What Mirror Provides The Widest Field Of View
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
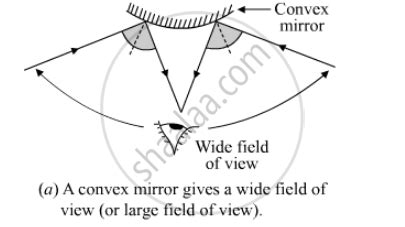
Table of Contents
What Mirror Provides the Widest Field of View? A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right mirror for a specific application hinges on several factors, including the desired field of view (FOV). A wider field of view allows you to see more of your surroundings, which is crucial in various applications, from security surveillance to automotive side mirrors. But what type of mirror provides the widest field of view? It's not a simple answer, as the optimal choice depends on the mirror's shape, size, and placement. This comprehensive guide explores the different types of mirrors and how their shape impacts their FOV, ultimately guiding you towards understanding which mirror offers the broadest perspective.
Understanding Field of View (FOV)
Before delving into mirror types, it's essential to grasp the concept of field of view. FOV is the extent of the observable world that is visible to an observer at a particular point and time. In the context of mirrors, it's the area a mirror reflects that can be seen by the observer. A wider FOV means a larger area is reflected and visible. The FOV is typically measured in degrees, representing the angular extent of the visible area. A larger angle indicates a wider field of view.
Types of Mirrors and Their FOV
Mirrors are broadly classified based on their shape:
1. Plane Mirrors
Plane mirrors have a flat reflecting surface. They produce a virtual image (an image that appears to be behind the mirror) that is the same size as the object and is laterally inverted (left and right are reversed). While plane mirrors are simple and common, their field of view is limited by their size and placement. The wider the mirror, the wider the field of view, but this is a linear relationship – doubling the size doesn't double the FOV. Plane mirrors offer a relatively narrow FOV compared to other types.
2. Convex Mirrors
Convex mirrors, also known as diverging mirrors, have a curved reflecting surface that bulges outwards. This curvature causes the reflected rays to diverge, resulting in a smaller, virtual, upright, and reduced image. The key advantage of convex mirrors is their wide field of view. Because the reflected rays spread out, a convex mirror can reflect a much larger area than a plane mirror of the same size. This makes them ideal for applications requiring a broad overview, such as:
- Security surveillance: Monitoring large areas like parking lots or hallways.
- Automotive side mirrors: Providing a wider view of the surrounding traffic.
- Shop security: Giving a comprehensive view of the store interior.
The wider the curvature of a convex mirror, the wider its field of view, but this also reduces image size and clarity. There's a trade-off between FOV and image quality.
3. Concave Mirrors
Concave mirrors, also known as converging mirrors, have a curved reflecting surface that curves inwards. Their reflective surface curves inward towards the observer. They can produce both real and virtual images, depending on the object's position relative to the focal point. Concave mirrors typically have a narrower field of view compared to convex mirrors. While they can magnify images, this magnification comes at the cost of a reduced FOV. Concave mirrors are often used in applications where a magnified image is needed, such as:
- Telescopes: Collecting and focusing light from distant objects.
- Microscopes: Magnifying small objects for observation.
- Headlights: Reflecting light to create a focused beam.
Factors Affecting Field of View Beyond Mirror Shape
The field of view isn't solely determined by the mirror's shape; other factors play significant roles:
1. Mirror Size
Larger mirrors naturally offer a wider field of view. A bigger mirror surface captures more reflected light, thereby increasing the visible area. This is true for all types of mirrors – plane, convex, and concave. However, increasing the size of the mirror might become impractical or costly depending on the application.
2. Mirror Placement
The position of the mirror significantly influences its field of view. For example, a convex mirror placed at a higher vantage point will have a wider view compared to the same mirror placed lower. Optimal placement is crucial for maximizing the field of view and ensuring that the desired area is effectively covered.
3. Observer's Position
The viewer's position relative to the mirror also affects the field of view. Moving closer to the mirror generally reduces the FOV, whereas moving further away increases it, although diminishing returns set in beyond a certain point.
4. Fish-Eye Lenses (in conjunction with mirrors)
While not strictly a mirror type, fish-eye lenses can be used in combination with mirrors to dramatically increase the field of view. These lenses have a very wide angle of view and can be combined with either a plane or a convex mirror to achieve an extremely broad perspective. However, significant image distortion will result.
Which Mirror Provides the Widest Field of View?
Taking everything into account, convex mirrors generally provide the widest field of view compared to plane and concave mirrors of similar size. Their outward curvature allows them to reflect light from a much larger area, offering a panoramic perspective. However, it's crucial to remember that this wider field of view comes at the cost of image distortion and reduction in image size.
Optimizing Field of View in Different Applications
The ideal mirror and its optimal field of view depend heavily on the application. Here's a breakdown for several common scenarios:
Security Surveillance
For large areas, multiple strategically placed convex mirrors are often used to provide overlapping coverage, ensuring no blind spots. The wider FOV of these mirrors makes them highly suitable for monitoring expansive environments.
Automotive Side Mirrors
Modern cars increasingly use convex mirrors on their passenger-side doors. These mirrors provide a much wider field of view, improving the driver's awareness of the surrounding environment. However, the image is smaller and more distorted, hence the common warning "Objects in mirror are closer than they appear."
Bathroom Mirrors
Plane mirrors are typically used in bathrooms, prioritizing image clarity and accuracy over a wide field of view. The focus is on providing a faithful reflection for personal grooming, not a panoramic view of the entire bathroom.
Telescopes
Telescopes utilize concave mirrors to concentrate light from distant celestial objects. While the FOV is relatively narrow, this allows for focused observation and magnification crucial for astronomical study.
Conclusion
The quest for the widest field of view often involves balancing image clarity and distortion with the desired breadth of perspective. While convex mirrors generally win when it comes to simply maximizing what's visible, the best choice ultimately depends on the specific application. Understanding the nuances of different mirror types and their limitations allows for informed decisions when selecting the ideal mirror for any given need. Considering the factors beyond just the mirror’s shape—size, placement, observer's position, and even the addition of lenses—is critical for achieving optimal results. The right mirror, correctly positioned and scaled, can unlock significantly improved visibility, thereby enhancing efficiency, safety, and functionality across numerous sectors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Relative Abundance In Chemistry
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Ribose And Deoxyribose
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Can 27 Be Divided By
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration Of Ti
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Nuclear Membrane Reappears In Mitosis During
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Mirror Provides The Widest Field Of View . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
