Shape With A Square Base And Four Triangular Faces
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
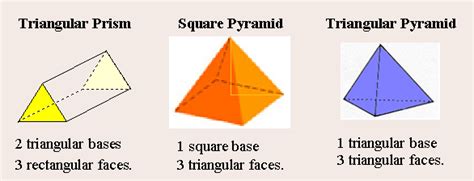
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into the World of Square Pyramids: Geometry, Properties, and Applications
A square pyramid, a three-dimensional geometric shape, captivatingly blends simplicity with intriguing mathematical properties. Defined by its square base and four triangular faces meeting at a single apex, this shape finds applications across various fields, from architecture and engineering to art and design. This comprehensive exploration delves into the square pyramid's geometrical aspects, explores its key properties, and unveils its diverse real-world applications.
Understanding the Geometry of Square Pyramids
At its core, a square pyramid is a polyhedron, specifically a type of pyramid. Let's break down its defining characteristics:
-
Base: The foundation of the square pyramid is a square. This square forms the bottom face of the structure. The sides of this square are crucial in determining many of the pyramid's properties.
-
Lateral Faces: Four triangular faces ascend from the sides of the square base, converging at a single point known as the apex. These triangular faces are isosceles triangles if the pyramid is a right square pyramid – meaning the apex lies directly above the center of the square base. If the apex isn't directly above the center, the lateral faces are simply scalene triangles, forming an oblique square pyramid.
-
Apex: The apex is the point where all four triangular faces meet. The height of the pyramid is the perpendicular distance from the apex to the center of the square base. This height is critical in calculating the volume and surface area.
-
Slant Height: The slant height of a square pyramid is the distance from the apex to the midpoint of any side of the square base. It's crucial in surface area calculations and understanding the inclination of the triangular faces.
-
Edges: A square pyramid has eight edges: four forming the square base and four connecting the base vertices to the apex.
-
Vertices: A square pyramid has five vertices: four at the corners of the square base and one at the apex.
Key Properties and Calculations
The beauty of the square pyramid lies in its elegant mathematical properties, enabling precise calculations of volume, surface area, and other geometric features. Let's explore some essential formulas:
1. Calculating the Volume
The volume of a right square pyramid is given by the formula:
V = (1/3) * b² * h
Where:
- V represents the volume.
- b represents the side length of the square base.
- h represents the height of the pyramid (perpendicular distance from the apex to the base).
For oblique square pyramids, the calculation becomes slightly more complex, often requiring more advanced geometrical techniques to determine the effective height.
2. Calculating the Surface Area
The surface area of a right square pyramid consists of the area of the square base and the four congruent triangular faces. The formula is:
SA = b² + 2bs
Where:
- SA represents the total surface area.
- b represents the side length of the square base.
- s represents the slant height of the pyramid.
Calculating the slant height (s) often requires using the Pythagorean theorem, relating the pyramid's height (h), half the base side length (b/2), and the slant height (s).
s = √(h² + (b/2)²)
3. Exploring the Relationship between Dimensions
The dimensions of a square pyramid—base length, height, and slant height—are intrinsically linked. Understanding these relationships is vital for solving various geometric problems and designing structures. The Pythagorean theorem plays a central role in establishing these connections.
Real-World Applications: Where You See Square Pyramids
The square pyramid, despite its seemingly simple structure, holds a significant place in various real-world applications:
1. Architecture and Engineering:
-
Ancient Pyramids: The most iconic examples are the Egyptian pyramids, monumental structures built as tombs for pharaohs. Their construction showcases impressive feats of engineering and mathematical understanding.
-
Modern Architecture: Square pyramids, or pyramidal shapes inspired by the form, appear in contemporary architecture, sometimes as roof designs, giving buildings a distinctive look.
-
Structural Support: The stability and strength of a square pyramid make it suitable for certain structural applications. The distribution of weight is efficiently handled, maximizing strength.
2. Art and Design:
-
Sculptures and Installations: Artists frequently use the square pyramid as a motif in their sculptures and installations, exploring its visual appeal and symbolic connotations.
-
Jewelry and Crafts: Miniature versions of square pyramids appear in jewelry design and other craft projects, offering a unique and geometric aesthetic.
-
Logo Design: The pyramid's form can often be found subtly integrated into logo designs, representing stability and ambition.
3. Packaging and Product Design:
- Packaging: Square pyramid-shaped containers can be used for various products, offering an aesthetically pleasing and sometimes functional design. This can lead to improved shelf appeal.
4. Games and Toys:
-
Board Games: Square pyramids can serve as game pieces or represent elements within a game's mechanics.
-
Building Blocks: The shape can be found as a component in some construction toys, aiding in the creation of various structures.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Variations and Advanced Concepts
The fundamental square pyramid can be further explored through various extensions and related geometrical concepts:
-
Truncated Square Pyramids: A truncated square pyramid is a square pyramid with its apex cut off by a plane parallel to its base. This results in a shape with two square bases and four trapezoidal faces.
-
Frustums: The truncated portion itself is known as a frustum. Understanding the properties of frustums is critical in various engineering calculations.
-
Regular vs. Irregular Pyramids: The discussions above primarily focused on regular square pyramids. Irregular pyramids exist with non-square bases or asymmetrical apex positions, altering volume and surface area calculations significantly. More advanced geometry techniques are necessary for their analysis.
-
Stellated Square Pyramids: Creating a stellated square pyramid involves extending the triangular faces beyond the apex, forming pointed extensions, leading to visually striking, complex shapes.
-
Tessellations: While square pyramids themselves don't tessellate (completely fill space without gaps or overlaps), they can be incorporated into more complex tessellations alongside other shapes.
Conclusion: The Enduring Appeal of the Square Pyramid
From ancient marvels to modern designs, the square pyramid's enduring appeal stems from its elegant simplicity and versatile applications. Its geometric properties, readily calculable using established formulas, make it a cornerstone shape in various fields. As we've explored, understanding its volume, surface area, and related dimensions is essential for practical applications in architecture, engineering, and design. Beyond its basic form, variations such as truncated pyramids and stellations open doors to even more complex geometric explorations and artistic expressions. The square pyramid, therefore, continues to fascinate and inspire, remaining a vital element in mathematics, art, and the built environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Percent Of 2 6
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 3 8
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is A Sound Wave A Transverse Wave
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Magnesium
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Common Factor Of 12 And 36
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Shape With A Square Base And Four Triangular Faces . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
