to coastal infrastructure and habitats.
Pollution: A Persistent Problem
Pollution from various sources, including industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste, contaminates the Atlantic Ocean. These pollutants harm marine life, disrupt ecosystems, and potentially impact human health through seafood consumption.
Overfishing: Depleting Resources
Overfishing has depleted many fish stocks in the Atlantic, impacting marine biodiversity and livelihoods that depend on fishing. Sustainable fishing practices are urgently needed to ensure the long-term health of fish populations and the industry.
Conservation Efforts: A Call to Action
Protecting the Atlantic Ocean requires concerted global efforts. International agreements, marine protected areas, and sustainable fishing practices are crucial for safeguarding its biodiversity and ensuring its continued contribution to human well-being. Addressing climate change is paramount to mitigate its far-reaching consequences on the Atlantic Ocean.
Conclusion: The Atlantic's Enduring Importance
The Atlantic Ocean is far more than just a geographical feature; it's a dynamic and complex ecosystem that plays a vital role in shaping our planet and our lives. From regulating global climate to supporting diverse marine life and facilitating international trade, the Atlantic's importance is undeniable. Protecting this valuable resource for future generations requires a collaborative and sustainable approach, addressing the challenges it faces while ensuring its enduring contribution to the well-being of humanity and the planet. Understanding the intricacies of this vast ocean is crucial for making informed decisions about its future and our collective responsibility to safeguard its health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Tungsten A Metal Or Nonmetal
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Many Seconds Is 24 Hours
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of The Collecting Duct
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Rectangle Is A Square Always Sometimes Never
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Are The First 5 Multiples Of 2
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Ocean Is Between North America And Europe . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
