What Is The Total Degree Of Angles For All Squares
Juapaving
Mar 05, 2025 · 5 min read
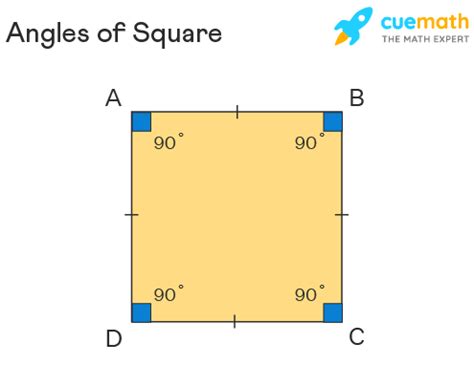
Table of Contents
What is the Total Degree of Angles for All Squares? A Deep Dive into Geometry
Understanding the fundamental properties of shapes is crucial in various fields, from architecture and engineering to computer graphics and game development. One of the most basic yet essential shapes is the square. This article explores the total degree of angles in squares, delving deeper into the underlying geometric principles and exploring related concepts. We'll tackle this seemingly simple question with rigorous detail, ensuring a comprehensive understanding.
Defining a Square: A Foundation in Geometry
Before diving into the total angle measurement, let's establish a clear definition of a square. A square is a two-dimensional geometric shape defined by the following characteristics:
- Four sides: It possesses four straight sides of equal length.
- Four right angles: Each of its four interior angles measures exactly 90 degrees.
- Parallel sides: Opposite sides are parallel to each other.
- Equal diagonals: The diagonals of a square are equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
These defining properties are interconnected and interdependent. If a shape satisfies all four criteria, it unequivocally qualifies as a square. Any deviation from these characteristics results in a different quadrilateral, such as a rectangle, rhombus, or parallelogram.
Calculating the Total Degrees of Angles in a Single Square
The total sum of interior angles in any quadrilateral is always 360 degrees. This is a fundamental theorem in geometry. Therefore, the total degrees of angles for a single square is directly derived from this theorem:
90° + 90° + 90° + 90° = 360°
Each of the four right angles in a square contributes 90 degrees to the total, resulting in a sum of 360 degrees. This is true regardless of the size of the square; whether it's a tiny square or a massive one, the sum of its interior angles will always remain 360 degrees.
Exploring the Concept of Angles: Interior vs. Exterior
It's crucial to distinguish between interior and exterior angles when discussing the angles of any polygon, including squares.
-
Interior angles: These are the angles inside the shape, formed by the intersection of two adjacent sides. In a square, these are all 90-degree angles.
-
Exterior angles: These are the angles formed by extending one side of the polygon and the adjacent side. For a square, each exterior angle measures 90 degrees (supplementary to the interior angles). The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360 degrees.
This difference is vital, especially when working with more complex polygons where interior and exterior angles differ significantly.
Beyond a Single Square: Extending the Concept
The question posed initially focuses on the total degree of angles "for all squares". This requires a shift in perspective. We're no longer dealing with a single square but with the collective angle sum of numerous squares. To properly address this, let's clarify the possible interpretations:
Interpretation 1: The total sum of angles in a specific number of squares:
If we're considering 'all' to mean a specific, finite number of squares (e.g., 5 squares), the calculation is straightforward:
- Total angles: 5 squares * 4 angles/square = 20 angles
- Total degrees: 20 angles * 90°/angle = 1800°
This demonstrates the scalability of the concept. The total degrees are simply the number of squares multiplied by 360 degrees (the angle sum of a single square).
Interpretation 2: The theoretical sum of angles for an infinite number of squares:
This interpretation shifts the discussion into the realm of infinity. Mathematically, the total sum of angles for an infinite number of squares would be infinite. This underscores the importance of clear problem definition. Unless a finite number of squares is specified, the question becomes ill-defined.
Real-World Applications and Relevance
Understanding the angle properties of squares has widespread practical applications:
-
Construction and Architecture: Squares are fundamental building blocks in architectural design. Understanding their angle properties is crucial for ensuring structural stability and accurate construction. From building foundations to window frames, the precision of 90-degree angles is paramount.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: Squares are frequently used in 2D and 3D modeling. Accurate calculation of angles is essential for creating realistic and functional digital environments. Game developers, for instance, rely on precise geometry to render accurate collisions and interactions within their virtual worlds.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Precise angle measurements are critical in manufacturing and engineering. From machining parts to designing mechanical systems, the accurate representation of squares and their angles is crucial for functionality and performance.
Expanding to Other Quadrilaterals
While our focus has been on squares, the total degree of angles within other quadrilaterals also follows a consistent rule:
-
Rectangles: Similar to squares, rectangles also have a total interior angle sum of 360 degrees. However, they only possess four right angles if they are also squares.
-
Parallelograms: Parallelograms, which have opposite sides parallel, also have a total interior angle sum of 360 degrees. The angles are not necessarily right angles, but opposite angles are equal.
-
Rhombuses: Rhombuses, characterized by four equal sides, also maintain a total interior angle sum of 360 degrees. Their angles are not necessarily right angles, but opposite angles are equal.
-
Trapezoids: Trapezoids, having at least one pair of parallel sides, also have a total interior angle sum of 360 degrees.
Beyond Quadrilaterals: The Polygon Angle Sum Theorem
The concept extends further to polygons with more than four sides. The polygon angle sum theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of an n-sided polygon is given by the formula:
(n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' is the number of sides. This formula encompasses squares (n=4) as a special case, reaffirming the 360° total. For pentagons (n=5), the total is 540°, for hexagons (n=6) it's 720°, and so on.
Conclusion: The Significance of Geometric Fundamentals
The seemingly simple question regarding the total degrees of angles in squares unravels into a broader exploration of geometry and its applications. Understanding the fundamental properties of squares, including their angle relationships, provides a robust foundation for tackling more complex geometric problems. The principles discussed here are relevant across numerous fields, highlighting the enduring significance of geometric knowledge in diverse disciplines. From the precision required in construction to the complexities of computer graphics, the angle sum of squares and polygons remains a cornerstone concept. The clarity and precision involved in geometric principles underscore their importance as essential tools for problem-solving and innovation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 2 A Composite Or Prime Number
Mar 06, 2025
-
Type Is A Grouping Based On Shared Characteristics
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles In A Hexagon
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is Water A Renewable Or Nonrenewable Resource
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Are The Multiples Of 11
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Total Degree Of Angles For All Squares . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
