What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Hexagon
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
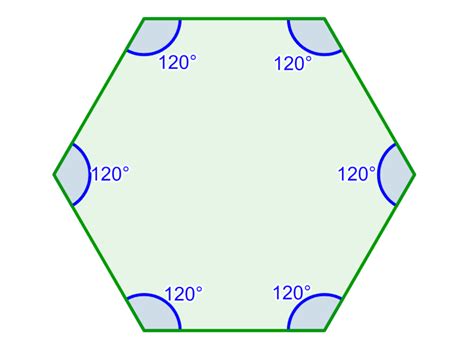
Table of Contents
What is the Sum of Interior Angles of a Hexagon? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the sum of interior angles of polygons, especially hexagons, is fundamental to geometry and has practical applications in various fields like architecture, engineering, and design. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept, providing different approaches to calculating the sum, exploring its relevance, and showcasing real-world examples. We'll also tackle some related concepts to give you a solid understanding of this geometrical principle.
Understanding Polygons and Hexagons
Before jumping into the sum of interior angles, let's define some key terms. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting three or more straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon. The points where the sides meet are called vertices.
A hexagon, specifically, is a polygon with six sides and six vertices. Hexagons can be regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not equal). Understanding this distinction is crucial because, while the formula for calculating the sum of interior angles remains the same, the measure of each individual angle varies between regular and irregular hexagons.
Calculating the Sum of Interior Angles of a Hexagon: The Formula Approach
The most efficient way to calculate the sum of interior angles of any polygon, including a hexagon, involves a straightforward formula. This formula relies on the number of sides (n) the polygon possesses. The formula is:
(n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' represents the number of sides.
For a hexagon, which has six sides (n = 6), the calculation is:
(6 - 2) * 180° = 4 * 180° = 720°
Therefore, the sum of the interior angles of any hexagon, regardless of whether it's regular or irregular, is 720°. This is a fundamental geometrical principle.
Visualizing the Sum: Triangulation Method
Another way to understand this sum is through triangulation. We can divide any polygon into triangles by drawing non-intersecting diagonals from one vertex to all other non-adjacent vertices. The sum of the angles in each triangle is always 180°.
Consider a hexagon. We can divide it into four triangles. Each triangle contributes 180° to the total sum of interior angles. Therefore:
4 triangles * 180°/triangle = 720°
This method provides a visual representation of why the (n-2) * 180° formula works. It demonstrates the direct relationship between the number of triangles formed and the total sum of interior angles.
Regular vs. Irregular Hexagons: Individual Angle Measures
While the sum of interior angles remains 720° for all hexagons, the measure of each individual interior angle differs significantly between regular and irregular hexagons.
Regular Hexagon: In a regular hexagon, all sides and angles are equal. To find the measure of each individual angle, we divide the total sum of interior angles by the number of angles (which is equal to the number of sides):
720° / 6 = 120°
Each interior angle of a regular hexagon measures 120°.
Irregular Hexagon: In an irregular hexagon, the angles are not all equal. The sum of the angles is still 720°, but the measure of each individual angle will vary depending on the shape of the hexagon. You would need to know the measure of five angles to determine the sixth using the fact that the sum must equal 720°.
Real-World Applications of Hexagon Geometry
The properties of hexagons, including the sum of their interior angles, find numerous applications in various fields:
Architecture and Design:
-
Honeycomb Structures: The hexagonal shape is prevalent in nature, most notably in honeycombs. Bees utilize this shape because it maximizes space and strength with minimal material. The 120° angles of a regular hexagon are crucial to this efficiency.
-
Floor and Wall Tiles: Hexagonal tiles are frequently used in flooring and wall designs due to their aesthetic appeal and ability to tessellate (fit together without gaps). Understanding the angular properties helps in planning and executing these designs effectively.
-
Architectural Structures: Hexagonal designs can be found in various architectural structures, often contributing to structural integrity and visual appeal.
Engineering:
-
Bolts and Nuts: Hexagonal heads on bolts and nuts allow for efficient gripping and turning with wrenches. The shape is chosen for its strength and ability to withstand torque.
-
Gear Systems: In some gear systems, hexagonal gears might be used for specific applications requiring precise angular relationships.
-
Cellular Networks: Hexagonal cells are often used in cellular network design to optimize coverage area and minimize signal overlap.
Other Applications:
-
Games and Puzzles: Hexagonal grids are used in various board games and puzzles, providing unique strategic challenges.
-
Graphics and Design: Hexagons are used in logo design, graphic design, and various artistic representations for their visual appeal and symmetrical properties.
Extending the Concept: Other Polygons
The formula (n - 2) * 180° applies to all polygons, not just hexagons. Here are examples for other common polygons:
- Triangle (n = 3): (3 - 2) * 180° = 180°
- Quadrilateral (n = 4): (4 - 2) * 180° = 360°
- Pentagon (n = 5): (5 - 2) * 180° = 540°
- Heptagon (n = 7): (7 - 2) * 180° = 900°
- Octagon (n = 8): (8 - 2) * 180° = 1080°
Understanding this formula empowers you to calculate the sum of interior angles for any polygon, regardless of its number of sides.
Exploring Exterior Angles: A Complementary Perspective
While interior angles are focused on the angles inside the polygon, exterior angles offer another perspective. An exterior angle is formed by extending one side of a polygon. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, regardless of the number of sides, always equals 360°. This is a fascinating contrast to the varying sums of interior angles. This property can be helpful in solving problems where both interior and exterior angles are involved.
Conclusion: The Significance of Hexagon Geometry
The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon, 720°, is more than just a mathematical concept. It’s a fundamental geometric principle with wide-ranging applications in numerous fields. From the natural efficiency of honeycomb structures to the precision engineering of bolts and nuts, the understanding and application of hexagonal geometry are crucial in many aspects of our world. By grasping the formula, the triangulation method, and the distinction between regular and irregular hexagons, you gain a deeper appreciation for this essential geometric concept and its real-world significance. Furthermore, exploring related concepts like exterior angles provides a more complete understanding of polygon geometry. This knowledge not only aids in solving mathematical problems but also contributes to a richer appreciation of the geometric principles underpinning our physical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Common Factor Of 12 And 36
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Organelles Are Found Only In Plant Cells
Mar 06, 2025
-
At What Temperature Does Water Boil Celsius
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Will Result In A Chemical Change
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Country Has The Most Natural Lakes
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Hexagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
