What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles In A Hexagon
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
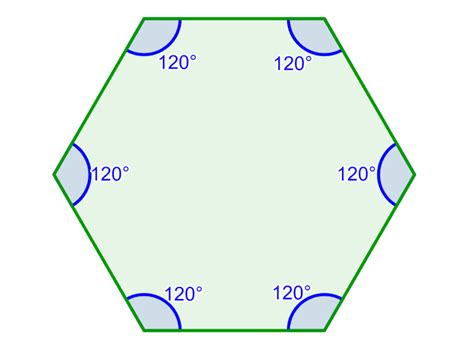
Table of Contents
What is the Sum of Interior Angles in a Hexagon? A Comprehensive Guide
The question, "What is the sum of interior angles in a hexagon?" might seem straightforward, but it opens the door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, particularly polygon properties. This comprehensive guide will not only answer this question definitively but also delve into the underlying principles, providing you with a robust understanding of interior angles and their calculation for polygons in general. We will explore different approaches, from the formulaic to the visual, ensuring you grasp the concept thoroughly.
Understanding Polygons and Hexagons
Before diving into the sum of interior angles, let's establish a firm foundation. A polygon is any closed two-dimensional shape formed by connecting straight line segments. Polygons are classified by the number of sides they have:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides (squares, rectangles, rhombuses, etc., are all quadrilaterals)
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon (or Septagon): 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- Nonagon: 9 sides
- Decagon: 10 sides
- And so on...
A hexagon, therefore, is a polygon with six sides and six angles. Hexagons appear frequently in nature and human-made structures, from the honeycomb of bees to the nuts and bolts that hold things together. Understanding their angle properties is crucial in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and design.
Calculating the Sum of Interior Angles: The Formulaic Approach
The most efficient way to determine the sum of interior angles in any polygon, including a hexagon, is using a mathematical formula. This formula relies on the number of sides (n) of the polygon:
(n - 2) x 180°
Where:
- n represents the number of sides of the polygon.
For a hexagon, n = 6. Substituting this into the formula, we get:
(6 - 2) x 180° = 4 x 180° = 720°
Therefore, the sum of the interior angles in a hexagon is 720°. This formula holds true for all polygons, regardless of whether they are regular (all sides and angles equal) or irregular (sides and angles of varying lengths and measures).
Visualizing the Sum: Triangulation Method
While the formula provides a quick and accurate answer, visualizing the process helps solidify understanding. One effective visualization technique is triangulation. This method involves dividing the polygon into triangles. The sum of the angles in any triangle is always 180°.
Imagine dividing a hexagon into triangles. You can do this by drawing lines from a single vertex to all other non-adjacent vertices. For a hexagon, you can create four triangles within the hexagon. Since each triangle has an angle sum of 180°, the total sum of angles in the hexagon is 4 x 180° = 720°.
This triangulation method elegantly demonstrates why the formula (n - 2) x 180° works. The (n - 2) part represents the number of triangles formed within the polygon, and multiplying by 180° accounts for the angle sum within each triangle.
Regular vs. Irregular Hexagons: A Closer Look
The formula (n - 2) x 180° applies to both regular and irregular hexagons. A regular hexagon has all sides of equal length and all angles of equal measure. An irregular hexagon, on the other hand, has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures.
While the sum of interior angles remains 720° for both types, the measure of each individual angle differs.
- Regular Hexagon: Each interior angle measures 720° / 6 = 120°.
- Irregular Hexagon: The individual angles will vary, but their sum will always be 720°.
This distinction highlights that the formula provides the total sum of interior angles, not the measure of each individual angle. To find the individual angle measures in a regular hexagon, simply divide the total sum by the number of angles (which is equal to the number of sides).
Applications of Hexagon Angle Properties
The understanding of hexagon angle properties extends far beyond theoretical geometry. It finds practical applications in various fields:
-
Architecture and Engineering: Hexagonal structures are often used in building designs due to their strength and stability. Understanding the angle properties is crucial for accurate structural calculations and ensuring the stability of the structure.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Development: Hexagonal grids are often used in game development and computer graphics to create realistic and efficient representations of terrain or other elements. Understanding the angles helps in positioning objects and calculating distances within the grid.
-
Nature and Biology: Hexagonal shapes appear frequently in nature, notably in honeycombs built by bees. The hexagonal structure maximizes space efficiency and minimizes the amount of wax needed to build the honeycomb.
-
Mathematics and Geometry: Hexagons serve as a fundamental building block in various geometric proofs and theorems. Their angle properties form the basis for more complex geometric concepts.
Extending the Concept: Polygons with More Sides
The principles discussed for hexagons can be extended to polygons with any number of sides. The formula (n - 2) x 180° remains consistent. Let's explore a few examples:
- Octagon (8 sides): (8 - 2) x 180° = 1080°
- Decagon (10 sides): (10 - 2) x 180° = 1440°
- Dodecagon (12 sides): (12 - 2) x 180° = 1800°
By consistently applying the formula, you can calculate the sum of interior angles for any polygon. Remember that the formula works for both regular and irregular polygons.
Conclusion: Mastering Polygon Angle Properties
Understanding the sum of interior angles in a hexagon, and polygons in general, is a fundamental concept in geometry with far-reaching applications. This comprehensive guide has provided multiple approaches to solving this problem, emphasizing both the formulaic and visual methods. We've explored the distinction between regular and irregular hexagons, highlighting the significance of the formula in providing the total angle sum. Furthermore, we've extended the concept to encompass polygons with various numbers of sides, demonstrating the universality of the angle sum formula. By grasping these principles, you've significantly strengthened your understanding of geometry and its practical relevance in various fields. Remember to practice applying the formula and visualizing the triangulation method to fully internalize the concepts. This understanding will undoubtedly prove valuable in further mathematical explorations and real-world applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Hexagon
Mar 06, 2025
-
Shape With A Square Base And Four Triangular Faces
Mar 06, 2025
-
Words That Have Oi In It
Mar 06, 2025
-
Hydrogen Is Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloids
Mar 06, 2025
-
The Correct Sequence Of Events In Viral Multiplication Is
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles In A Hexagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
