What Is The Square Root Of 128
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 4 min read
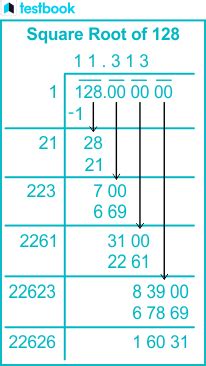
Table of Contents
What is the Square Root of 128? A Deep Dive into Square Roots and Simplification
The question, "What is the square root of 128?" might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding the answer fully involves exploring the concepts of square roots, prime factorization, and simplifying radicals. This article will not only provide the answer but also delve into the underlying mathematical principles, equipping you with a comprehensive understanding of how to solve similar problems.
Understanding Square Roots
Before tackling the square root of 128, let's establish a fundamental understanding of square roots. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 * 3 = 9. We denote the square root using the radical symbol (√).
Key Properties of Square Roots:
- Non-negative: The principal square root (the one we typically use) is always non-negative. While (-3) * (-3) = 9, the principal square root of 9 is 3.
- Perfect Squares: Perfect squares are numbers that have integer square roots (e.g., 1, 4, 9, 16, 25...).
- Non-perfect Squares: Many numbers don't have integer square roots. Their square roots are irrational numbers, meaning they cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
Prime Factorization: The Key to Simplification
Simplifying square roots often requires prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves). This is crucial for simplifying radicals because we can extract perfect squares from the radical.
Let's find the prime factorization of 128:
128 = 2 * 64 = 2 * 2 * 32 = 2 * 2 * 2 * 16 = 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 8 = 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 4 = 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 = 2<sup>7</sup>
Therefore, 128 can be written as 2 raised to the power of 7.
Calculating the Square Root of 128
Now, let's apply this prime factorization to find the square root of 128:
√128 = √(2<sup>7</sup>)
Remember, we can simplify square roots by taking out pairs of factors. Since 2<sup>7</sup> = 2<sup>6</sup> * 2<sup>1</sup>, we have:
√(2<sup>7</sup>) = √(2<sup>6</sup> * 2) = √(2<sup>6</sup>) * √2 = 2<sup>(6/2)</sup> * √2 = 2<sup>3</sup> * √2 = 8√2
Therefore, the simplified square root of 128 is 8√2.
Understanding the Decimal Approximation
While 8√2 is the exact and simplified answer, we can also find a decimal approximation. Using a calculator:
√128 ≈ 11.3137
This decimal approximation is useful for practical applications where an exact value isn't necessary, but remember that it is an approximation and not the precise mathematical representation.
Further Exploration of Square Roots
Let's explore some related concepts to enhance your understanding of square roots and their applications:
Square Roots of Negative Numbers
The square root of a negative number involves imaginary numbers. The imaginary unit, denoted as i, is defined as √(-1). Therefore, the square root of -128 would be expressed as:
√(-128) = √(-1 * 128) = √(-1) * √128 = 8i√2
Solving Equations with Square Roots
Square roots are frequently used in solving quadratic equations and other mathematical problems. For example, consider the equation:
x² = 128
To solve for x, we take the square root of both sides:
√(x²) = ±√128
x = ±8√2
Note the ± symbol, indicating that there are two solutions: 8√2 and -8√2.
Applications of Square Roots
Square roots have numerous applications across various fields:
- Physics: Calculating distances, velocities, and accelerations.
- Engineering: Designing structures and analyzing forces.
- Computer Graphics: Generating curves and transformations.
- Finance: Calculating investment returns and risk.
- Geometry: Determining the lengths of diagonals and sides of shapes.
Advanced Techniques for Simplifying Radicals
While the prime factorization method is effective for simpler radicals, more complex expressions might require additional techniques.
Combining Like Terms: If you have multiple terms with the same radical, you can combine them:
3√2 + 5√2 = 8√2
Rationalizing the Denominator: This technique removes radicals from the denominator of a fraction. For example, to rationalize the denominator of 1/√2, we multiply both the numerator and denominator by √2:
(1/√2) * (√2/√2) = √2/2
Conclusion: Mastering Square Roots
The seemingly straightforward question of "What is the square root of 128?" opens a door to a deeper understanding of square roots, prime factorization, radical simplification, and their broader applications. By mastering these concepts, you'll be equipped to tackle more complex mathematical problems and confidently navigate various fields that rely on these fundamental mathematical principles. Remember that the simplified form, 8√2, provides the most precise mathematical representation, while the decimal approximation offers a practical, albeit less precise, value. Understanding both representations is crucial for a complete grasp of the concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 69 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 21, 2025
-
15 Gallons Is How Many Liters
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Two Planets Have No Moons
Mar 21, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 3 And 6
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Highest Common Factor Of 12 And 4
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Square Root Of 128 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
