What Is The Difference Between Ribose And Deoxyribose
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
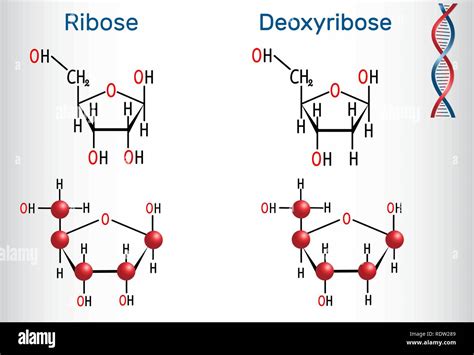
Table of Contents
What's the Difference Between Ribose and Deoxyribose? A Deep Dive into Sugar's Role in Life
Ribose and deoxyribose. These two names might sound similar, and they are indeed closely related, but their subtle differences have monumental consequences for life as we know it. Understanding these differences is crucial to grasping the fundamental building blocks of life – DNA and RNA. This article will delve deep into the structural, functional, and chemical distinctions between these two pentose sugars, examining their roles in biological processes and exploring the implications of their unique properties.
The Structural Differences: A Single Oxygen Atom Makes All the Difference
Both ribose and deoxyribose are pentose sugars, meaning they are five-carbon sugars. Their chemical formulas are deceptively similar: ribose is C₅H₁₀O₅, and deoxyribose is C₅H₁₀O₄. This seemingly small difference – one less oxygen atom – is responsible for the significant variations in their properties and functions.
Ribose: The Sugar of RNA
Ribose is a pentose sugar with a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to each of its carbon atoms (C1' to C5'). This hydroxyl group at the 2' position is what distinguishes it from deoxyribose. The presence of this hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon makes ribose a more reactive molecule than deoxyribose.
- Structure: The hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon plays a critical role in its reactivity. It can participate in hydrogen bonding, influencing the stability and three-dimensional structure of RNA molecules.
Deoxyribose: The Sugar of DNA
Deoxyribose, as the name suggests, is a deoxyribose sugar, lacking the hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon. Instead of a hydroxyl group, it has a hydrogen atom (-H). This seemingly minor structural change has profound implications for the stability and function of DNA.
- Structure: The absence of the hydroxyl group at the 2' position in deoxyribose makes it less reactive than ribose. This reduced reactivity is essential for the stability of the DNA double helix, a structure crucial for maintaining the integrity of genetic information.
Functional Differences: RNA's Versatility vs. DNA's Stability
The structural differences between ribose and deoxyribose lead to significant differences in the functions of RNA and DNA. These differences arise from the inherent chemical properties of each sugar.
Ribose and RNA: The Versatile Workhorse
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, plays multiple roles in the cell, including:
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Carries amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): A structural and functional component of ribosomes.
- Regulatory RNA: Involved in gene regulation.
The presence of the hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon in ribose makes RNA more susceptible to hydrolysis, meaning it's less stable than DNA. This inherent instability is, paradoxically, beneficial. The shorter lifespan of RNA allows for more rapid turnover and regulation of gene expression. The increased reactivity also allows for RNA's involvement in various catalytic processes (ribozymes). The flexibility imparted by the 2' hydroxyl group allows RNA to adopt various secondary and tertiary structures critical to its diverse functional roles.
Deoxyribose and DNA: The Stable Guardian of Genetic Information
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, serves as the primary repository of genetic information. It carries the hereditary blueprint for all living organisms. The absence of the hydroxyl group at the 2' position in deoxyribose makes DNA a more stable molecule. This stability is crucial for the reliable storage and transmission of genetic information across generations.
- Stability: The increased stability of DNA arises from the lack of the 2' hydroxyl group, preventing the susceptibility to alkaline hydrolysis prevalent in RNA.
- Double Helix Structure: The deoxyribose sugar's structure contributes directly to the formation of the stable double helix structure of DNA. The hydrogen bonding between base pairs, combined with the backbone structure provided by the deoxyribose-phosphate units, creates a robust and stable molecule capable of storing vast amounts of genetic information.
Chemical Differences: Reactivity and Hydrolysis
The key chemical difference lies in the reactivity of the 2' hydroxyl group in ribose. This group makes ribose more prone to chemical reactions, particularly hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is the breakdown of a molecule by the addition of water. RNA, being constructed with ribose, is more vulnerable to hydrolysis, which can break the phosphodiester bonds linking the nucleotides. This vulnerability makes RNA molecules generally less stable than DNA molecules.
Implications of Hydrolysis
The susceptibility of RNA to hydrolysis explains its typically shorter lifespan compared to DNA. This is advantageous for RNA's roles in gene regulation and protein synthesis, where rapid turnover is often required. The instability of RNA also contributes to its diverse functional roles. The ability of RNA to fold into complex three-dimensional structures is partly attributed to its increased reactivity.
DNA's Enhanced Stability
In contrast, the absence of the 2' hydroxyl group in deoxyribose leads to increased resistance to hydrolysis. This is crucial for DNA's function as the long-term repository of genetic information. The stability of the DNA double helix ensures the faithful replication and transmission of genetic material across generations. Any error in replication or damage to DNA can have severe consequences. The absence of this hydroxyl group provides a crucial element of structural integrity for this critical molecule.
Beyond Structure and Function: Evolutionary Significance
The differences between ribose and deoxyribose are not just biochemical curiosities; they hold significant evolutionary implications. It is believed that RNA, with its greater reactivity and versatility, predates DNA in the early stages of life. The RNA world hypothesis suggests that RNA molecules played both the roles of information storage and catalysis before the evolution of DNA. The increased stability of DNA may have provided an evolutionary advantage in protecting and reliably transmitting genetic information over longer periods. The transition from an RNA-centric world to a DNA-centric world is a pivotal moment in the history of life on Earth.
Conclusion: Two Sugars, Two Worlds
Ribose and deoxyribose, despite their close chemical similarity, exhibit significant structural and functional differences. These differences underlie the distinct roles of RNA and DNA in biological systems. Ribose's hydroxyl group at the 2' position leads to greater reactivity and instability in RNA, making it ideal for its various regulatory and catalytic roles. Deoxyribose's lack of this hydroxyl group makes DNA more stable and suitable for long-term storage of genetic information. Understanding these differences is fundamental to comprehending the molecular basis of life and the fascinating interplay between these two essential sugars. The story of ribose and deoxyribose is a compelling testament to the elegance and efficiency of biological systems, highlighting how seemingly small chemical variations can have enormous implications for the development and maintenance of life. The continuing exploration of these sugars and their roles in diverse organisms promises further insights into the intricacies of molecular biology and evolution.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Find The Missing Values In The Ratio Table
Mar 15, 2025
-
Organelles That Are Only Found In Plant Cells
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Legs Does A Bird Have
Mar 15, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 9 12 And 15
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Step Down Transformer
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Difference Between Ribose And Deoxyribose . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
