What Are The Multiples Of 11
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
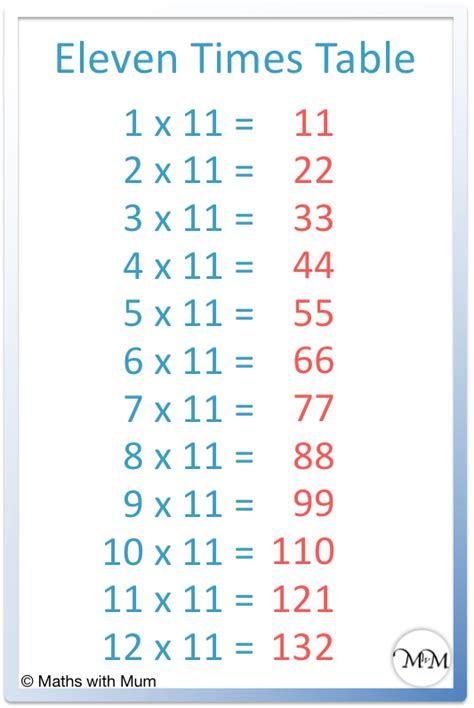
Table of Contents
What Are the Multiples of 11? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Understanding multiples is fundamental to grasping number theory, and the multiples of 11 offer a fascinating exploration into patterns and properties within the number system. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of 11's multiples, exploring their characteristics, identifying patterns, and demonstrating their applications in various mathematical contexts. We'll go beyond simple multiplication and uncover some intriguing secrets hidden within this seemingly straightforward sequence.
Defining Multiples: A Quick Refresher
Before we dive into the specifics of 11's multiples, let's establish a clear definition. A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any integer (whole number). In simpler terms, it's the result you get when you multiply that number by any whole number, including zero. For example, the multiples of 2 are 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on. Similarly, the multiples of 5 are 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, and so on. These are all obtained by multiplying 2 and 5, respectively, by different integers.
Generating the Multiples of 11
The multiples of 11 are generated by multiplying 11 by each consecutive integer. The sequence begins as follows:
0, 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 110, 121, 132, 143, 154, 165, 176, 187, 198, 209... and so on to infinity.
Notice the clear and consistent pattern: each subsequent number increases by 11. This consistent increment is a key characteristic of multiples of any number.
Identifying Patterns in Multiples of 11
While the simple addition of 11 is apparent, let's delve deeper into more subtle patterns within the multiples of 11.
The Alternating Sum/Difference Pattern:
One fascinating characteristic of multiples of 11 is revealed when we examine the alternating sum of their digits. Consider the number 143, a multiple of 11. If we alternate between adding and subtracting the digits (1 - 4 + 3), the result is 0. Let's try another: 99. 9 - 9 = 0. This pattern holds true for many, but not all, three-digit multiples of 11. For larger numbers, this alternating sum/difference approach will yield a multiple of 11. This property provides a quick way to check if a three-digit number might be a multiple of 11. However, it's crucial to remember this is a heuristic and not a definitive rule. There are exceptions, especially with larger numbers.
Divisibility Rule for 11: A More Robust Method
A more reliable method for determining if a number is divisible by 11 is the divisibility rule for 11 itself. This rule involves an alternating sum of digits, similar to the previous pattern, but with a more rigorous approach:
-
Start from the rightmost digit: Assign alternating positive and negative signs to the digits, starting with a positive sign for the rightmost digit.
-
Calculate the alternating sum: Add the digits with positive signs and subtract the digits with negative signs.
-
Check the result: If the result is divisible by 11 (including 0), then the original number is divisible by 11.
Example: Let's test the number 187.
- Digits: 1 8 7
- Alternating sum: 7 - 8 + 1 = 0
- Since 0 is divisible by 11, 187 is a multiple of 11.
Let's test a larger number: 528.
- Digits: 5 2 8
- Alternating sum: 8 - 2 + 5 = 11
- Since 11 is divisible by 11, 528 is a multiple of 11.
This rule provides a significantly more reliable method than the simpler alternating sum method discussed earlier, particularly for larger numbers.
Applications of Multiples of 11
The multiples of 11, while seemingly simple, find applications in several areas:
Mathematical Puzzles and Games
Many mathematical puzzles and brain teasers involve multiples of 11. Understanding their properties can provide shortcuts to solving these problems more efficiently. For instance, the divisibility rule can be extremely useful in quickly identifying solutions that are multiples of 11.
Computer Science and Programming
In computer science, particularly in algorithms involving modular arithmetic or number theory based computations, understanding multiples of 11 (and other numbers) is crucial. Operations involving divisibility checks and modular reductions frequently depend on these properties.
Number Patterns and Sequences
The study of multiples provides valuable insight into number patterns and sequences. The regular progression of multiples of 11, as well as the patterns within their digits, provides a rich area for exploration in number theory.
Financial Calculations
While less obvious, multiples of 11 can appear in scenarios where calculations are based on evenly divisible quantities or patterns of increments. For instance, certain financial models or pricing structures might utilize multiples of 11 (or other specific numbers) in some specific context.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
The study of multiples of 11 extends beyond simple identification and pattern recognition. We can explore more advanced concepts:
Prime Factorization and its Role
The prime factorization of a number is the expression of that number as a product of its prime factors. Understanding the prime factorization of multiples of 11 helps us grasp their divisibility properties. Since 11 itself is a prime number, any multiple of 11 will always have 11 as one of its prime factors. This is a fundamental concept in number theory.
Modular Arithmetic and Congruences
Modular arithmetic, which involves working with remainders after division, plays a significant role in number theory. Understanding congruences (relationships between numbers based on their remainders after division) helps us analyze the behavior of multiples of 11 within larger mathematical structures. For example, all multiples of 11 are congruent to 0 (mod 11).
Relationship to Other Number Sequences
Multiples of 11 can be related to other number sequences, such as Fibonacci sequences or arithmetic progressions. Exploring these connections opens up new avenues for investigation and the discovery of deeper patterns.
Conclusion: The Enduring Fascination of Multiples of 11
The multiples of 11, while seemingly a simple concept, provide a gateway into the fascinating world of number theory. Understanding their properties, identifying patterns, and applying these to various mathematical contexts demonstrates their importance beyond basic arithmetic. From divisibility rules to their application in more advanced areas such as modular arithmetic, the exploration of multiples of 11 offers a rewarding journey into the elegance and intricacy of the number system. The patterns and properties discovered here lay a foundation for further exploration into more complex numerical relationships and theories. Continued investigation and a curious mind will uncover even more fascinating aspects of these seemingly simple multiples.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Function Of The Fine Adjustment Knob On A Microscope
Mar 06, 2025
-
Can Sugar Dissolve In Cold Water
Mar 06, 2025
-
Provide At Least Three Reasons Why Friction Is Needed
Mar 06, 2025
-
Can Acids Or Bases Conduct Electricity
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Hexagon
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Multiples Of 11 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
